Original title: "The era of super-speculative capitalism: Liquidity becomes the decisive factor, will BTC peak in September? "
Original author: arndxt
Original translation: AididiaoJP, Foresight News
Welcome to the age of hyper-speculative capitalism.
Keep an eye on the M2 money supply in mid-September.
In the current irrational economic environment, hyper-speculative attention has become a natural reaction.
Fiscal and monetary policy were once tools that anchored markets in a stable state, but that stability is now showing cracks:
- The United States is running a 7% of GDP deficit, and this is happening at full employment.
- Interest rates remain at 5%, but Bitcoin is approaching its all-time high.
- Monetary policy has been replaced by fiscal dominance, with stimulus measures continuing even during economic "boom times."
The market no longer reflects fundamentals, it reflects liquidity.

The Bitcoin Madness: Is It Justified in a Chaotic World?
Bitcoin no longer requires a weak economy or interest rate cuts. In fact, the optimal macro environment may be one in which there are no new shocks and liquidity conditions continue to improve.
And liquidity is surging:
- Global M2 money supply remains high and may have peaked.
- If Bitcoin rises 10%, more than $13 billion in short positions will be liquidated, indicating that there is still ample capital in the market to drive its parabolic rise.
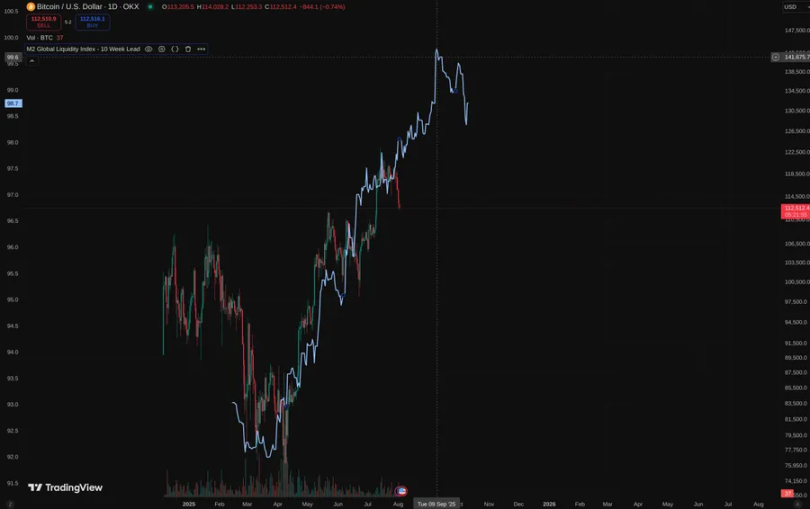
- Bitcoin typically peaks within 525 to 530 days after the halving, meaning late September 2025 could be a key time point.
@MintedMacro provides a clear roadmap based on historical halving cycles:
Liquidity-driven cycle: When M2 grows, Bitcoin performs strongly. Currently, M2 has formed a double top pattern, with the second high point lower than the first.
Top time prediction:
- 2013: 525 days after the halving
- 2017: 530 days after the halving
- 2021: 518 days after the halving
- 2025: Around September 21
Expected top range:
Bitcoin could reach $135,000-$150,000
But the upside may be limited by macro-tightening policies.
Key conclusions:
There may be a rebound in September, which may be followed by a liquidity-driven correction.
Against a backdrop of distorted fundamentals and liquidity becoming the dominant force, market participants are adapting.
