Original title: "Original title: "》
In terms of source, ETH Staking Extractable Value can be divided into three categories: Consensus Income, Execution Income, and MEV; in terms of flow, ETH Staking Extractable Value can be divided into two categories: Validator Captured Value (Validator Staking Income) and Validator Uncaptured Value.
TL; DR:
In terms of source, ETH Staking Extractable Value can be divided into three categories: Consensus Income, Execution Income, and MEV; in terms of flow, ETH Staking Extractable Value can be divided into two categories: Validator Captured Value (Validator Staking Income) and Validator Uncaptured Value.
Validator Infra Provider, Pooled Staking Protocol, CEX and Staker can get a share of Validator Staking Income; Searcher and Block Builder can get a share of Validator Uncaptured Value.
Validator Infra Provider, Pooled Staking Protocol, CEX and Staker can get a share of Validator Staking Income; Searcher and Block Builder can get a share of Validator Uncaptured Value.
There are noteworthy investment opportunities in Validator Infra Provider, Stake Pool, Products based on DVT and External MEV Market.
Since The Merge happened, Ethereum under the PoS consensus mechanism has been running steadily for nearly three months, and ETH 2.0 has successfully taken a critical first step.
So what opportunities does the transformation of the consensus mechanism bring?
A quick look at the value extraction track of Ethereum staking: what investment opportunities are worth paying attention to?
A quick look at the value extraction track of Ethereum staking: what investment opportunities are worth paying attention to?
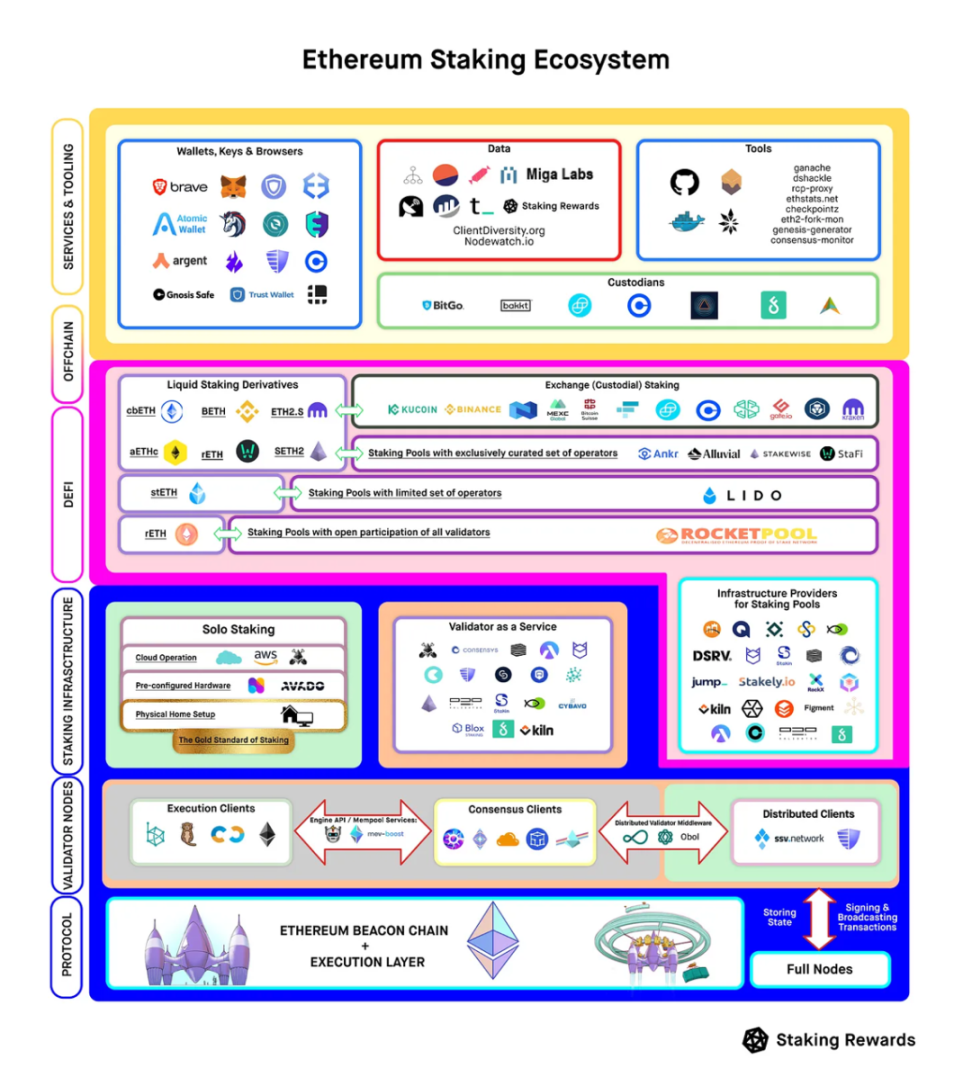
How is Staking Extractable Value composed?
