foreword
forewordKnow Chuangyu Blockchain Security LabOn May 16, 2022, Beijing time,
On May 17, the multi-chain DeFi protocol FEG was attacked again. The attacker stole 291 ETH and 4343 BNB, and lost about $1.9 million, of which BSC was $1.3 million and the Ethereum chain was $600,000.
analyze
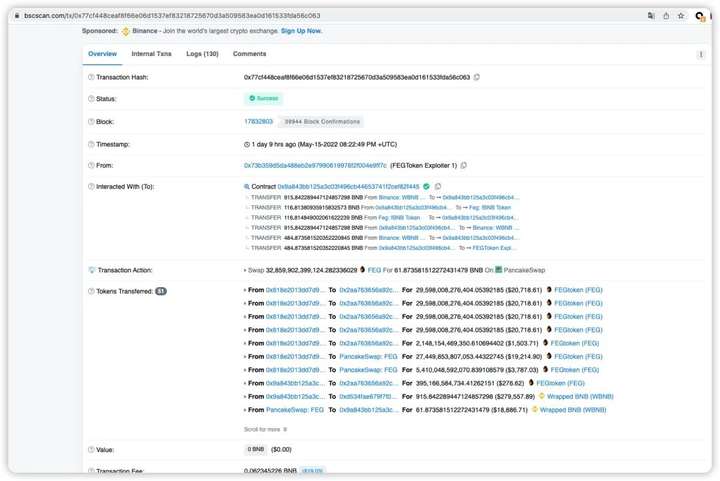
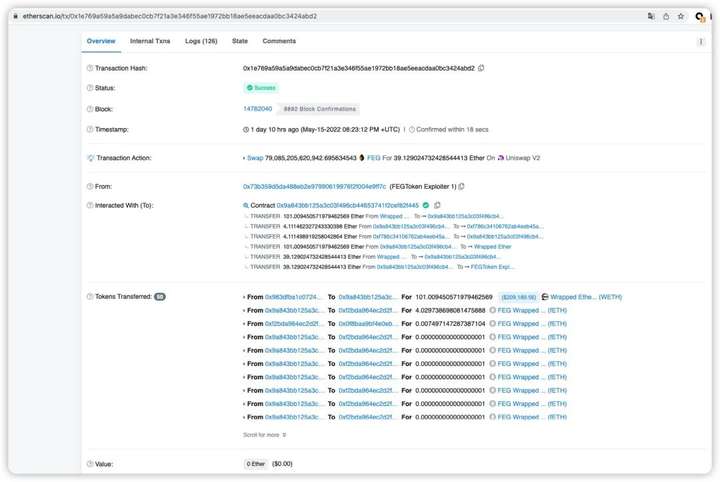
The protocol was attacked on both BSC and Ether, and the figures below are the transaction hashes of the attack events on the two chains. The main reason for this attack is that the path address in the swapToSwap() function can be controlled by the attacker.
basic information
secondary title
Attack contract: 0x9a843bb125a3c03f496cb44653741f2cef82f445
Vulnerability contract address:
BSC: 0x818e2013dd7d9bf4547aaabf6b617c1262578bc7
Ether: 0xf2bda964ec2d2fcb1610c886ed4831bf58f64948
Vulnerability contract address:
BSC:0x77cf448ceaf8f66e06d1537ef83218725670d3a509583ea0d161533fda56c063
Ether:0x1e769a59a5a9dabec0cb7f21a3e346f55ae1972bb18ae5eeacdaa0bc3424abd2
attack process
Attack tx:
attack process
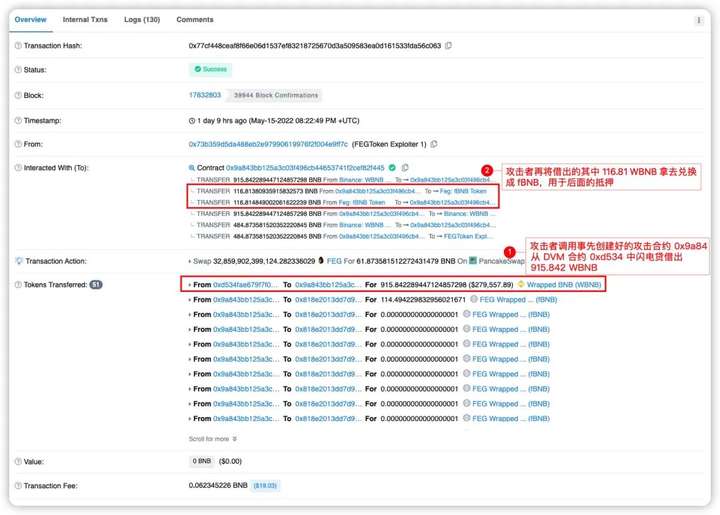
1. The attacker 0x73b3 calls the pre-created attack contract 0x9a84 to borrow 915.842 WBNB from the DVM, and then converts 116.81 WBNB into 115.65 fBNB.
