Author: Kylo(Twitter: @kylohanks_eth)
Editor: Sarah; Ashely
As an extension of the financial system on the blockchain, DeFi will naturally have fixed-rate products and floating-rate products. In the encrypted financial industry, fixed-rate products and floating-rate products were launched at close to the same time, but due to the traction of user demand on the chain, the current DeFi pattern dominated by floating-rate products has resulted.
The current DeFi market lacks fixed-rate products. The lack does not mean that there is no demand for fixed-rate products in DeFi, but that compared to TradFi, which has a large amount of fixed-rate funds, there are only a handful of fixed-rate-related products in DeFi. The TVL is less than a fraction of a floating rate loan.
secondary title
1. Fixed rate product form
On the whole, the product forms of fixed interest rate products are divided into three categories: C2C, B2B and B2C.
These three forms are suitable for different tracks. C2C is suitable for fixed rate lending and fixed rate income products; B2B is suitable for institutions to sign a fixed rate agreement through OTC; B2C is a fixed rate asset management product for retail investors. However, there is a certain degree of overlap between C2C and B2C in terms of fixed-rate income products. This is because fixed-rate income products are essentially formed due to the existence of counterparties. In the C2C model, the counterparties are all retail investors, while in the B2C model, The counterparty of retail investors is a unified asset management product agreement.
Of the above three product forms, only the C2C and B2C forms can really promote the development of on-chain fixed-rate products. This is because even if there will be a large number of financial institutions participating in transactions on the chain in the future, the most convenient way to sign fixed-rate agreements between different institutions is still to use off-chain OTC means rather than through on-chain fixed-rate agreements. Therefore, from this perspective, the overall narrative of fixed-rate products is actually limited to the C-end, and it is difficult to form a pattern in which the scale of fixed-rate products in TradFi far exceeds that of floating-rate products. The supplementary service of interest rate products serves users on the chain.
secondary title
text
text
text
The above formula expresses a quantity relationship rather than a value relationship, that is, the market values on the left and right sides may not be equal, so arbitrage opportunities often exist when liquidity is poor. After the duration expires, epyvUSDC can be exchanged for USDC at 1: 1, and eyyvUSDC can also be directly exchanged for the income generated by 1 yearn USDC (epyvUSDC is a zero-coupon bond that meets a certain rate of return for 1 USDC, and eyyvUSDC is the future income that 1 USDC may generate discounted). The price of zero-coupon bonds is essentially one-to-one with the yield. Therefore, when the market demand for epyvUSDC fluctuates, the price of epyvUSDC will fluctuate accordingly, making the implied yield in a state of change.
secondary title
text
Based on the above basic mechanism, Element Finance can provide three products: interest rate swap products, leveraged products, and fixed-income products.
Interest rate swap products are essentially the same as fixed income products. For the buyer of Principal Token, buying Principal Token is equivalent to buying a zero-coupon bond, and the yield is determined by the purchase price. This Principal Token is a fixed-income product; for the seller of Principal Token, the cash obtained can be invested Other floating rate products are equivalent to exchanging the fixed rate product (Principal Token) in hand for a floating rate product (such as putting it into a machine gun pool), completing the process of interest rate swap. Interest rate swaps are essentially user-risk swaps. The fixed-rate seller hopes to obtain excess risk returns, while the fixed-rate buyer hopes to lock in future returns. The above process actually explains why fixed rate products are limited to the C side.
