At present, in the Layer 2 (L2) expansion solution of Ethereum, the solution using Rollup technology has become the mainstream, and the L2 network has been formed with different consensus mechanisms. The mainstream network represents Optimism, Arbitrum, ZkSync and StarkNet.
With the migration of applications after the network is completed, the L2 network has begun to fall into the battle for encrypted asset lock-ups.
The data website L2Beat shows that as of July 20, the value of encrypted assets (TVL) locked in the entire L2 network from high to low is Arbitrum > Optimism > ZkSync > StarkNet.
Under the backward situation, StarkNet began to imitate other L2 networks and put the issuance of native Token on the agenda. You must know that incentives are the best way to attract traffic in the blockchain world. On July 13, StarkWare, a blockchain expansion technology service provider, published three blogs in a row, introducing the native Token of its Layer 2 expansion network StarkNet, including economic governance model, application scenarios, issuance quantity and distribution, etc.
Earlier in April, Optimism issued the native Token OP, which was officially launched on the secondary market on May 30. After the release of OP, Optimism began to show its advantages in TVL.
Arbitrum and ZkSync are the only Rollup L2 networks that have not yet issued Tokens, but judging from the recent and past ecological dynamics, Tokens will be issued sooner or later.
ZkSync stated in the official user documentation that it will issue Tokens, but did not disclose the specific release time. Open the ZkSync user documentation page, the first question is about "whether there will be a Token", and the official answer is "Yes".
Arbitrum did not explicitly state that it will issue Tokens, but it released an ecological exploration activity called "The Arbitrum Odyssey" on April 20, encouraging users to use on-chain projects to obtain NFT rewards. Many users speculated that participating in activities and obtaining NFT rewards is likely to be the "user eligibility" threshold set by Arbitrum for the subsequent issuance of Tokens.
first level title
Optimistic Rollup L2 network has higher TVL
The Rollup technology, which can not only ensure the security of the blockchain network, but also improve the network throughput, is becoming the mainstream technology of the Ethereum Layer 2 (L2) expansion solution. The solutions based on this technology have formed two schools of Optimistic Rollup and ZK Rollup due to the different consensus algorithms, and these two solutions have L2 networks that have already been implemented.
Currently, Optimistic Rollup’s L2 representative networks are Optimism and Arbitrum; the main players of ZK Rollup’s L2 landing network are StarkNet and zkSync.
image description
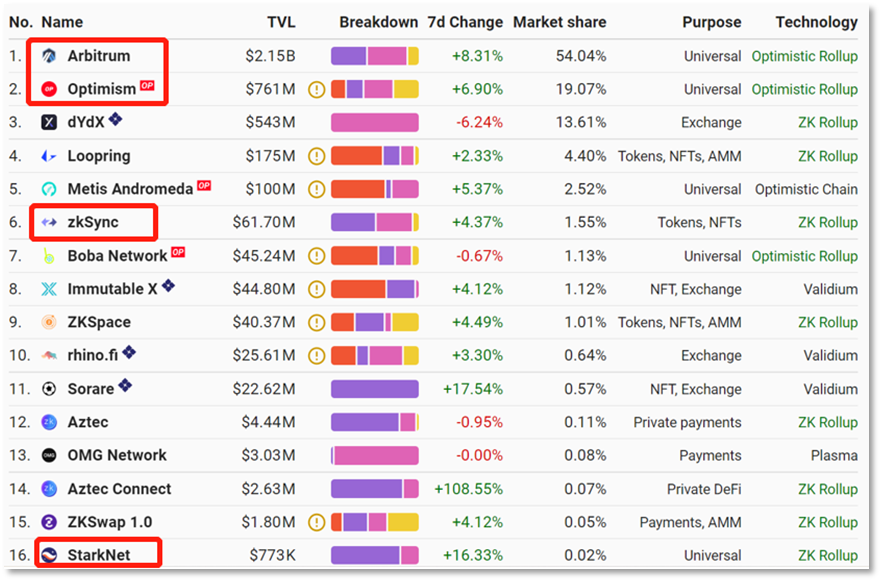
L2 network TVL and market share data
It can be seen that zkSync and StarkNet of the ZK Rollup series are far inferior to Optimism and Arbitrum of the Optimistic Rollup series in terms of TVL and market share.