Staking Extractable Value=Consensus Income + Execution Income + MEV
Staking Extractable Value=Validator Captured Value + Validator Uncaptured Value
Two angles:
From the source, it can be divided into three categories:
Consensus Income: The newly issued ETH Token from the network is the reward for the honest Validator by the consensus mechanism
Execution Income: From the Tip part of Gas Fee, it is the tip paid by the user to the Proposer/Builder who helps package its transaction on the chain
MEV: The most diverse form of economic benefit from the execution of certain transactions, mostly arbitrage profits
From the flow upward, it is divided into two categories:
Validator Captured Value (Validator Staking Income): allocated to Validator as an economic incentive for maintaining ETH network security and participating in block establishment and consensus
Validator Uncaptured Value: Shared by other participants in the ExternalMEV Market, expressed as MEV plus External Block's Execution Income minus MEV Rewards for Validator
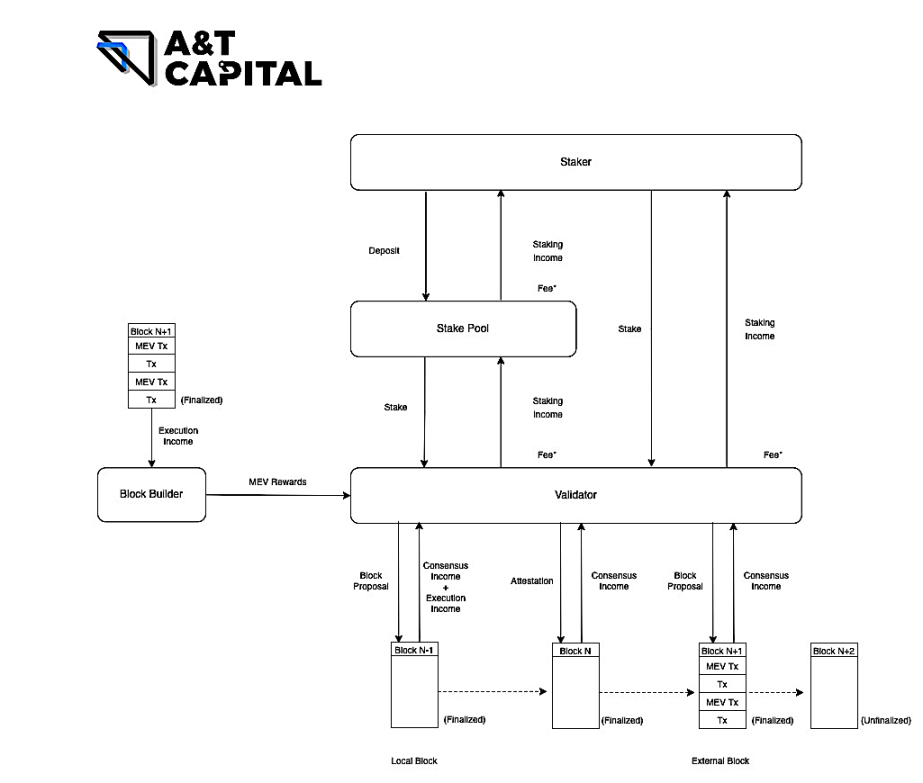
Validator Staking Income=Consensus Income + Local Block’s Execution Income + MEV Rewards
How is Validator Captured Value (Validator Staking Income) constituted?
There are three different sources of Validator Staking Income, namely Consensus Income, Local Block's Execution Income and MEV Rewards.
For a Validator, Consensus Income is the most basic and stable income; Local Block's Execution Income and MEV Rewards are relatively accidental, and can only be obtained when the Validator is selected as the Proposer of a new block.