The interest rate leverage product means that users can use Element Finance to obtain the benefits of Yield Bearing Assets interest rate changes, and eliminate the price fluctuations of Underlying Assets themselves. To give a simple example, user A has 1 ETH and deposits it in Yearn Finance to obtain income. It predicts that Yearn Finance's ETH income will be higher than 10% in the long term in the future. Therefore, he hopes to use the leverage tools on the chain as much as possible to increase his interest rate exposure to Yearn ETH. Then use Element Finance to expand your leverage without the risk of liquidation. The specific implementation steps are as follows:
Divide 1 Yearn ETH to get one epyvETH and one eyyvETH It is estimated that Yearn Finance's ETH annualized return is higher than 10% Sell epyvETH at a discount of less than 10%, let's say 6%, and get 0.94 ETH in cash Reinvest 0.94 ETH into Yearn Finance, and then divide it... As long as the average floating interest rate of Yearn ETH is higher than 6% before the redemption period expires, the above operations will always be profitable. (If it is 10%, then the profit of the above strategy is 66.7%) As long as the average floating interest rate of Yearn ETH is higher than 6% before the redemption period expires, the above operations will always be profitable. (If it is 10%, then the profit of the above strategy is 66.7%)
This process has obvious advantages. It erases the price risk of Underlying Assets itself, allowing users' risk exposure only to the interest rate part, and multiple risks are reduced to one dimension. However, the above strategy constructed through Yield Token can only be bullish on floating interest rates, and cannot be applied to the bearish scenario of floating interest rates.
