Original Author: Ben Schecter
Compilation of the original text: Gu Yu

Original Author: Ben Schecter
In the future, ordinary people will most likely not work for companies. Instead, people will earn income in non-traditional ways through activities such as playing games, learning new skills, creating art, or curating content. This shift in the way we work is not unusual or unexpected - the idea that most people would be employed by large corporations seemed crazy to some in 1800.
In the future, ordinary people will most likely not work for companies. Instead, people will earn income in non-traditional ways through activities such as playing games, learning new skills, creating art, or curating content. This shift in the way we work is not unusual or unexpected - the idea that most people would be employed by large corporations seemed crazy to some in 1800.
This new future of work is enabled by networks forming around cryptographic protocols that are emerging as new ways to coordinate, measure, and reward contributions to complex ecosystems. This shift has begun to unlock new income-generating potential for individuals and is causing value capture to increasingly shift from organizations to the people who participate in crypto networks as individuals.
The traditional way of earning money is "earning money through work", but the future of income is "X-to-earn" - playing games to make money, learning to make money, creating money to make money, and working to make money.
However, this won’t happen magically — it will require new decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) that can coordinate all this new activity in the context of enterprise systems. This article provides a framework for understanding the options available in future work.
01
Think Apple and the developers who create the App Store apps, YouTube and the creators, or Uber and their drivers - players contribute externally to the company's growth, but companies struggle to align incentives with these stakeholders be consistent.
First, we need to explain the shortcomings of the existing monetization model. In the information age, traditional corporate employment is rapidly becoming obsolete as a means of coordinating activities - we are already seeing this in the emergence of alternative forms of income such as influencers, contractors, creators, gig economy participation Those who wait. These ways of making money don’t necessarily feel like “jobs,” but they are all examples of people participating in complex networks as individual value providers and earning income through their contributions.
However, these non-traditional opportunities are limited in number and, when available, often undervalue contributors. This is because these efforts are still based on the web2 paradigm, in which companies continue to control the business model.