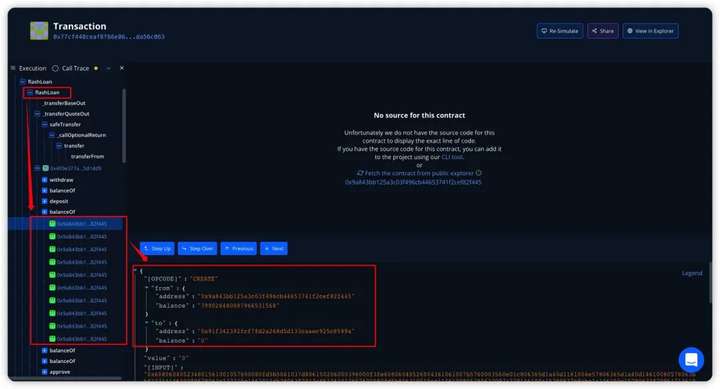
2. Attacker 0x73b3 created 10 contracts by attacking contract 0x9a84 to exploit the vulnerability later.
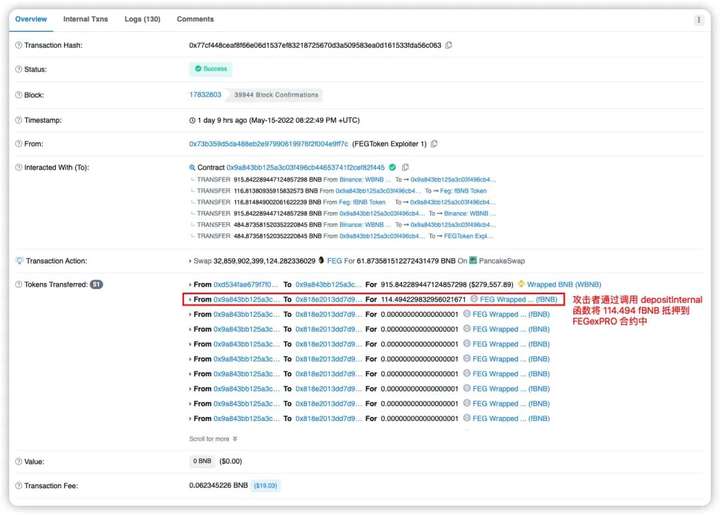
3. The attacker 0x73b3 mortgages the fBNB exchanged in the first step to the FEGexPRO contract 0x818e through the function depositInternal().

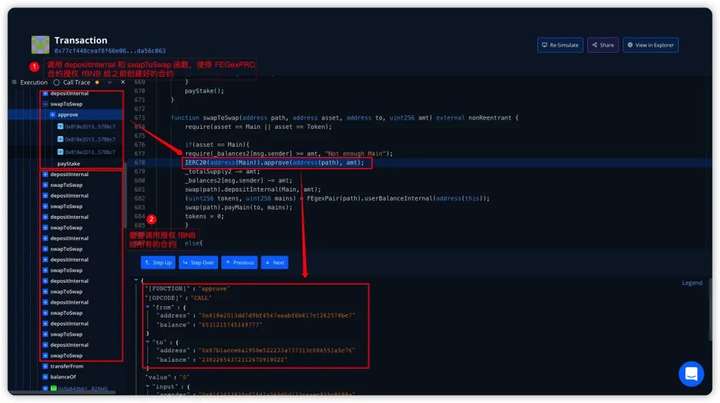
4. The attacker 0x73b3 calls the depositInternal() and swapToSwap() functions to make the FEGexPRO contract 0x818e authorize fBNB to the contract created in the second step, and repeatedly calls the authorized fBNB to the created 10 contracts.