The macro analysis is updated to August 3, 2025, and covers the following topics:
- Macro events this week
- Bitcoin Heat Index
- Market Overview
- Key Economic Indicators
- India Focus
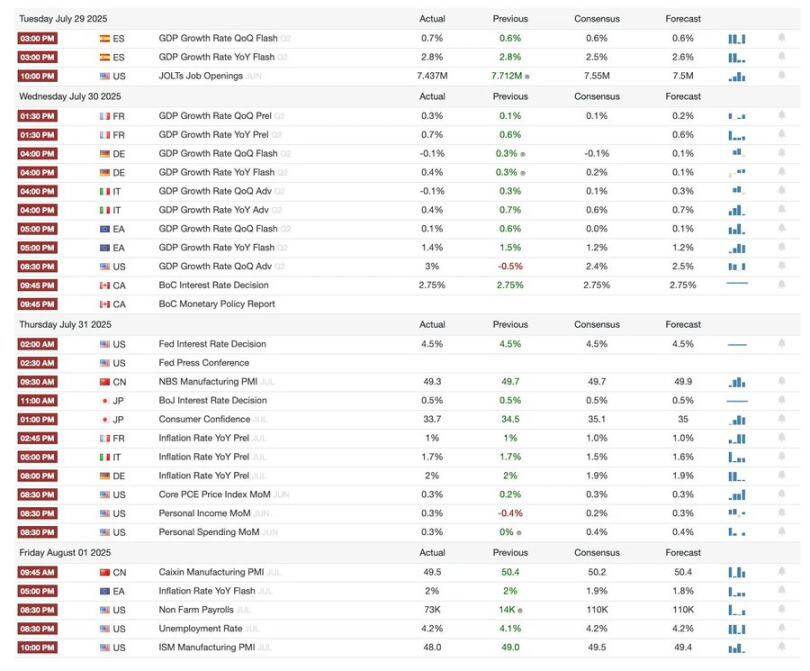
Summary of macro events this week
Bitcoin Heat Index
Banking and Regulatory Developments:
- The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has launched a "Crypto Initiative" aimed at strengthening regulation and enhancing the United States' leadership in digital finance.
- PayPal launches "Crypto Payments" feature, allowing US businesses to accept 100 cryptocurrencies.
- Visa expands stablecoin settlement capabilities, adding new supported tokens and blockchains.
- BNB hits a new all-time high, with institutional demand and corporate funds influx driving the gains.
Institutional Investment and Project Development:
- Tron Inc. filed a $1 billion securities statement, becoming the largest holder of TRX.
- Strategy Inc. acquired $739.8 million worth of Bitcoin, expanding its holdings to $43 billion, and launched a preferred stock IPO.
- Tether reported $4.9 billion in second-quarter profits, with strong demand for Bitcoin and gold.
- SharpLink Gaming acquired $295 million worth of Ethereum, becoming the second largest holder with 438,017 ETH.
- Syntetika Hub is launched: the hub for learning, contributing, and rewards within the ecosystem.
NFT and digital collectibles market:
- NFT sales surged to $574 million in July, the second highest in 2025, driven by demand from whale assets.
- The reserve price for CryptoPunks reached $208,000, a three-year high, with Ethereum's rise driving the market.
Market Overview
US economy: Signs of a broader slowdown
- This week's economic data sent a clear and consistent signal: US economic growth momentum slowed sharply in the first half of this year.
- Consumer behavior is changing, with credit card use tightening despite healthier household balance sheets, reflecting rising uncertainty rather than optimism.
- Housing affordability has hit record lows: Even with modest price declines, mortgage rates and ownership costs (taxes, insurance, maintenance) have surged. The Atlanta Fed report shows that owning a median-priced home now consumes 53% of middle-class income, a record high, highlighting structural barriers to homeownership.
Global central banks: diverging policy paths
- Policy divergences are emerging: central banks in Japan, Canada, Brazil, Colombia and Singapore kept interest rates unchanged, while Chile and South Africa cut rates by 25 basis points prematurely due to slowing inflation and economic weakness.
- Eurozone GDP in the second quarter was slightly higher than expected, increasing by 0.1% quarter-on-quarter, but core inflation remained stable at 2.3% year-on-year, indicating that the ECB will remain cautious.
- China's PMI weakened in July, suggesting its economic recovery momentum is fading faster than expected, which could drag down regional demand and supply chains.