Increasingly, traditional companies have “peripheral stakeholders,” actors who blur the line between internal and external members of the organization.Think Apple and the developers who create the App Store apps, YouTube and the creators, or Uber and their drivers - players contribute externally to the company's growth, but companies struggle to align incentives with these stakeholders be consistent.
As companies grow, they are no longer able to maintain sustainable relationships with these external network participants. The relationship between companies and participants becomes a zero-sum game, and companies start to extract value from these participants in order to maximize profits.
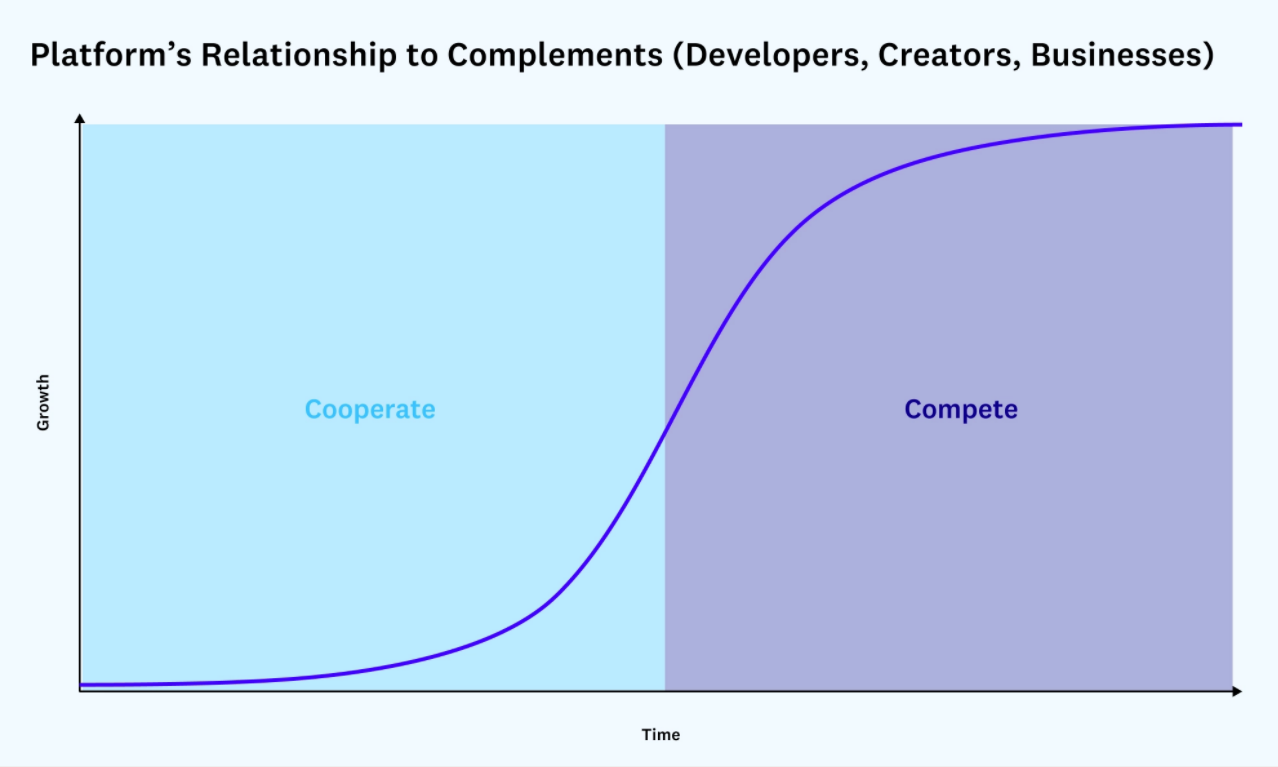
A corporate model with strict boundaries between internal and external might have made sense in the industrial age, but in the information age, such a model leads to incentive misalignment and unsustainable extraction. In our world of complex information and peripheral stakeholders, corporations are no longer appropriate to help us coordinate our activities.
Encrypted networks create better consistency among participants, and DAOs will be the coordination layer for this new world.
02
These elements that differentiate DAOs from traditional organizations actually enable DAOs to develop more symbiotic relationships with their stakeholders and participants. DAOs function as open economies, encouraging the accumulation of value wherever value is provided, not based on arbitrary legal boundaries. Chris Dixon once pointed out:
DAOs will eventually replace traditional models. A DAO is an internet-native organization whose core functions are automated through smart contracts and made up of people working on things that cannot be automated (e.g. marketing, software development). In practice, not all DAOs are decentralized or autonomous, so it is best to think of DAOs as internet-based organizations that are jointly owned and controlled by their members.
Although DAOs are still in their early stages of development, they are no longer just a promising concept. They are real organizations, managing billions of dollars in capital, providing real products and services to millions of people, and creating new ways for people to generate income.
Here's a good overview of the current DAO landscape by Cooper Turley:
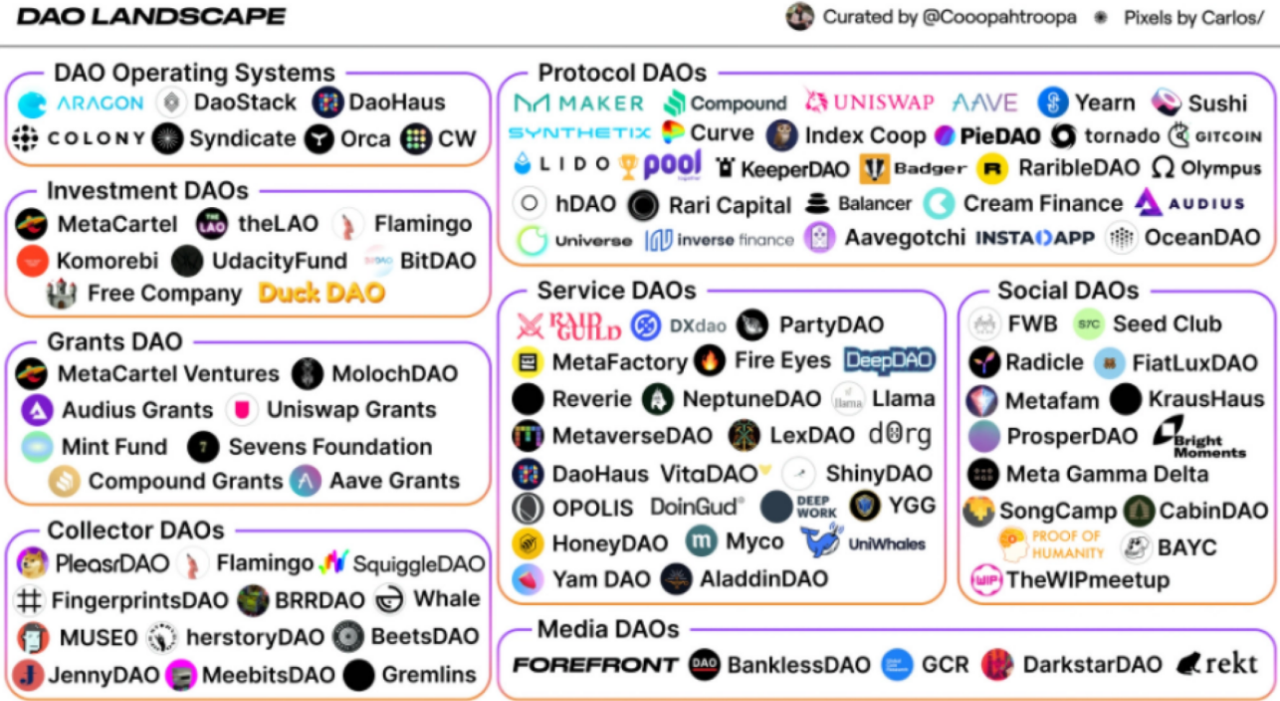
There are many different types and sizes of DAOs: DAOs that manage crypto protocols (Protocol DAOs), DAOs that make venture capital investments (Investment DAOs), DAOs that provide services to other DAOs (Service DAOs), DAOs that buy NFTs (Collector DAOs) ) ), There are a lot more.