Consensus Income:A quick look at the value extraction track of Ethereum staking: what investment opportunities are worth paying attention to?
The newly issued ETH Token from the network is the reward of the consensus mechanism for the honest Validator, which can be subdivided into three categories:
Proposer rewards: When a Validator is selected to become a Proposer, if the new block it proposes is recognized by the network, it will receive Proposer rewards for the correct new block contributed by the network
Attestor rewards: Validators not selected as Proposer can verify whether the new block proposed by Proposer is correct, and Validators participating in the verification can get Attestor rewards
Local Block’s Execution Income:Whistleblower rewards: If the block proposed by the Proposer contains evidence that can prove that other Validators violate the consensus rules, it will receive Whistleblower rewards
MEV Rewards:From the Tip part of the Gas Fee, it is the tip paid by the user to the Proposer/Builder who helps package its transaction on the chain. In the case of Local Block Building, the Proposer (Validator) builds a block by itself and can get all the Tips in the block. This part of the income is called Local Block's Execution Income.
The fee paid from Block Builder to Proposer is essentially a part of MEV. In the case of External Block Building, the Proposer (Validator) proposes the block built by the Block Builder, and the fee paid by the Block Builder to the Proposer is called MEV Rewards (the Block Builder obtains the Execution Income of the block). This fee may be higher than all Tips in the block (Block Builder additionally subsidizes Proposer), or it may be equal to or lower than all Tips in the block (Block Builder retains zero or partial profits).
Note: After EIP-1559, the Gas Fee for each transaction on ETH is divided into Base Fee and Tip. Among them, the Base Fee will be burned, and the Tip will be paid to the coinbase address in the block (this address can be the Proposer's or the Block Builder's).
It is worth mentioning that Consensus Income cannot be withdrawn at present, it is locked in the Validator's Balance in Beacon Chain; while Execution Income and MEV Rewards can be withdrawn because it is transferred to a designated account.
Validator Uncaptured Value=MEV + External Block’s Execution Income - MEV Rewards
How is Validator Uncaptured Value formed?
MEV: The most diverse form of economic benefit from the execution of certain transactions, most of which are arbitrage
External Block's Execution Income: From the Tip part in the Gas Fee, it is the tip paid by the user to the Builder who helps package its transaction on the chain. In the case of ExternalBlock Building, the Builder sets the coinbaseaddress (the address used to receive tips) in the block it builds as the address of the Builder, so the Builder can get all the Tips in the block,
MEV Rewards: The fee paid from Block Builder to Proposer is the part of MEV captured by Proposer.
Who gets a share of Staking Extractable Value?
About Validator Captured Value:
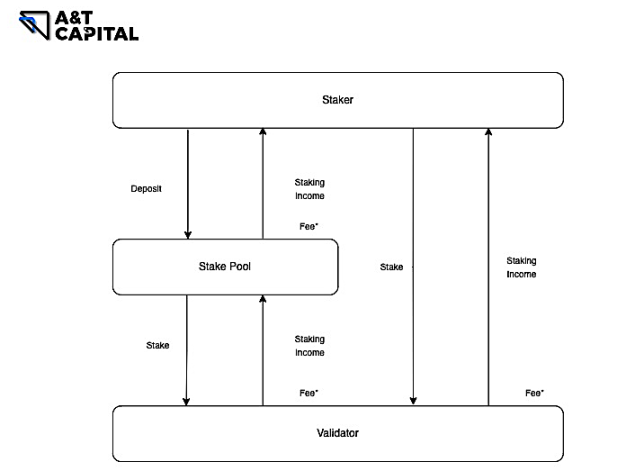
Solo Staking:Staker-100%
Staking as a Service:Staker-90 ~ 95% ,Validator Infra Provider-5 ~ 10%
Pooled Staking:Staker-90% ,Pooled Staking Protocol-5% ,Validator Infra Provider-5%
Centralized Exchanges:Staker-85 ~ 95% ,CEX-0 ~ 10% ,Validator Infra Provider-5%
A quick look at the value extraction track of Ethereum staking: what investment opportunities are worth paying attention to?