This is mainly due to the first-mover advantage of Optimism and Arbitrum’s mainnets. The mainnet of Arbitrum was officially launched as early as August last year, and the mainnet of Optimism was launched in July last year. The ZkSync network version 1.0 of the ZK Rollup series was launched in July last year, but due to underlying technical reasons, the usage scenario is limited to payment. It was not until the release of zkSync 2.0 in February this year that it was compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), suitable for developers. ; while the StarkNet mainnet is still in the public beta stage and has not yet been officially launched.
The network implementation of the ZK Rollup system is slightly slower than that of the other faction. This is mainly because the ZK Rollup technical solution based on the "zero-knowledge proof algorithm" is more complicated and takes time to implement. More importantly, the compatibility between the L2 network and EVM of this series has been difficult to make a breakthrough. It was not until the zkSync 2.0 version that there was a new turning point, claiming to be 99% compatible. The compatibility between L2 network and EVM is directly related to the time and economic cost of application developers, and it is difficult for a blockchain network without applications to attract users and assets.
first level title
Optimism first issued tokens
The Arbitrum and Optimism networks, which rank the top two in TVL, have their own characteristics in ecological layout and different development routes. The former pays more attention to user experience, while the latter has achieved TVL growth after issuing native tokens.
Speaking of which, the Optimism mainnet launch time is one month earlier than Arbitrum. However, in July last year, when the network was launched, it was not yet 100% EVM, and it could not realize the one-click migration of DApps on the Ethereum chain. The ecological development on the chain was overtaken by the latecomer Arbitrum.
In November last year, the OVM virtual machine version 2.0 deployed by Optimism was fully equivalent to EVM, and it could also simplify the development process for developers and reduce costs. This is the official "germination" of the network's on-chain ecology.
However, in the early days, the applications on the Optimism chain mainly revolved around the synthetic asset protocol Synthetix to derive new products. Since these products are mostly complex options, contracts and other DeFi financial derivatives, it is not easy for ordinary trading users to operate, and is more suitable for professional traders. use. Therefore, the on-chain application failed to attract a large number of users and funds.
It was not until April 27 this year that Optimism announced the issuance plan of the native token OP that users’ attention was attracted. It is also the first L2 network to issue tokens based on the Rollup technical framework.
The total amount of OP issued is about 4.29 billion, and the total supply will expand at a rate of 2% per year, mainly for community governance, voting rights and project incentives. A total of 19% of OP will be airdropped to users, of which 5% will be airdropped to the community in the first round, and the other 14% will be distributed in the future.
After the airdrop, OP quickly went online on the secondary market, forming a transaction price, with a maximum of $2. According to data, the minimum number of airdrops for OP is 409.42. According to the high price, the minimum airdrop value of OP is about $800. The wealth effect of early users quickly attracted the attention of the market, and external users began to participate in its ecology, hoping to be selected in the next wave of OP airdrops.
After completing the first round of airdrops, on June 9th, Optimism took out 231 million OPs to create an incentive fund, aiming to subsidize builders and projects in the OP ecosystem, and determine the value of OPs based on the project’s TVL, daily trading volume and other indicators. Number of incentives.
The Token Incentive Program has successfully introduced users and projects into the Optimism ecosystem. According to data from the Optimism browser, on June 2, a week before the news of the creation of the incentive fund, the number of daily transactions on the chain reached a peak of 487,000, and the number of daily increasing addresses was 39,000. As of July 20, the network has a total of 1.21 million addresses on the chain.
representative application
Optimism Bridge——The official cross-chain bridge of Optimism, which supports cross-chaining of assets on L1 public chains such as Ethereum, Polygon, BSC and L2 network Arbitrum to Optimism.
Layerswap——A tool for directly withdrawing encrypted assets from the centralized exchange (CEX) to the L2 network, developed by the encrypted payment basic service provider Bransfer.