But across all DAOs, there are some common threads that distinguish them from traditional organizations (these are generalizations, so note that they vary by specific instance):
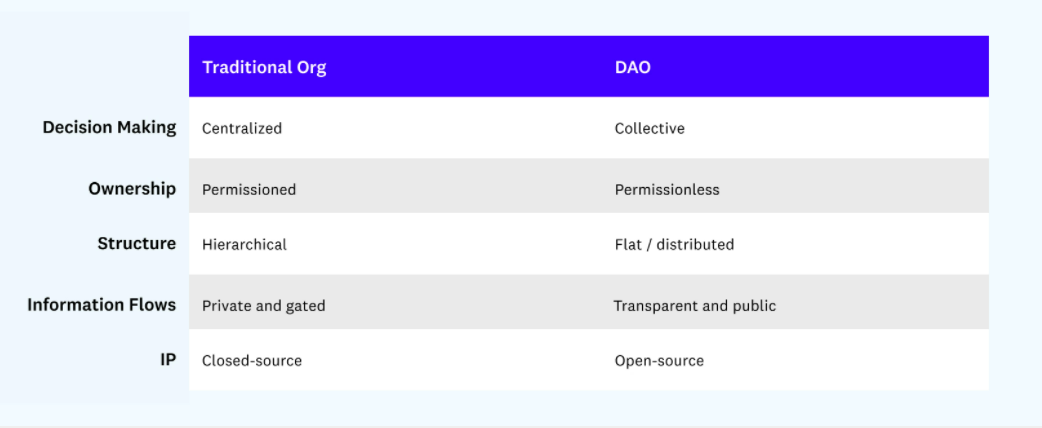
These elements that differentiate DAOs from traditional organizations actually enable DAOs to develop more symbiotic relationships with their stakeholders and participants. DAOs function as open economies, encouraging the accumulation of value wherever value is provided, not based on arbitrary legal boundaries. Chris Dixon once pointed out:
Cryptonetworks use a variety of mechanisms to ensure they remain neutral as they grow, preventing bait-and-switch from centralized platforms. First, the contracts between the encrypted network and its participants are executed in open-source code.
Second, they are controlled through "voice" and "exit" mechanisms. Participants gain a voice through community governance, both "on-chain" (through the protocol) and "off-chain" (through the social structure surrounding the protocol). Participants can exit by leaving the network and selling their tokens, or in extreme cases by forking the protocol.
Cryptonetworks use a variety of mechanisms to ensure they remain neutral as they grow, preventing bait-and-switch from centralized platforms. First, the contracts between the encrypted network and its participants are executed in open-source code.
Second, they are controlled through "voice" and "exit" mechanisms. Participants gain a voice through community governance, both "on-chain" (through the protocol) and "off-chain" (through the social structure surrounding the protocol). Participants can exit by leaving the network and selling their tokens, or in extreme cases by forking the protocol.This emerging positive-sum dynamic underlies the X-to-earn trend that will shape the future of work.