As for the problem of interest rate speculation, Voltz Protocol provides a more comprehensive solution.
Voltz Protocol provides users with a more comprehensive interest rate swap mechanism. Interest rate swap, also known as interest rate swap, refers to a transaction in which both parties to a fixed-rate transaction and a floating-rate transaction exchange cash flows in the future. However, there are still some differences between the interest rate swap represented by Voltz Protocol and TradFi. The interest rate swap in TradFi is based on the premise that the two parties to the transaction hold fixed-rate products and floating-rate products respectively, and exchange the income cash flow at a certain point in the future. The common method is B2B through OTC .
However, in DeFi, the common method of interest rate swap is that both parties use an existing fund pool as the counterparty, and indirectly realize the pairing of C2C scenarios on the chain, which requires the vAMM mechanism of Voltz Protocol.
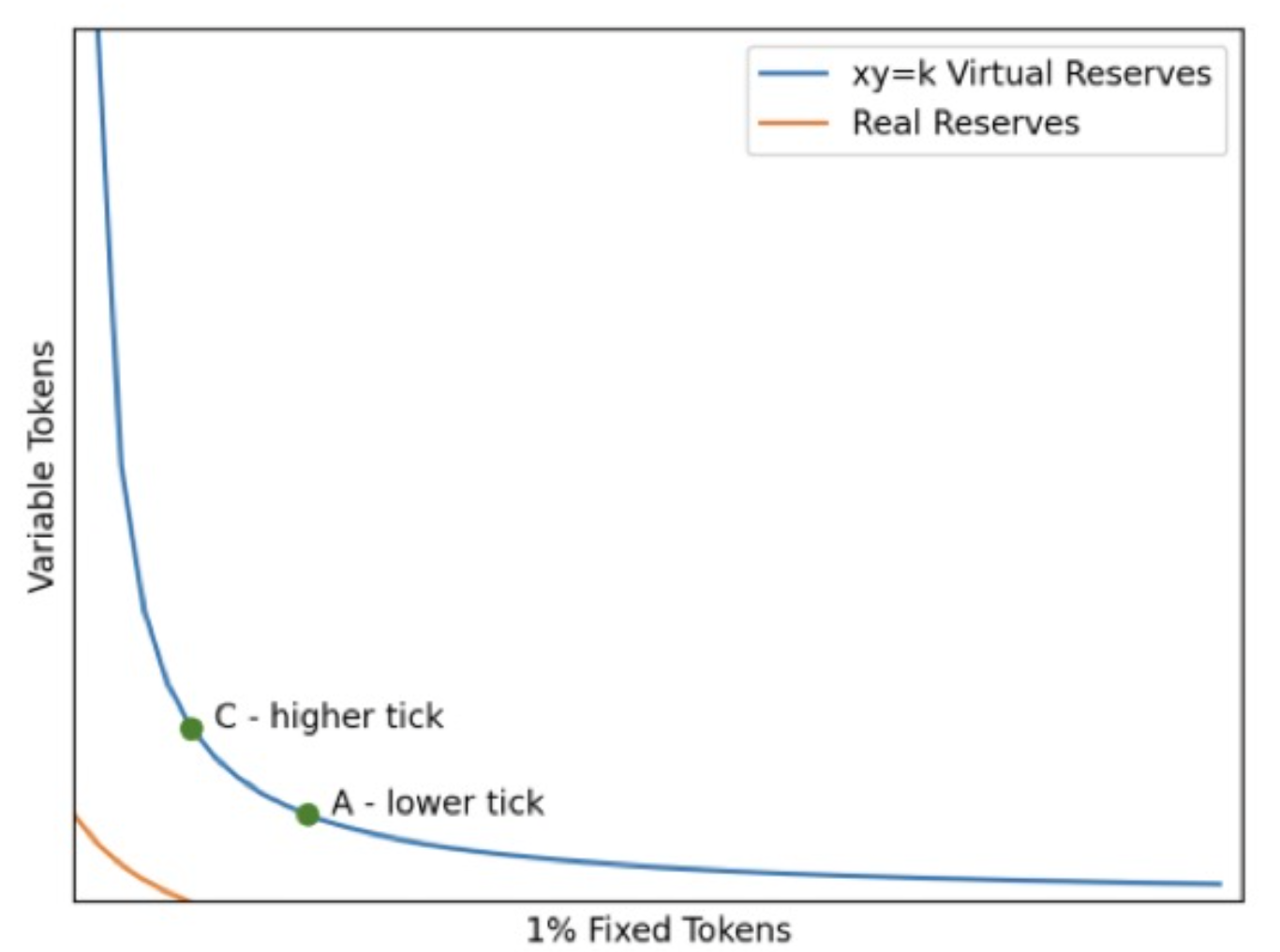
The trading pairs traded in vAMM are virtual assets, and the virtual asset trading pairs determine the current tradable fixed interest rates through the Uni V3 pricing model. The specific calculation formula is
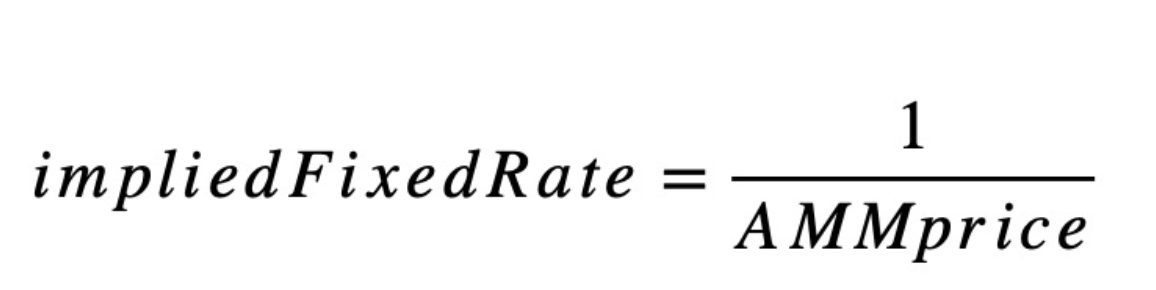
Therefore, the above-mentioned vAMM mechanism is actually a market-based discovery mechanism for tradable fixed interest rates. As for why 1% Fixed Tokens is used as a parameter in AMM, the main reason is that it is easy to use for 100% conversion of interest rates. Due to the adoption of the Uni V3 pricing model, LP can choose an acceptable fixed interest rate range for market making when making a market. In other words, it is the range of fixed interest rates that LP can bear when conducting counterparty transactions with Trader.