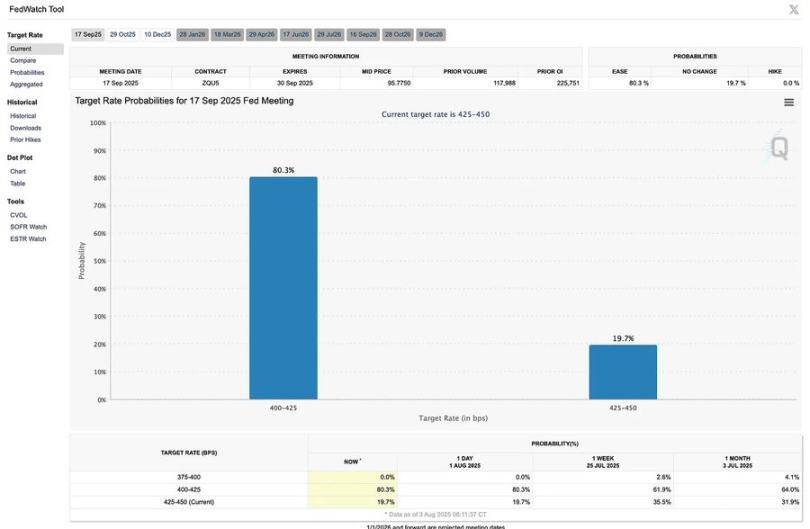
The Federal Reserve: The Dilemma of Data Dependence
- The Federal Reserve held interest rates at 4.25%–4.50% for the fifth consecutive meeting, reinforcing its cautious stance amid mixed signals.
- Interest rates may still be adjusted at the September meeting, but a rate cut is not certain. Fed officials have made it clear that they need to wait for clearer evidence on the labor market, inflation and consumer data.
- The outlook depends on the depth of the economic slowdown and whether inflation continues to ease without triggering a recession.
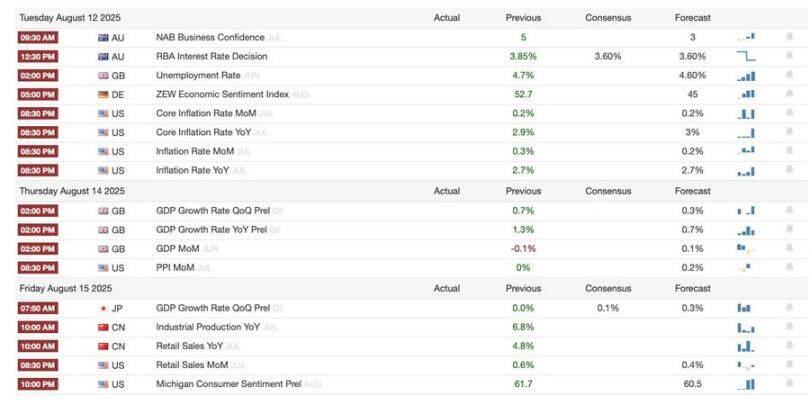
Key Economic Indicators
US-Japan Agreement:
New tariff agreement: Lower than threatened but still high
- The United States announced a 15% tariff on all Japanese imports, up from the previous 10% and significantly higher than the 2.5% at the beginning of the year.
- The previous tariff on cars and auto parts was 27.5%, but it has now been unified to 15%, driving up Japanese auto stocks and stocks.
Inflation risk comes from rising import prices
- While avoiding an extreme 25% tariff, a 15% tariff would still raise consumer prices for Japanese goods, adding to inflationary pressures and weakening the purchasing power of American households.
- Broader trade policy shifts could further push up import costs elsewhere.
Japan's $550 billion investment pledge: Terms unclear
- Trump said Japan will invest $550 billion in the United States, with 90% of the profits going to the United States, calling it a "signing bonus."
- However, Japanese negotiators said the figure was a ceiling, not a guarantee, and expected the United States to share risk and financing.
- The lack of a written agreement raises questions about enforceability and sets the stage for future disputes.
U.S. manufacturing push faces labor constraints
- The agreement aims to shift more manufacturing activity to the United States, but it is unclear how the jobs will be filled amid labor shortages and tightening immigration policies.
- This contradiction undermines the strategy of reducing the trade deficit through reshoring.