03
first level title
Core Contributors: work-to-earn
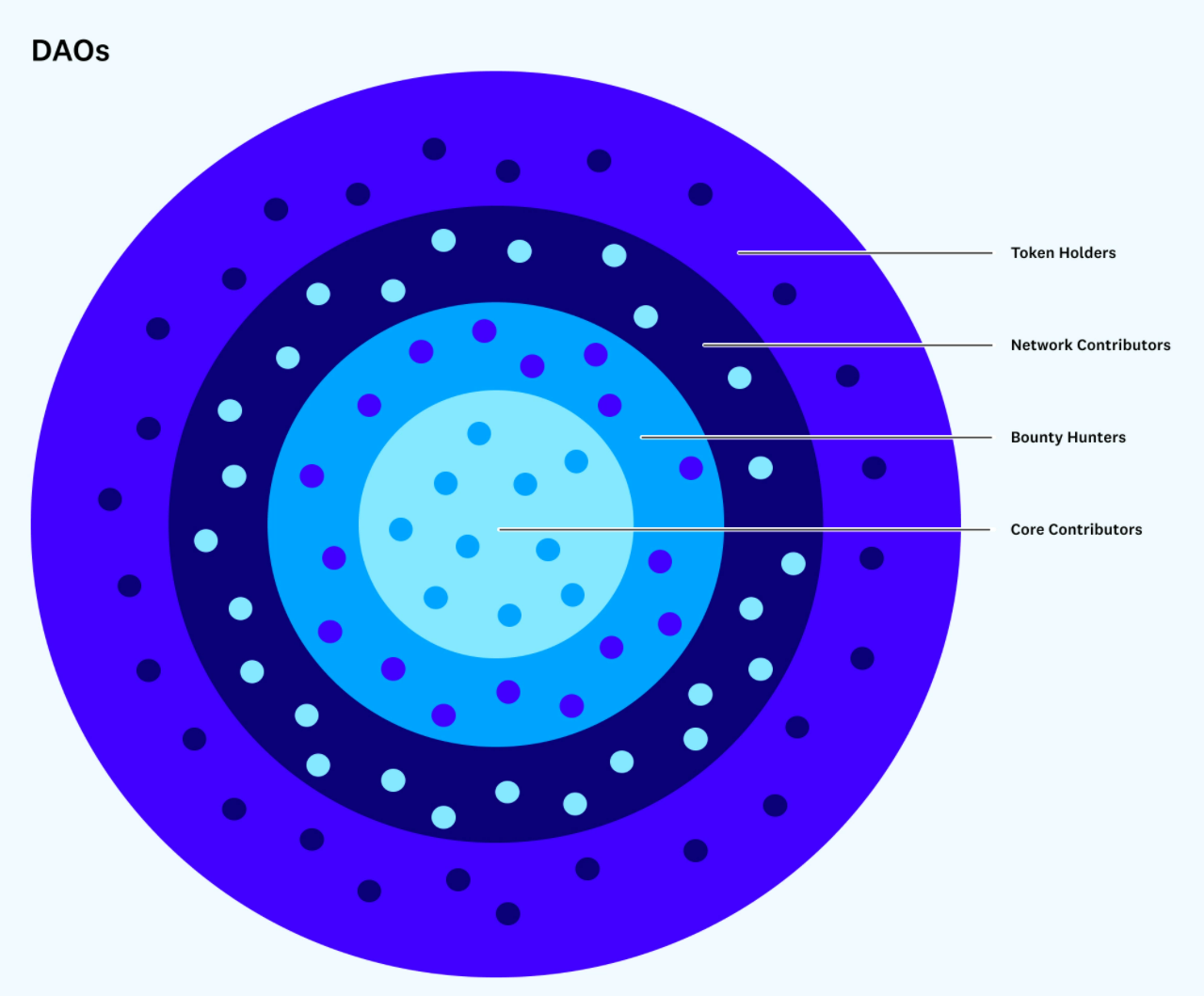
Graphic inspiration from Brian Flynn, Zakku and the Orbit team
DAOs as open economies will drive the X-to-earn trend, which will make work more flexible, fluid, and fun than the 9-to-5 we are used to.
The openness of these crypto economies will allow people to participate in multiple DAOs and crypto networks, mixing and matching different revenue streams and returns on ownership (remember, the best DAOs distribute ownership to their participation via their own native tokens By).
People's income will be things we currently do in our lives already (e.g. playing games), things we consider traditional jobs (e.g. bonuses/contracts) and things currently only available to a small percentage of people (e.g. investing, passive income). in other words,The DAO will expand the type and amount of opportunities open to multiple types of participants, including token holders, bounty hunters, and core contributors.