LP needs to use Voltz Protocol's margin system when providing funds and Trader conducts transactions. LP provides single-currency liquidity. For example, when providing liquidity for the aDAI interest rate swap pool in June, only DAI needs to be deposited. Therefore, LP does not have the problem of gratuitous loss. However, since the role of LP in the entire system is similar to the role of matching retail investors from both parties, it is inevitable to end up as the counterparty of retail investors in person. When the two parties fail to reach a balance, LP itself has a certain risk exposure. If the floating rate changes in the opposite direction to the LP's risk exposure, then the LP will incur a direct loss.
secondary title
4. Where are the problems in the development of fixed rate products?
From a narrative point of view, Element Finance has introduced new asset classes (zero-coupon bonds and floating rate sub-products) and interest rate leverage tools for DeFi. It stands to reason that the development of this track should have been on the fast track, not the current one. in its infancy. The problem actually lies in multiple aspects.
secondary title
text
secondary title
text
text
The derivation of the AMM formula is very simple, only one-step ordinary differential equation solution is required.
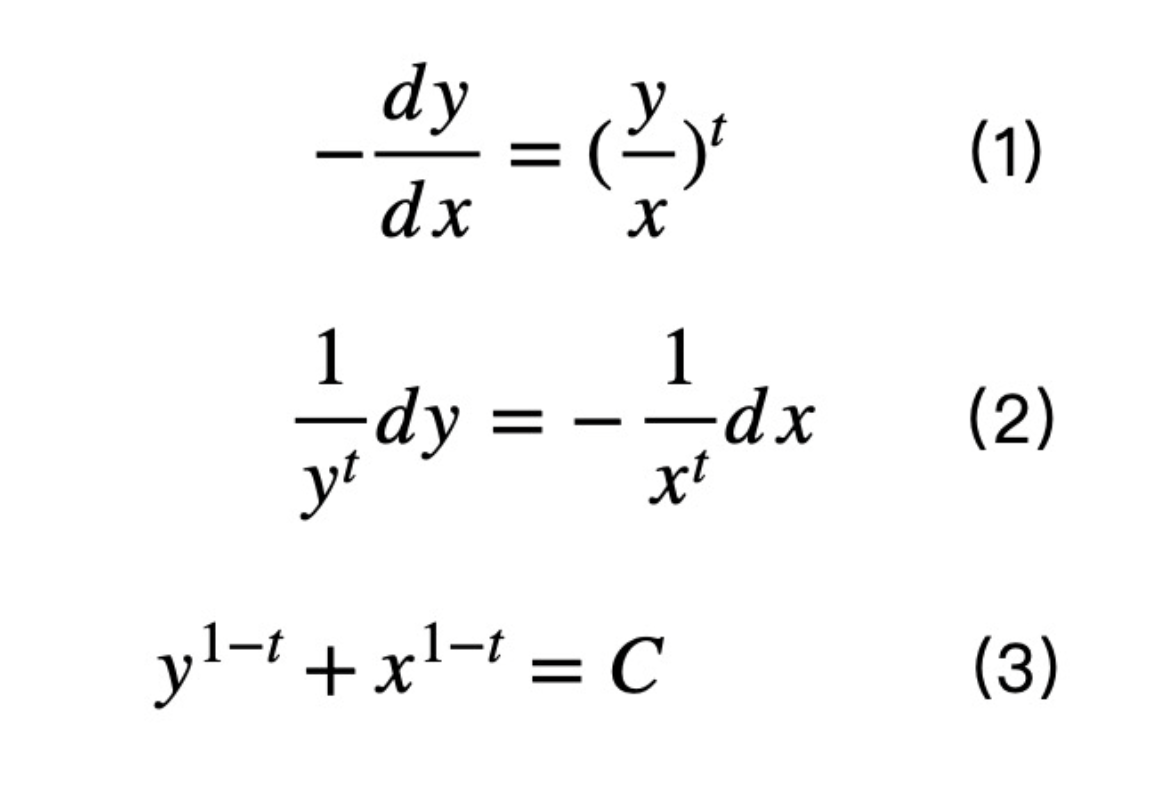
The core of understanding formula (1) is to understand the consistency between the price and yield of zero-coupon bonds. When the remaining time to maturity is t, the yield can be expressed as
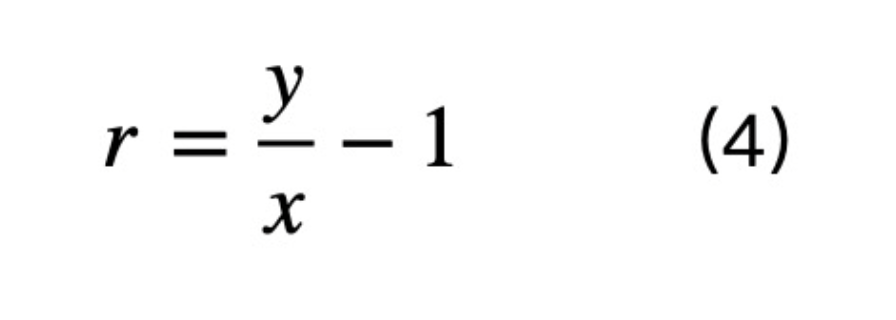
Equation (4) is an official hypothetical definition of the rate of return. According to the practical economic meaning, the formula for calculating the yield of zero-coupon bonds is
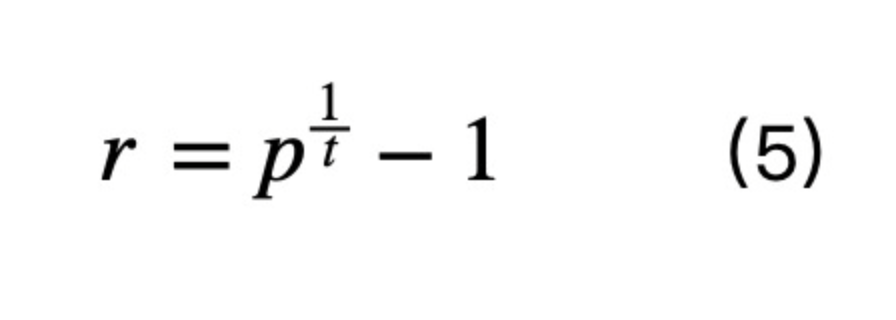
When the hypothetical definition is equal to the actual definition, it follows that
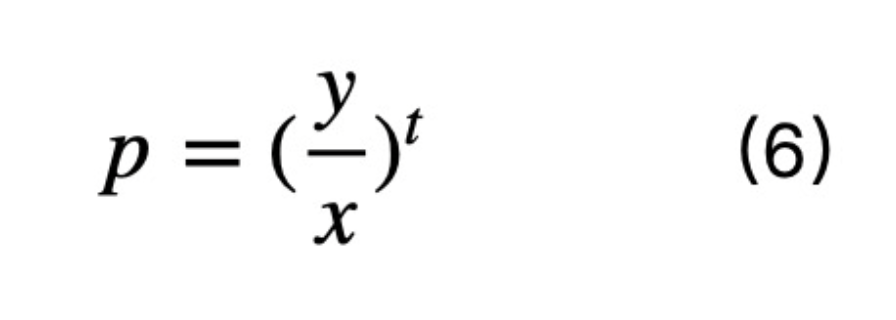
where p is the price and t is the time to expiration. As for the price p itself, another calculation formula for p is
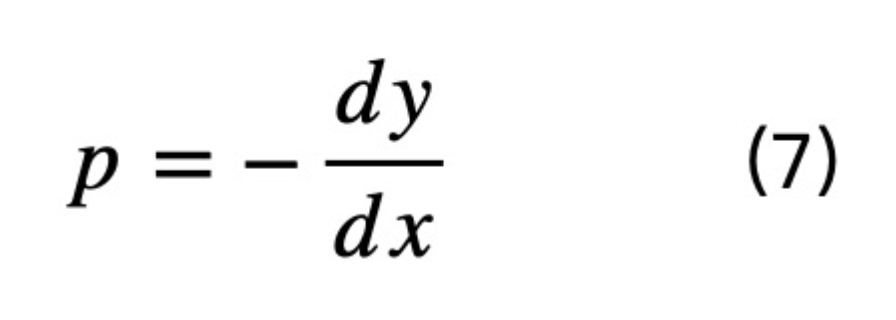
This leads to the above AMM formula.