Synthetix (SNX) Ecosystem——It was originally a synthetic asset issuance and trading application built on Ethereum. Users can generate various synthetic assets through the over-collateralized governance token SNX.
In September 2021, Synthetix announced the migration of applications from the Ethereum mainnet to the Optimism network, becoming the first Ethereum head application to support the L2 network. Among them, synthetic assets such as sUSD, sETH, sBTC, and sLINK have become mainstream assets on the Ethereum and Optimism networks.
Based on these synthetic assets, Synthetix has built multiple application scenarios on the Optimism network, including synthetic asset comprehensive trading platform Kwenta, option trading platform Lyra, one-stop option investment platform Polynomial, asset management platform dHEDGE, derivatives trading platform Thales, etc.
ZipSwap(ZIP)——The decentralized exchange application (DEX) native to the Optimism network, which is built on the code of the Uniswap v2 version, hopes to provide Optimism users with a low-cost asset exchange place.
Quixoticfirst level title
Arbitrum sucks on user experience
The release of OP has indeed brought capital flow to the Optimism ecosystem, but the TVL of the network is still inferior to that of Arbitrum, which was born only one month later. Why?
Arbitrum is developed by the Offchain Labs team. Although it does not issue Token, it also focuses on incentives. On April 20 this year, the official announcement of the ecological project exploration activity plan called "The Arbitrum Odyssey" is aimed at encouraging users to interact with ecological applications through NFT, allowing users to understand and experience the chain by performing tasks on the chain. Use on DApp.
The event lasts for 8 weeks, and the applications that encourage user interaction cover a variety of scenarios such as cross-chain bridges, DeFi and NFT, games, etc. Users can experience the applications listed in each issue, complete relevant tasks, and obtain official NFTs. Many users have speculated that NFT is likely to be an air investment qualification certificate after Arbitrum issues tokens.
On June 22, The Arbitrum Odyssey launched its first campaign, which successfully attracted traffic. According to the Arbiscan browser, on June 27, the number of daily transactions on the chain was 287,000, and the number of new addresses was 56,000. The surge of users once caused serious congestion on the Arbitrum chain, and the gas fee increased.
According to L2fees data, on June 29, on the Arbitrum network, the average gas fee per transaction soared to more than $9 at its peak, which was twice the gas fee of the Ethereum mainnet during the same period, and the complaints of participating users were boiling. Subsequently, Arbitrum officially announced the suspension of activities.
In terms of improving user experience, Arbitrum even developed a new chain. On July 12, the network announced the construction of a new chain "Arbitrum Nova", which is currently running on the Ethereum mainnet, and developers can deploy related applications on the chain.
In this way, Arbitrum has become a dual-chain ecosystem - Arbitrum One and Arbitrum Nova, the former is the existing main network, and the latter is built on AnyTrust technology, which is designed for games, social applications and more cost-sensitive use cases. design.
The reason why the Arbitrum Nova chain was launched is because the main network Arbitrum One has a data objection period due to the underlying consensus algorithm. The direct result is that users need a 7-day waiting period when withdrawing Token back to the Ethereum network, which affects user experience. It is not friendly enough for application scenarios with high throughput requirements.
Arbitrum Nova is suitable for cost-sensitive application scenarios with high transaction volume expectations, such as games and social applications, while Arbitrum One will continue to cover DeFi and NFT projects.
representative application
Hop Protocol cross-chain bridge——Mainly support the transfer of encrypted assets between L2 network and L1 network.
Arbitrum bridge——Arbitrum's official cross-chain bridge, which supports cross-chaining of Ethereum assets to the Arbitrum network. It should be noted that it takes a 7-day waiting period for assets to return from L2 to L1.
GMX——A decentralized perpetual contract trading application built on the Arbitrum chain.
Treasure DAO—— Metaverse and NFT base layer platform on Arbitrum, integrating NFT, DeFi and GameFi applications.
Stargate—first level title
ZkSync focuses on improving network performance
Regarding Rollup technology, Vitalik Buterin, the founder of Ethereum, has repeatedly stated in public that ZK Rollup is the ultimate choice for L2, but due to the complexity of its underlying technology, it will take a long time to implement.