For example, token holders may earn by receiving grants from major DeFi protocols, passive income from various tokens, etc.; bounty hunters will earn by completing incentivized on-chain actions; network participants can earn by playing Axie Infinity or other upcoming P2E games to make money.
In this new future of work, work will be more ephemeral and dynamic - switching between jobs will be less costly, opportunities will be more apparent, jobs will be reduced to more atomic units, and the entire world will be united in one workforce Get all the opportunities below. We will discover new opportunities based on our on-chain history, ownership and reputation, and we will be matched to contribute where we have the best comparative advantage.
Here are the details of how participants see earning opportunities through the DAO.
Core Contributors: work-to-earn
A core contributor is what we typically think of an employee today - someone who is dedicated full-time to one (maybe 2-3 in some cases) projects or organizations. A single focus enables individuals to engage with projects and accumulate contextual and strategic knowledge.
The need for dedicated and embedded workers will never go away, but in web3 there will be far fewer of these people than ever before. Software and to a greater extent smart contracts enable a small group of people to have a huge impact. Instagram was acquired by Facebook for $1 billion with a team of 13 people. Results of this type will become common in the future,Play-to-earn is a new game mode that rewards players for playing and earning achievements within the game. Traditional gaming models involve a unilateral transfer of value to the game creator or platform, while play-to-earn games also reward users.
In the future, there will be no clear difference between working for this team and working for a company - the DAO will still have core contributors whose interests are most directly aligned with the health of the organization. Because DAOs are more transparent than corporations and can be held accountable by a larger community, however, with more pressure (think scrutiny of public officials).
Bounty Hunter: contribute-to-earn
"Bounty hunters" perform well-defined jobs for an agreed upon price and/or duration. These people are usually functional experts in fields such as finance, development, and design, and they serve multiple DAOs at the same time, and complete specific tasks with clear boundaries.
Bounties are usually posted publicly for anyone to claim, and can sometimes be competitive, rewarding the best submissions based on the merit and value of contributions after the fact, rather than based on a pre-application process or bidding war.
Many bounty hunters will band together to form their own service DAOs - think of these organizations as outsourcing help to DAOs that don't have the required skills at hand. These service DAOs arise to accomplish tasks that require functional knowledge, such as treasury management (eg, Llama), software development (eg, RaidGuild), governance (eg, Fire Eyes), and more.
While bounty hunters and service DAOs may sound like contractors and professional services firms, they will be different and more popular among DAOs for several reasons:
Smart contracts will automate a large portion of the DAO's core functionality, leaving more peripheral work that is well-defined, functionally specialized, and well captured through bounties.
DAOs will deliberately try to push work to the periphery to maintain decentralization and avoid large hierarchies, and bounties create a sustainable way to do this.
The transparency of the DAO will reduce the coordination cost of bounties.
Network Participants: participate-to-earn
This is the latest and perhaps the most exciting part of the future of work. In any given DAO, this is where most people will fall.
Networks gain power with more activity and more participants, however, users, consumers, and participants have been adding value to the network for years without getting their share of the value (e.g. Apple's app developers, YouTube creator and Uber driver)).
More like an open economy than a closed organization, a DAO will reward each individual's contribution based on the value it provides, regardless of who it comes from. This means that everyday actions that are valuable to the network will be transformed into revenue generating opportunities.
Almost everyone can earn some income simply by living their lives online, using products, and participating as users. For people who get paid for participating in the network, earning an income can feel like a game.
Play-to-earn (earn while playing)
Play-to-earn is a new game mode that rewards players for playing and earning achievements within the game. Traditional gaming models involve a unilateral transfer of value to the game creator or platform, while play-to-earn games also reward users.
Playing money-making games functions like an economy: players contribute labor (their time and effort) and capital (often buying NFTs to participate in the game), and are rewarded with fungible tokens for their achievements and progress in the game. Earning currency from games is nothing new, but instead of rewarding players with an in-game currency that is limited to being used in the game, the game distributes fungible token rewards that can be exchanged for Other encrypted tokens or fiat currencies.
That means video gamers can pay their bills through their in-game achievements, especially for people in countries with lower wages and living costs. This phenomenon has become a source of income for millions, especially through Axie Infinity.
Axie opened the way to earning income, and more importantly, it gave people a look at the larger X-to-earn trend, showing how people can earn income by contributing to the network.