Yield Protocol's loan funds come from the liquidity provided by users, and users can choose a 3-month or 6-month fixed deposit pool. After the user provides USDC liquidity, Yield Protocol will mint the corresponding amount of fyUSDC according to the current implied yield, and form a trading pair between USDC and fyUSDC.
For example, when the pool is just opened in 3 months, the agreement decides that the initial fixed interest rate of the pool is 3%, then the price of fyUSDC at this time is 1/1.03, and one fyUSDC will be destroyed at a ratio of 1: 1 after 3 months. Change to USDC. Before the 3-month period expires, fyUSDC will be subject to market price fluctuations under the influence of demand, which also means that the yield will fluctuate, but no matter how it fluctuates, fyUSDC will be redeemed in time after the 3-month period expires.
The fixed deposit pool is open at any time, and users can deposit into the deposit pool at any time, but the fixed rate of return is determined by the price of fyUSDC at that time, so there will be situations where the same user deposits funds in the pool at different times There will be different yields.
The special thing about Yield Protocol is that it uses the AMM mechanism for lending. The borrower and the lender essentially conduct fyUSDC-USDC transactions. The agreement deliberately separates the terms Lend and Pool.
The funds of the Yield Protocol's Pool are used to construct the fyUSDC-USDC transaction pair, that is, to increase the k value in the AMM. Lend and Borrow trade fyUSDC without changing the value of k.
When Lending, the user uses USDC to purchase fyUSDC in AMM, and the yield is determined by the price of fyUSDC; when Borrowing, the user uses the excess collateral mint fyUSDC, and then sells fyUSDC through AMM to obtain USDC, and the loan interest rate is determined by the price of fyUSDC at this time of. It is precisely because AMM is responsible for the entire Yield Protocol lending process that it needs to adopt the above-mentioned AMM mechanism that introduces t. The main purpose is to calculate the price of fyUSDC to price in the expiration time and reduce slippage during transactions. The details are as follows As shown in the figure:
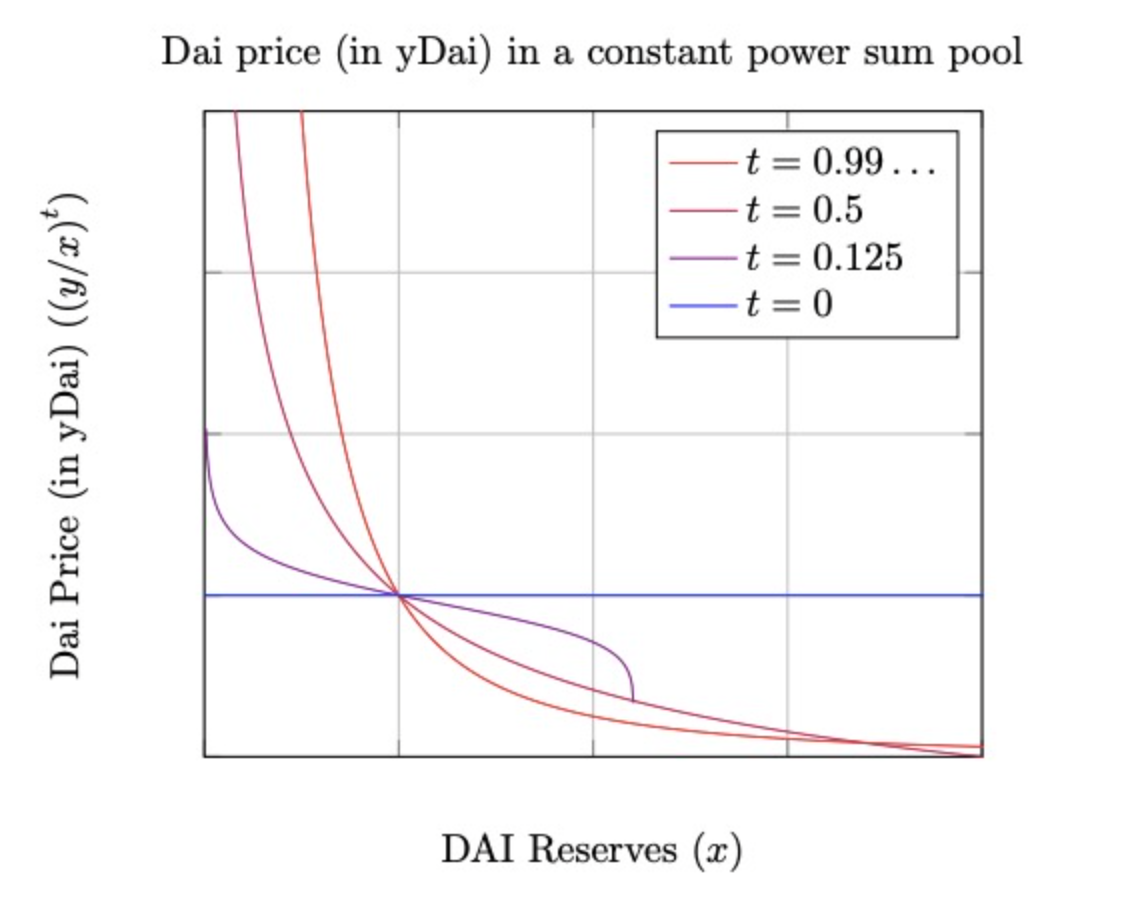
The use of the AMM mechanism for fixed-rate lending has opened up a new narrative for fixed-rate lending, but the mainstream of lending is still AAVE's floating-rate lending.