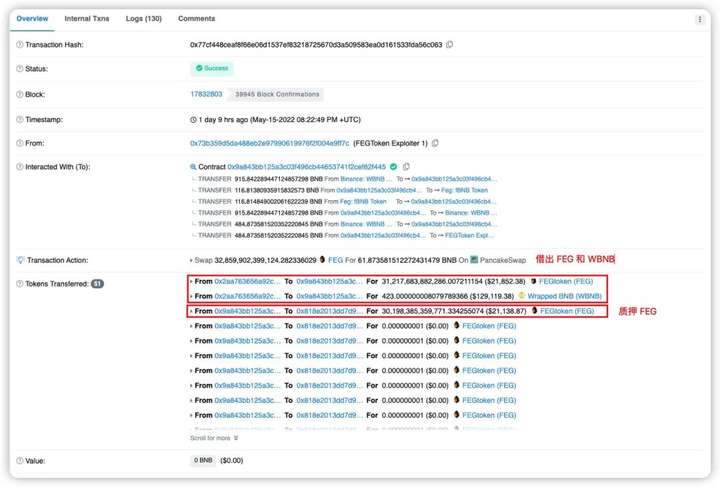
5. Since the 10 contracts created by the attacker 0x73b3 have been authorized in the previous step, the attacker uses these authorized contracts to call the transferFrom() function to transfer 113.452 fBNB each time from the FEGexPRO contract 0x818e.
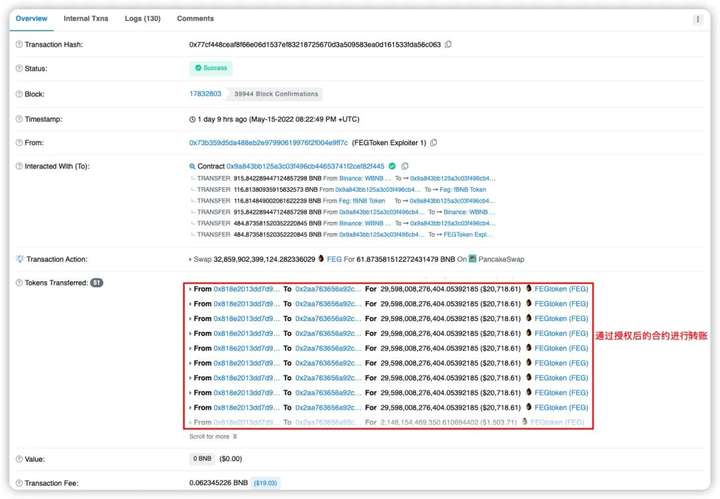
6. The attacker 0x73b3 borrows 31217683882286.007 FEG and 423 WBNB from PancakePair's LP transaction pair 0x2aa7 and repeats the above steps 3, 4 and 5 to finally get it.