Auto industry backlash: unfair competition
U.S. automakers face higher costs than Japanese importers for a number of reasons:
- 25% tariff on imported parts.
- 50% tariff on imported steel and aluminum.
- The complex duty refund process under the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA/USMCA).
Industry leaders warned the agreement favored Japan over American manufacturers and workers, fearing it would set a precedent for future trade deals.
Agreement in doubt: negotiation rather than contract signing
- No formal treaty has been signed; the two sides have disagreed over the interpretation of its terms.
- This has sparked widespread concerns about the United States' reliance on non-binding trade commitments, which could erode trust and stability in future negotiations.
Job Market:
New grads face unprecedented hiring slump
- The unemployment rate for recent college graduates is at a decade high, just one percentage point lower than for all young workers, an unusually narrow gap.
- Historically, college graduates have had far better job prospects than their peers, and this convergence is a warning sign for white-collar employment trends.
AI isn’t the main reason, at least not yet
- While generative AI has been blamed for eliminating entry-level jobs, its impact remains limited to specific industries, such as technology.
- Broader measures are not yet sufficient to explain the widespread weakness in graduate recruitment.
Policy uncertainty cools markets
- Uncertainty about trade policy, the direction of Federal Reserve interest rates and immigration restrictions could hinder hiring, especially for skilled positions.
- This uncertainty also affects employee behavior, with low turnover rates reflecting a hesitation to change jobs in an unstable market.
- Fewer departures = fewer job openings, leading to slower labor market mobility.
Skilled worker shortages ease
- The long-standing shortage of college graduates, once a key driver of high wage premiums, is weakening.
- As more workers enter the skilled labor pool, wage premiums flatten or decline, potentially further dampening creativity in traditional high-growth industries.
India Focus
UK-India trade deal: A major un-American shift
- The UK and India have reached a landmark trade deal that will cut tariffs on more than 90% of British exports to India.
- The UK expects exports to India to grow by 60% by 2040, thanks to rapidly growing access to the Indian market.
Big winner in the automotive industry
- India is cutting import duties on cars to 10% from 100%, a dramatic change that could reshape the auto market.
- But the quotas limit the total volume of imports, dampening short-term commercial gains for UK carmakers.
India has benefited significantly
While the headlines focused on the UK's export growth, India benefited more from its own tariff cuts:
- Lower prices for consumers
- Intensified domestic competition
- Indian companies' global competitiveness increases
These structural advantages are likely to enhance India's long-term export capabilities and productivity.
India to offer 50% duty-free export to UK
Around 50% of Indian exports that previously faced tariffs of 4%–16% will enter the UK duty-free, helping Indian textile, pharmaceutical and food exporters.
Strategic trade restructuring
- The agreement reflects a global trend in which countries are trying to diversify their partnerships as U.S. tariffs disrupt existing trade patterns.
- India is actively pursuing trade liberalization with the EU, ASEAN and even the United States, positioning itself as a key player in the post-globalization reset.
Summarize
The core characteristics of the era of hyper-speculative capitalism are liquidity-driven, fiscally-dominated, and a market's departure from traditional economic logic. The Bitcoin craze, the restructuring of trade patterns, and the evolution of the labor market are all microcosms of this era. Investors and policymakers need to adapt to this new reality and flexibly respond to the challenges posed by liquidity fluctuations and policy uncertainty.
A prominent feature of the current global economy is liquidity-driven market behavior. Traditional economic theory holds that asset prices should reflect their intrinsic value or the discounted value of future cash flows. However, in the era of hyper-speculative capitalism, liquidity—the abundance of available funds—has become the core factor driving market prices.
Take Bitcoin, for example. Its price fluctuations are highly correlated with the growth of the global M2 money supply. When central banks inject large amounts of money into the market through quantitative easing or other measures, these funds tend to flow into high-risk, high-return assets, such as cryptocurrencies. This phenomenon was particularly evident in 2025, when Bitcoin continued to rise despite the Federal Reserve maintaining high interest rates, reflecting the market's reliance on liquidity over traditional economic indicators.