There may be four problems: First, MakerDAO's D 3 M works closely with AAVE and Compound to stabilize the loan interest rate on DAI at a low level, so that users hardly have excessive interest rates when borrowing DAI The second is that the AMM loan mechanism needs to provide LP liquidity first, and LP has a fixed impermanent loss. If the handling fee in the process of providing LP and the appreciation of some assets cannot exceed the impermanent loss, then the LP for the AMM will face direct losses. The third is that the current DeFi users are mainly retail investors, and the demand of retail investors for fixed-rate loans is actually not high; the fourth is that the current large-amount fixed-rate loans are restricted by the liquidity in AMM.
secondary title
7. Overview
The focus of the narrative of fixed-rate products comes from the analogy between floating-rate products and fixed-rate products in TradFi. In TradFi, the scale of fixed-rate products is larger than that of floating-rate products. Therefore, in the DeFi field, the scale of fixed-rate products on the chain should theoretically be higher on the scale of floating rate products.
However, the main participants in TradFi are financial institutions. Due to the existence of OTC, the signing of fixed interest rate agreements between financial institutions often becomes the cooperation method between institutions, and the asset size of each large transaction is large enough, and there is no liquidity problem. Therefore, it has achieved a pattern of fixed-rate products as the mainstream.
For DeFi, the current composition of users on the chain is mainly retail investors. The focus of retail investors participating in DeFi lies in convenience. Risk-controllable products such as fixed interest rates may not be the core demands of retail investors. Therefore, current DeFi and TradFi players The types are completely different. If you use the development law of TradFi to speculate on the development of DeFi, the result may be a thousand miles away.
We don’t know what the fixed rate product will look like in the future, but its narrative as a supplementary product should be the safest description at present.
image description
https://yieldprotocol.com/YieldSpace.pdf
https://docs.yieldprotocol.com/#
BinaryDAO is a semi-closed DAO organization that focuses on project research. It originated from the joint investment research of several WEB3 investment institutions. It is mainly for VCs and researchers. It focuses on research projects. Bear markets focus on depth and focus on secondary structural track leaders ; The bull market focuses on breadth and tends to be a first-level trend hotspot.
So far, we have conducted research and discussions on more than 50 projects in DEFI 2.0, derivatives, ZK, NFTFi, SocialFi and other sectors. We plan to conduct relative in-depth research on 200 representative projects in each sector in this bear market. Welcome Researchers and VC friends who are interested in completing these 200 projects with us will join us.