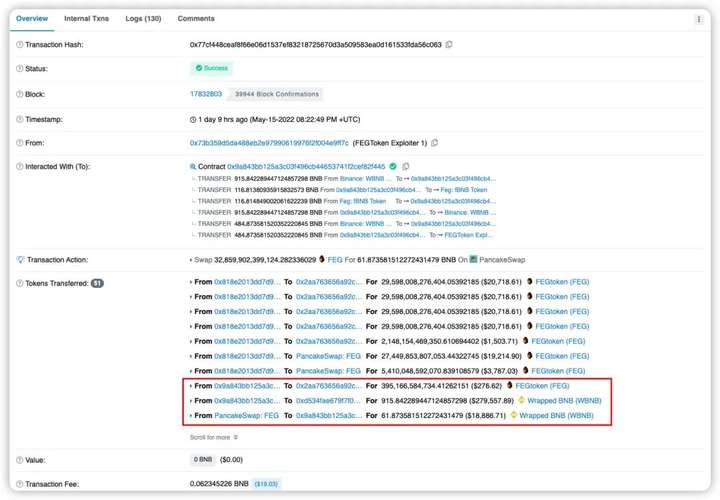
7. Finally, return the flash loan and transfer all the WBNB obtained from the above attack to the attack contract 0x9a84.
detail
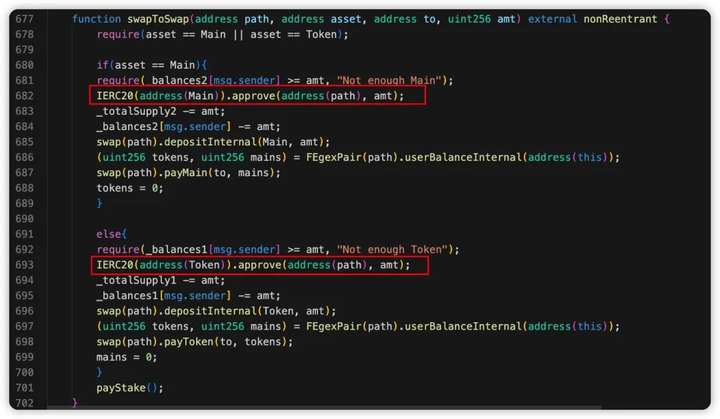
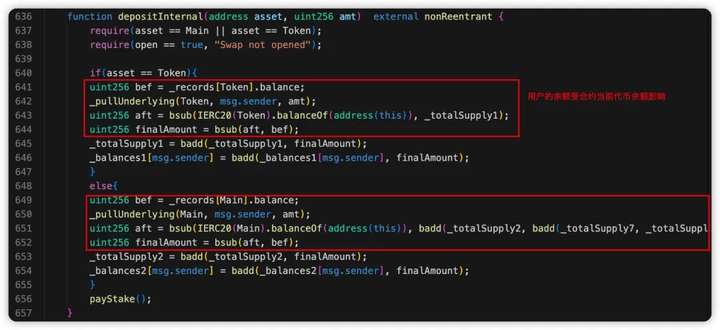
By calling the swapToSwap() function to pass in the malicious path address parameter, the current contract token balance will not be affected, IERC20(address(Main)).approve(address(path), amt); Authorization of the current contract fBNB.
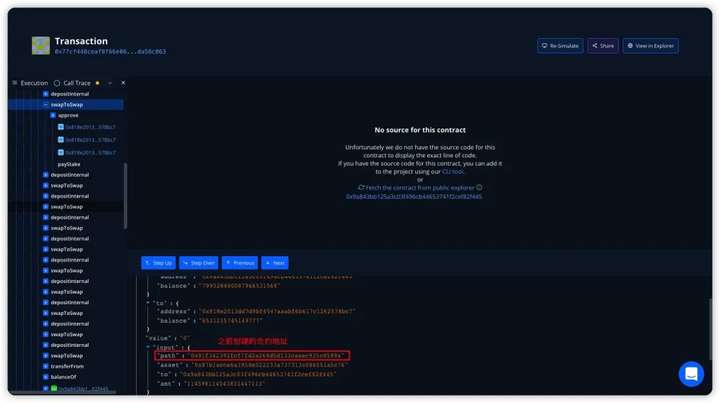
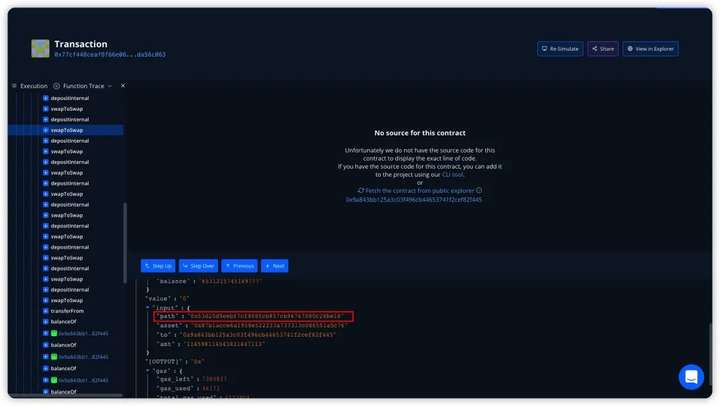
Follow up
By repeatedly calling depositInternal() and swapToSwap(), the attacker can make the FEGexPRO contract repeatedly authorize fBNB to the malicious contract path address passed in by the attacker. The amount of tokens transferred from other addresses is the amount of tokens that the attacker pledged for the first time minus the amount of handling fees. By checking the information in the Debugger, we can find that the path address parameters passed in are all contract addresses created in the attack process.