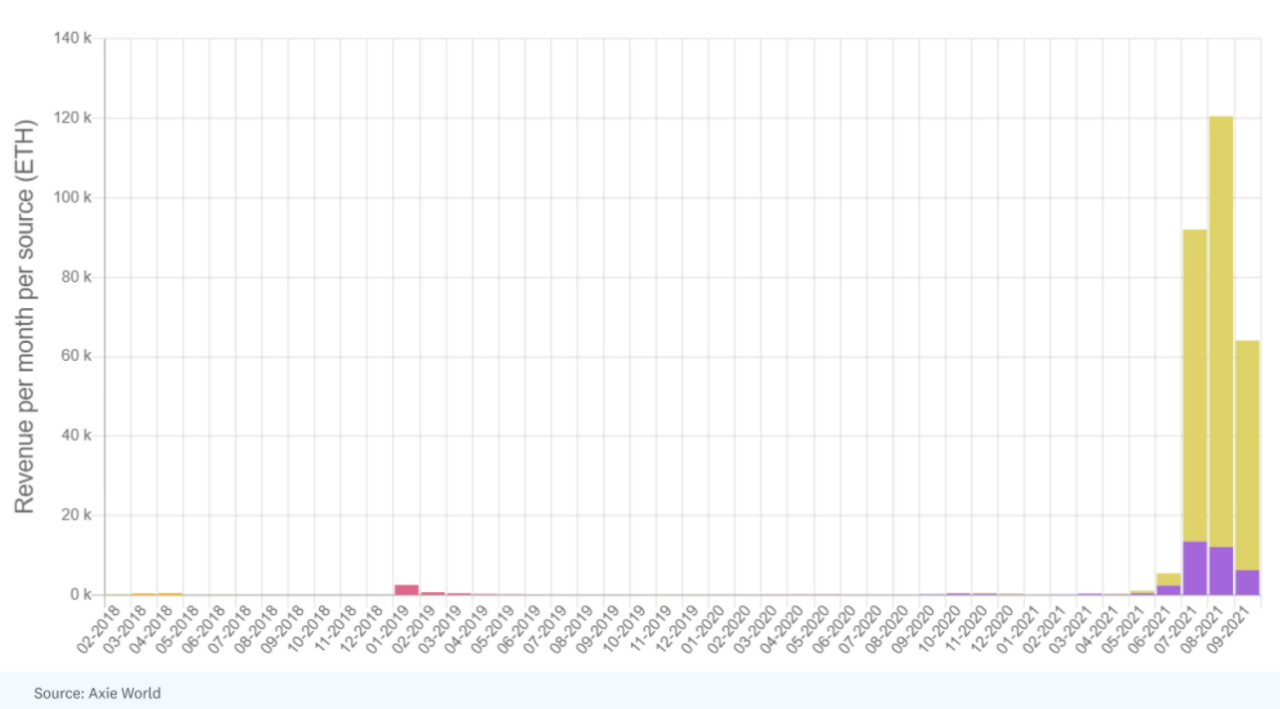
Source: Axie World
This explosive growth is due to the incentive alignment between Axie and its users, which Axie describes in the following way:
Axie has a real money economy that is 100% player owned. Instead of selling game items or copies, game developers focus on growing players into a player economy and monetize for a small fee. Axies are created by players using in-game resources (SLP and AXS) and sold to new/other players. Holders of AXS tokens are governments that receive tax revenue. Game assets and items are tokenized, which means they can be sold to anyone, anywhere on an open peer-to-peer marketplace.
Axie opened the way to earning income, and more importantly, it gave people a look at the larger X-to-earn trend, showing how people can earn income by contributing to the network.
Learn-to-earn
Learn-to-earn is a new model of education where instead of paying to learn, a person is actually paid for proving they learned something. This is possible when a skill, knowledge or information learned by an individual adds value to the network and the network is willing to fund the learning.
Token Holders: Invest-to-earn
This new positive-sum interaction helps all parties:
Users learn new skills or methods to use the crypto industry and earn tokens for it
Crypto protocols gain knowledgeable new users
RabbitHole gets a percentage of revenue to drive interactions
This new model is similar to Google sharing some of their ad revenue to learn about new products, or paying your university for you strengthening their alumni network. In both cases, you are providing value to the network without being rewarded, but now, you can.
Since launch, RabbitHole has distributed over $750,000 in rewards, paid out by some of the largest crypto protocols (eg Uniswap, Aave, Compound, The Graph, Pool Together, and Polygon). While it’s early days for this space, the potential for earning rewards through learning is huge when you factor in the education and advertising-generated revenue currently unavailable to users.