About Validator Uncaptured Value:
External MEV Market Architectures:
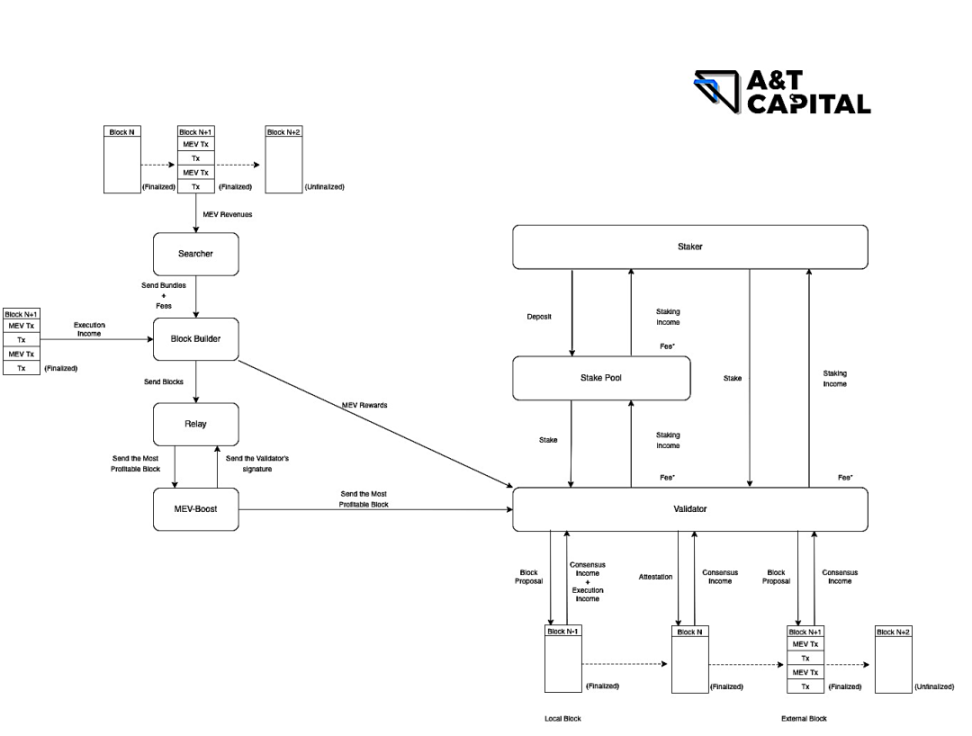
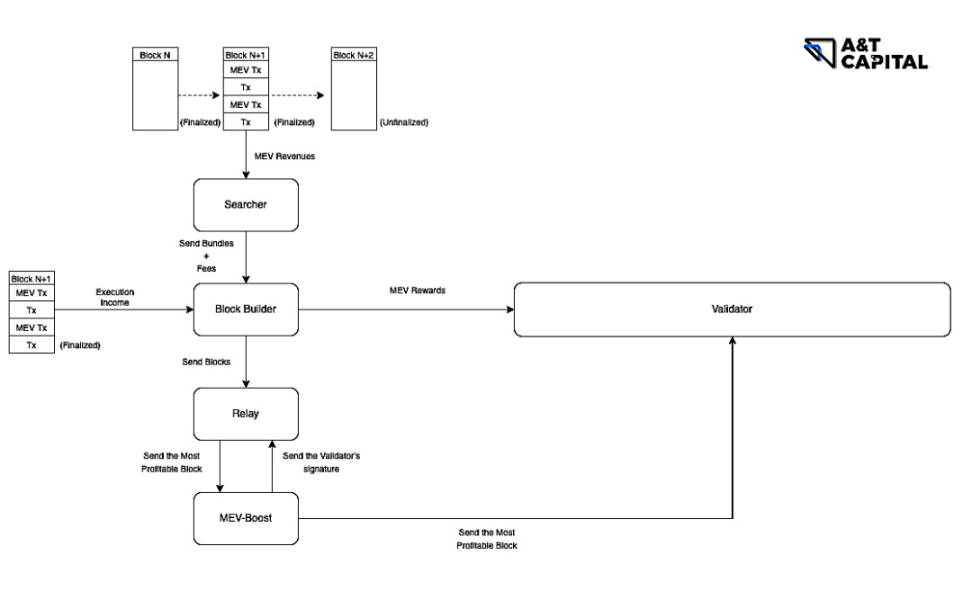
Searcher:
A quick look at the value extraction track of Ethereum staking: what investment opportunities are worth paying attention to?
