fromTwitter & Coinmarketcap, by Tom Wan, Research Analyst, 21 Shares
Odaily Translator |
Odaily Translator |
Launched by blockchain research and engineering firm Matter Labs, the zkSync Era has been years in the making. Matter Labs released zkSync 1.0 (now zkSync Lite) in June 2020, followed by zkSync 2.0 in Q4 2022. Polygon zkEVM is developed and released by Polygon, an Ethereum expansion company. Polygon started their expansion journey with its proof-of-stake sidechain. Polygon zkEVM effectively integrates the development of Polygon Hermez and the technological breakthrough derived from Polygon Zero.
secondary title
similarities and differencesSimilarities:
ZkSync Era's code is licensed under the MIT/Apache 2.0 license, Polygon zkEVM is licensed under AGPL V3, both zkSync Era and Polygon zkEVM support account abstraction, albeit in different ways.
In terms of security, the current contracts of both chains have no time lock, allowing for instant upgrades, this is mainly to be able to upgrade or fix in time if any mistakes are made in the contracts, as both are still in their early stages. However Polygon zkEVM has a security committee that requires four out of seven signers to enable any upgrades, while zkSync Era currently operates without a security committee but plans to implement such a mechanism in the future.the difference:
zkSync Era and Polygon zkEVM are very different in nature, ZkSync Era is EVM compatible while Polygon zkEVM is EVM equivalent.
ZkSync Era uses its LLVM compiler, Polygon zkEVM is closer to the EVM and doesn't use a compiler. The zkSync Era aims to generate proofs faster by optimizing with their custom VM, not for EVM equivalence.
Polygon zkEVM uses a unique proof-of-efficiency consensus mechanism combined with a state machine cluster to increase the efficiency of the prover. In terms of data availability, ZkSync Era only publishes state differences and not transaction inputs, provides data compression, and seamless integration with zkPorter, which is based on StarkWare's Volition model, although ZkSync has tuned it to "strictly focus on decentralized change". In contrast, Polygon zkEVM uses a hybrid model (Validium or Volition), where validity proofs are stored on-chain, while some data is stored either on-chain or off-chain.
Let's dig into the relevant data and see what happened on the zkSync Era and the Polygon zkEVM.
secondary title
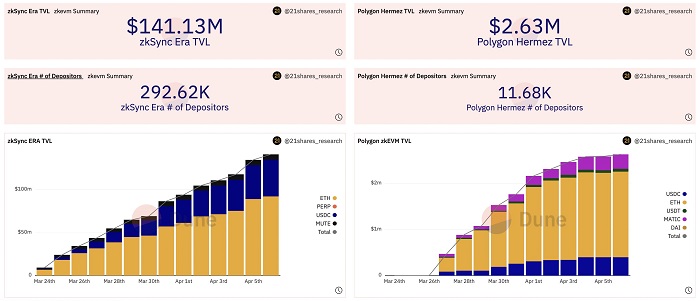
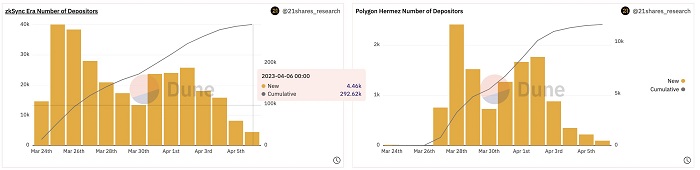
1. The number of new deposit addresses slowed down
Although the number of deposit addresses has increased significantly since the launch, the bridging activities of both zkSync Era and Polygon zkEVM have slowed down. In terms of the total number of unique deposit addresses, zkSync has a more obvious advantage, leading Polygon zkEVM with 292,620 unique deposit addresses (only 11,680). Although zkSync Era has about 280,000 more unique deposit addresses than Polygon zkEVM, how many of them are airdrop users? Next, the analysis will focus on three aspects:
Have they used Optimism/Arbitrum before?
Are they all real DEX/NFT traders?
secondary title
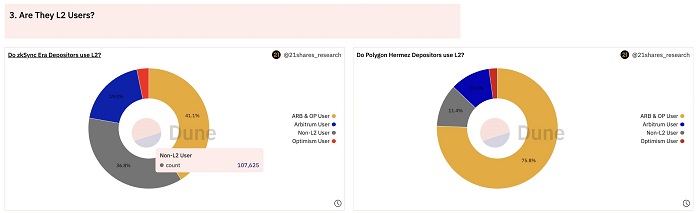
36.8% of zkSync Era deposit users have never used Optimism/Arbitrum before, and Polygon zkEVM performed better in this respect. Only 11.4% of Polygon zkEVM deposit addresses have not used Optimism/Arbitrum. In addition, more than 75.8% of deposits have used Optimism/Arbitrum at the same time.
secondary title
The data shows that more than 36.5% of deposit addresses were created after zkSync Era was launched, which means that the potential purpose of people creating wallets to use zkSync Era is to participate in airdrops.
secondary title
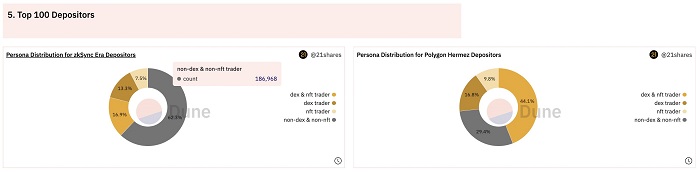
4. Are they all real DEX/NFT traders?