Create-to-earn
Cryptocurrencies have created new wealth and digital scarcity, which has paved the way for the explosion of the NFT market in the past few months. This provides opportunities for artists around the world to earn a living, and in some cases even generate wealth for generations.
But this is no different functionally than any artist getting paid when their work is successful. What's more interesting is that creators get paid for their added value to the network, not just the personal profits they make from their work.
For example, NFT marketplace SuperRare airdropped 15% of its tokens to early users, collectors, and artists on its platform in recognition of the role these value creators played in its early network success.
Audius is a decentralized protocol for music streaming that allows creators to earn tokens for uploading music and curating playlists. Because of the value creators bring, Audius empowers them to own the web.
Token Holders: Invest-to-earn
Anyone with an internet connection and a crypto wallet will be able to invest in high growth opportunities.
In a world where there is a token per network, tokens are earned by participating in the network, the ability to buy tokens is permissionless, and everyone becomes an investor.
Investing will become the main source of income for a growing population. Not every investment will appreciate in value, but individuals will have access to opportunities previously reserved for the few, and a whole class of income-earning opportunities will be unlocked.
04
first level title
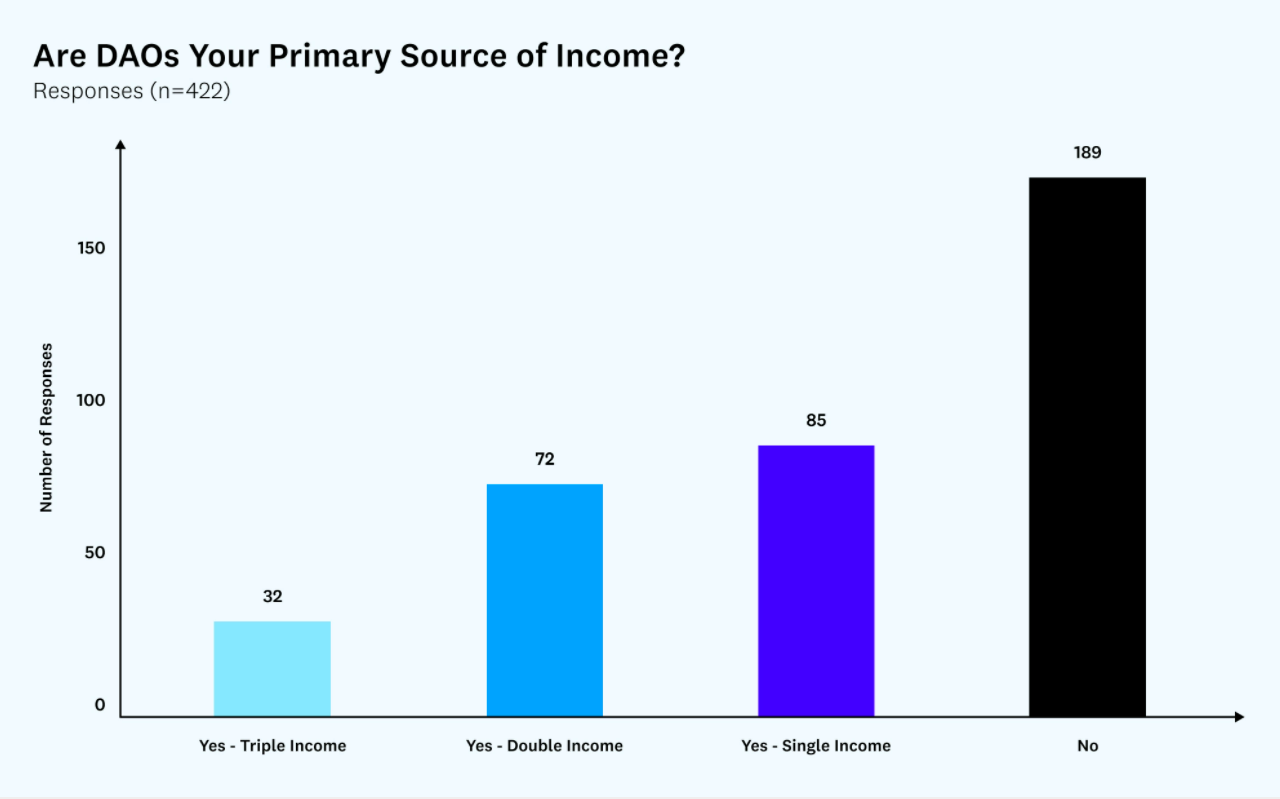
X-to-earn opportunities will only become mainstream when DAOs become mainstream. DAOs are showing a lot of promise, but they are still in their early stages and have a long way to go before realizing the future of work. In a recent survey of 422 DAO participants conducted by Gitcoin and Bankless, <45% of respondents indicated that DAOs were their primary source of income.
coordination tool
coordination tool
Most DAOs currently rely on a combination of Web2 software that was not designed for DAOs, or very young web3 software. In both cases, the DAO's needs were not fully met.