Follow up
After the attack on the 16th, the attackers carried out another attack the next day, but changed the attack address.
Attack contract: 0xf02b075f514c34df0c3d5cb7ebadf50d74a6fb17
Attacker address: 0xf99e5f80486426e7d3e3921269ffee9c2da258e2
BSC:0xe956da324e16cb84acec1a43445fc2adbcdeb0e5635af6e40234179857858f82
Ether:0c0031514e222bf2f9f1a57a4af652494f08ec6e401b6ae5b4761d3b41e266a59
Attack tx:
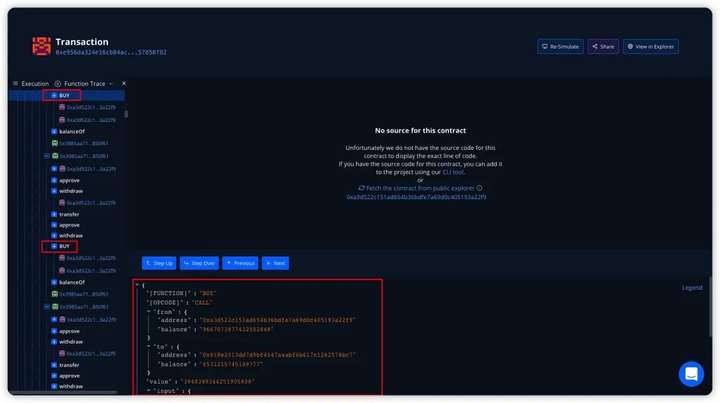
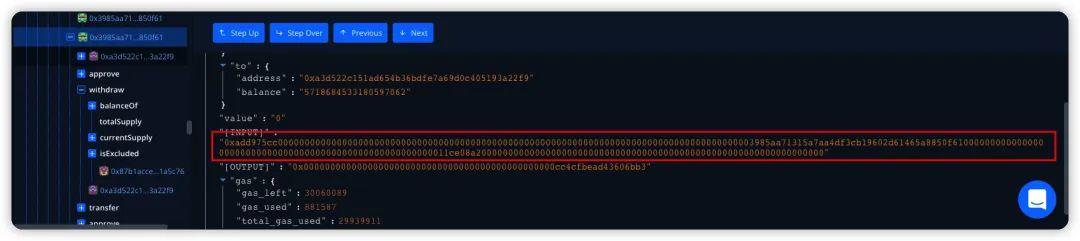
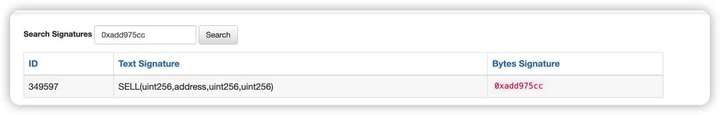
Summarize
Since the R0X vulnerability contract 0xa3d5 is not open source, we tried to analyze it from the Debugger and found that it was similar to the first attack process, but also used the BUY() function for auxiliary deposit and SELL() function for auxiliary extraction.