Behavior: Insert your own MEV TXs into a group of TXs to form Bundles and send them to Builder
Revenue: Proceeds from execution of MEV TXs (MEV)
Block Builder:
Cost: Gas fee (Base fee+Tip) of MEV TXs and the fee paid to Builder
Behavior: Compose a Full Block based on the obtained Bundles and TXs in the Mem Pool, and send it to the Proposer. Among them, the coinbase address in the Full Block (the address used to receive the tip) is set to the address of the Builder, and the last TX in the Full Block is the address that the Builder transfers to the Proposer
Income: Fees paid by Tips and Searchers in the Full Block
Relay:
Cost: the fee paid to the Proposer
Behavior: Accept FullBlocks sent by many Builders, and send the FullBlock that is most beneficial to the Proposer to the Proposer
Revenue: No fees yet
Cost: server operation and maintenance costs
Validator Infra Provider
Stake Pool
Products based on DVT
External MEV Market
Which directions have investment opportunities worthy of attention?
Validator Captured Value is "the value floating on the water". This market is relatively mature, and the proportion of value extracted by each stakeholder is relatively fixed.
The two most obvious investment directions are Validator Infra Provider and Stake Pool. A&T Capital has layouts.
《For investment logic, please refer to our previous articles:》
《A&T Family: Unicorn company InfStones completes new round of financing of 66 million US dollars》
A&T Family: Liquidity staking solution Meta Pool completes seed round financing
However, this is by no means a static market. The maturity and application of DVT (Distributed Validator Technology) will become a new "catfish".
DVT shares the responsibility of a Validator through Node Operators running on different hardware, making Validator more decentralized and avoiding single point of failure of hardware devices.
Based on DVT, different forms of products can be realized and commercialized through different paths. SSV Network and Obol Network are a good set of examples.
SSV Network aims to establish an open market that matches Stakers and Node Operators. Stakers can select different Node Operators and maintain a Validator for them at the same time to prevent single points of failure. Node Operators also have certain redundancy and can respond more flexibly All kinds of emergencies.
Obol Network is currently more like a SaaS solution, and it takes into account both To C and To B.
A quick look at the value extraction track of Ethereum staking: what investment opportunities are worth paying attention to?
MEV is more important than you think.
MEV originates from the profits generated by executing certain special transactions, and it takes various forms. In theory, the more active transactions on the chain, the higher the upper limit of MEV. Sometimes MEV will be higher than Consensus Income + Execution Income.
A quick look at the value extraction track of Ethereum staking: what investment opportunities are worth paying attention to?
Since the Merge, the External MEV Market has distributed nearly 60,000 ETH to the Validator, and the total amount of MEV will only be higher than this number.
It is worthy of recognition that the MEV-Boost system proposed by Flashbots has played a role in promoting the decentralization of Ethereum Validator. Each Validator can receive the Blocks sent by each Relay through the MEV-Boost client, and select the best one, without needing to rely on a large pledge pool to obtain higher income.