DAOs have incredible potential to harness the power of decentralized networks and the collective intelligence of people, but they require better software tools to coordinate. DAOs will need tools that support governance (e.g., Snapshot, Orca), software collaboration (e.g., Radicle), treasury management (e.g., Parcel, Multis, Gnosis), discussion (e.g., Discourse), access (e.g., CollabLand), and more.
DAOs are open and permissionless, but new ways are still needed to determine who to trust, cooperate, and reward.
reputation system
DAOs are open and permissionless, but new ways are still needed to determine who to trust, cooperate, and reward.
The traditional company solution is to have an extensive interview process, but this goes against the spirit of the DAO. To further complicate matters, many of the people involved in a DAO are anonymous. In this new world, DAOs need a new way to determine who to allocate scarce resources to.
This highlights the need for an on-chain reputation system. An on-chain reputation system will capture our actions happening on the blockchain: our contributions to the DAO, our governance voting history, our token holdings, and more. Ultimately, reputation systems will use these on-chain behaviors to predict our future behavior to determine who is trustworthy, trustworthy, and consistent. On-chain reputation will replace the way companies currently use credentials, resumes, and interview processes.
However, there are many privacy and security concerns with distributed ledgers that track public activity related to individual identities. Right now, blockchain identities mostly revolve around addresses, but for these reputation systems to become viable, we will need stronger decentralized identifier solutions (such as Ceramic/IDX) and identity management.
05
However, the ongoing debate around the sustainability and scale of certain revenue-generating opportunities does not take away from the main theme of this article: creating value within the network should be rewarded, and a DAO will coordinate the return of value within a crypto network, enabling new revenue-generating opportunities.
How much revenue can be earned through these channels in the long run is unclear. X-to-earn doesn't mean everyone can make art and play video games for a living.
X-to-earn is about rewarding value where value is created. DAOs make these non-traditional paths more sustainable and accessible to more people, but the market won't reward everyone.Market dynamics are still relevant, and to get a return you need to provide value. Creators need to find an audience, gamers need to achieve results, and bounty hunters and contributors need to create impact.
However, the ongoing debate around the sustainability and scale of certain revenue-generating opportunities does not take away from the main theme of this article: creating value within the network should be rewarded, and a DAO will coordinate the return of value within a crypto network, enabling new revenue-generating opportunities.
More broadly, the future of work won't be perfect. As with any major technological shift, there are usually positives and negatives. DAO will lead to the same result. Here are some directions to watch:
Competitiveness and Gap
There is a common metaphor that the future is already here, it's just not evenly distributed. This is certainly the case with DAOs and the future of work. Every day, more and more people join DAOs and commit to web3 full-time. DAOs are growing rapidly and are in great need of talent to help them achieve their mission.
cognitive overload
The processing power of the human brain is limited. The Dunbar number is the well-known limit on how many social relationships the human brain can manage, but the "DAObar number" is the DAO version of that concept: How many DAOs can a person meaningfully participate in? Each subsequent DAO engagement adds processing power to maintain context and awareness of everything that is happening. DAO tools for communication and collaboration (discussed above) will try to mitigate this, but one may struggle with the additional overhead.
state separation
On the one hand, DAOs allow people to choose how they work and connect with communities whose values align with theirs. On the other hand, by reducing most work to atomic units and purely economic incentives, we run the risk of reducing what it means to people to purely economic rewards. We run the risk of turning work into discrete, meaningless tasks in which labor is reduced to a commodity service.
***
There is a common metaphor that the future is already here, it's just not evenly distributed. This is certainly the case with DAOs and the future of work. Every day, more and more people join DAOs and commit to web3 full-time. DAOs are growing rapidly and are in great need of talent to help them achieve their mission.
The future of work is emerging, and it's going in unexpected and fascinating directions.
Thanks to Brian Flynn, Jesse Walden, and all others who inspired this article.