In the L2 network based on ZK Rollup technology, StarkNet and zkSync are the main representatives. Although both of them lag behind the L2 network based on Optimistic Rollup technology in terms of development progress and ecological data performance, they are still favored by the outside world because they can achieve instant transfer . Especially with the launch of zkSync 2.0, which is compatible with EVM, the development progress has exceeded industry expectations.
The zkSync network is built by the Matter Labs team, and all its products are open source and more inclined to community-based operations. Matter Labs has even stated many times that "it doesn't matter if you are replaced", the purpose is only to promote the development of the Ethereum community. On the development route, the team has been working on improving the network and improving performance.
The zkSync 1.0 version was launched in June 2020, mainly focusing on payment. Due to incompatibility with EVM, the usability of the network is limited, and the application scenarios that can be supported are very limited. However, due to the low transfer fee and instant arrival, it shows its superiority in payment scenarios.
In February of this year, the public testnet of zkSync version 2.0 was launched, realizing EVM compatibility, and will most likely become the first blockchain network that uses the ZK Rollup solution and is compatible with EVM. zkSync2.0 supports developers to use Ethereum’s native programming language Solidity to deploy DApps on the network. Existing DeFi applications on the Ethereum mainnet can also be integrated into the zkSync2.0 network to enjoy the advantages of high efficiency and low fees brought by the L2 network.
However, the official mainnet of zkSync2.0 has not been launched yet. Some users speculate that its mainnet launch is likely to be launched at the same time as the issuance of Token. Of course, the actual situation still needs to wait for official news.
representative application
Decentralized trading application ZigZag——A DEX with an order book model, trying to become an on-chain alternative to centralized exchanges (CEXs).
Cross-chain bridge Orbiter Finance——Applied to the L2 network, it supports the cross-chain transfer of assets between L2 networks such as zkSync, Arbitrum, and Optimism, and also supports the mutual transfer of assets between L2 and L1 networks.
SyncSwapfirst level title
StarkNet will issue Token
StarkNet is built by StarkWare, which solves the expansion problem for L2 through the idea of productization.
Founded in 2018, StarkWare has a complete set of L2 system solutions. In terms of expanding the capacity of Ethereum, it has produced two landing products, StarkNet (L2 network) and StarkEx (expansion engine).
StarkEx is a set of scalable engine technology that provides services specifically for Ethereum DApp applications. It is essentially a data processor connecting L1 and L2. This technology has served many well-known DApps, including the decentralized perpetual contract trading application dYdX, the decentralized trading application DeversiFi, and the NFT ecosystem Immutable X, etc.
StarkNet is a general-purpose L2 network. The testnet has been launched in November 2021 to support developers to deploy applications. Since StarkNet is not yet compatible with EVM, it has not been migrated to the top application of Ethereum, and the ecology has been unstable.
In this state, StarkNet decided to issue Token.
On July 13th, StarkWare released 3 consecutive blogs, introducing StarkNet’s native tokens, including Token’s economic governance model, application scenarios, issuance quantity and distribution, etc., and said that the StarkNet network has minted 10 billion tokens and started Assigned to contributors and related investors of the StarkNet ecosystem.
According to the plan, StarkNet tokens will be circulated on Ethereum with the ERC-20 standard in September this year, and will be used as the only means of payment for StarkNet network Gas fees in the future. Currently, StarkNet network gas fees are settled in ETH.
representative application
Cross-chain bridge StarkGate——Official cross-chain bridge, supporting L1 assets to be stored in the StarkNet network
One-stop trading application JediSwap- Decentralized trading application of Automated Market Maker (AMM) mechanism on StarkNet.
Starkswap——The native AMM-style DEX on StarkNet.
Perpetual contract application ZKX——The first decentralized financial derivatives application on Starknet, which received US$4.5 million in seed round financing on July 18 this year.
Zklend——Decentralized lending application, completed a $5 million seed round of financing in March this year.