However, the current market still has a series of problems that need to be solved urgently:
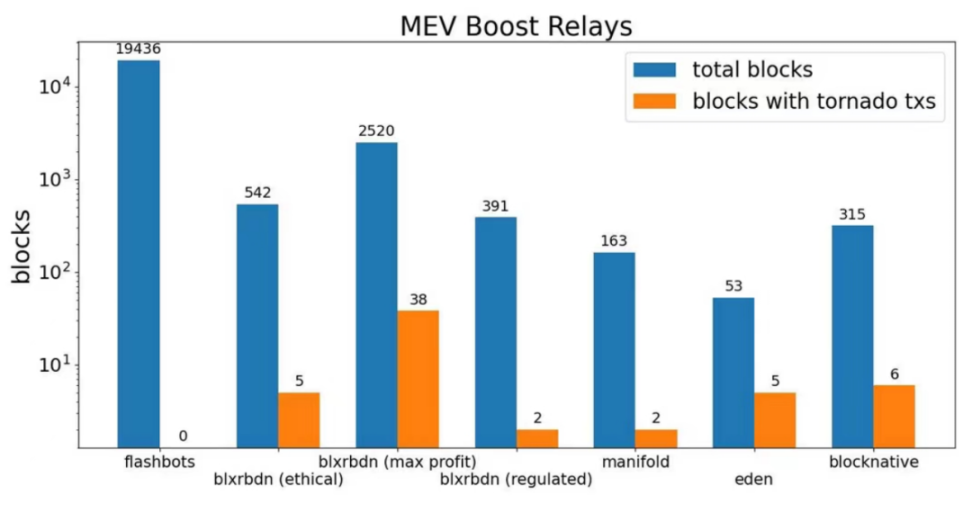
There are many structures in the market that need to be trusted, and there is a risk of censorship
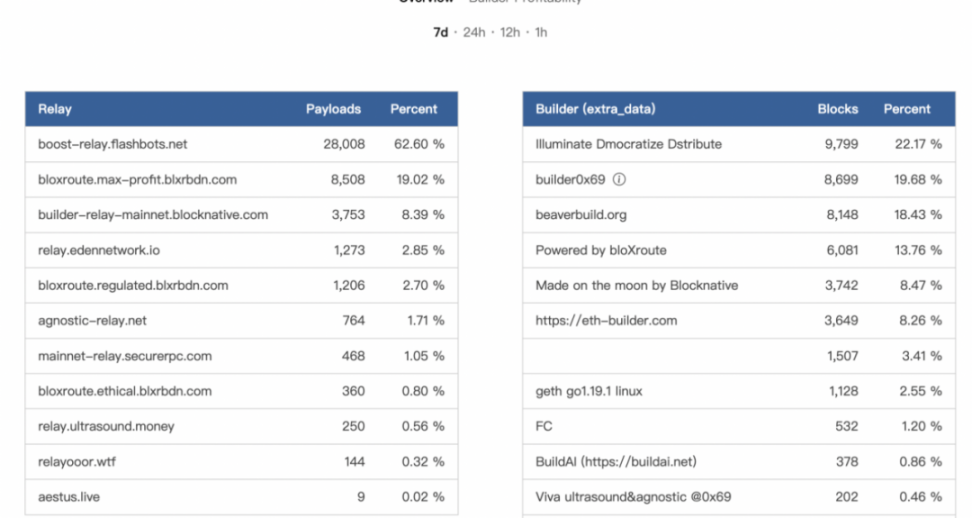
BlockBuilder and Relay have a tendency to centralize
In External MEV Market, Searcher needs to trust Builder, and Builder needs to trust Relay. In fact, Builder has the ability to review Searcher's Bundles, and Relay has the ability to review Builder's Block.
(source: https://twitter.com/nero_eth)
image description
(source: https://www.relayscan.io/overview? t= 7 d)
image description
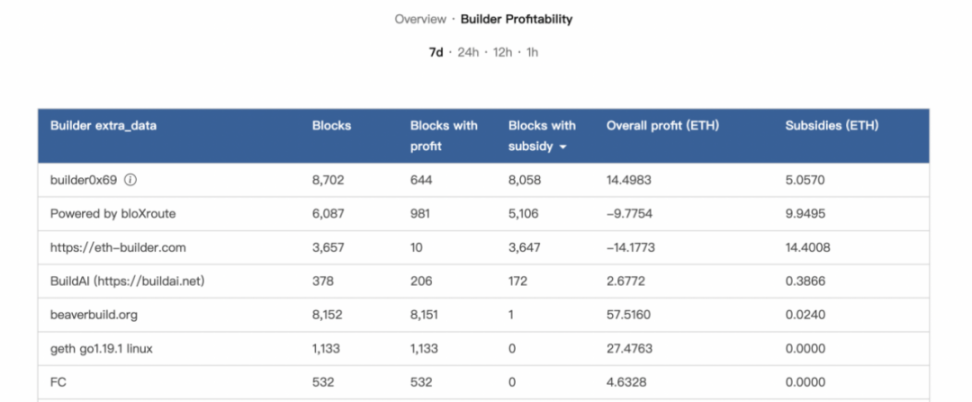
(source: https://www.relayscan.io/builder-profit? t= 7 d)
image description
It is worth mentioning that some Builders even subsidize the Proposer in order to win the block they built (the fee paid by the Builder to the Proposer is greater than the Tip received in the coinbase address). The possible reason for this phenomenon is that the Builder itself is also a Searcher, which can profit from special transaction execution.
There are investment opportunities in the External MEV Market