Article translation: Block unicorn
Article translation: Block unicorn

First DeFi, then NFTs, and now DAOs.
What are DAOs?
What are DAOs?
DAO stands for Decentralized Autonomous Organization and refers to crypto-native groups formed around a common purpose, which usually (but not always) involves pooling funds to invest according to a specific goal/mission.
image description

The 2021 DAO Landscape, Curated by Coin 98 Analytics
Given the variety of use cases and the speed at which new DAOs are emerging, it remains difficult for market participants and observers to understand what a DAO really is.
This is why we thought it would be useful to clarify the rationale for DAOs, show how they differ from traditional organizations, and provide guidance on how to get in touch with this revolutionary wave.
DAO Governance Model Explained
The easiest way to explain DAO is to start with the acronym. First, DAOs are autonomous, meaning they are organizations run by smart contracts. These smart contracts are self-executing lines of code agreed to by the DAO's initial developers and stored on the blockchain. They enable organizations to be self-sustaining when it comes to recruiting, assigning rewards, and other bureaucratic or critical issues that you typically find in organizations.
Second, unlike traditional organizations, decisions are made collectively rather than by the CEO or senior management. In fact, according to the DAO, members who own one or a predetermined number of the DAO's native tokens can submit and vote changes to smart contracts, propose initiatives, invest in ideas, etc., allowing the DAO to develop and grow. It’s worth noting that the access, economic rights, and governance rights that members are entitled to vary from DAO to DAO.
Membership in the DAO takes the form of ownership of the DAO's native token. The amount of tokens required to join varies from DAO to DAO. People can either buy tokens on or after the launch date, or receive those tokens for contributions, again depending on the DAO. While DAOs are often known for being open to all, smaller DAOs are more permissioned than larger protocol DAOs. In this case, owning tokens is not enough, a written application and an invitation from other members are required.
After joining a DAO, owning the DAO's native token can provide different benefits, from voting rights to sharing in the profits generated by the organization. Members also benefit from the overall appreciation of the token when increased demand for the token is met through a hard supply cap.
Typically, in large protocol DAOs that act as financial services platforms (e.g. multi-chain platforms like BitDAO or lending platforms like COMP), token ownership unlocks voting rights on issues related to fees and distribution matters. Members are primarily rewarded for staking their tokens and providing liquidity to the protocol. In other cases of large DAOs, governance tokens may provide more governance rights, but have no intrinsic monetary value. For example, this is the case with Aavegotchi's native token GHST.
In smaller DAOs (500 members and under), membership usually involves working for the DAO. In addition to voting rights, members can receive tokens, token rewards, pre-determined shares of the treasury and/or cryptocurrencies (such as Ether, Dai, and Cash) in exchange for their contributions. This is especially true for investment DAOs (e.g. Laos, MetaCartel Ventures) and collector DAOs (e.g. PleasrDAO). Some of them, such as MetaCartel Ventures, also require members to continue to participate in governance duties, due diligence, proposals, and investment voting if they want to stay in the DAO.
Once a member, you also have the right to vote, which varies greatly between DAOs. The minimum requirement for voting might be holding one of the DAO's native tokens, a predetermined number of tokens, or a threshold of total supply (eg 1% noun DAO). Once a proposal is proposed and voted on, the quorum required to validate the proposal also varies, such as 10% quorum, 20% quorum, 50% quorum (for example in Laos), etc.
How can the DAO model be a paradigm shift for human organization?
This model is revolutionary and constitutes a paradigm shift in human organization in two ways. First, for the first time in history, Internet users can collectively create and exchange value in a trusted environment. This environment is the blockchain. Blockchain technology first powered DeFi, then non-fungible tokens, and now is creating a collective space for groups of people to work. In effect, it eliminates the need to involve third parties in financial transactions, as all financial transactions and rules are recorded on the blockchain. This makes the DAO independent of government agencies as the blockchain is a third party.
image description
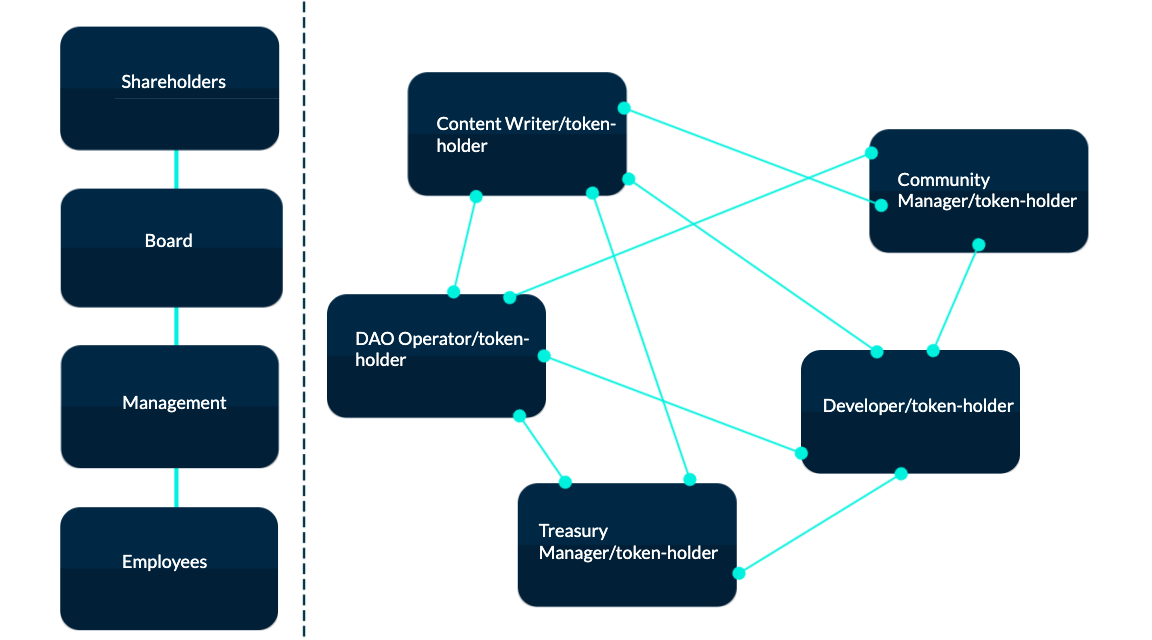
Potential limitations of simplified corporate relationship models in traditional organizations and DAOs
However, the same characteristics that make DAOs fundamentally superior to traditional organizations can also be a source of vulnerability. The blockchain technology it relies on makes it trustless and transparent, but also makes its code accessible to everyone, including would-be hackers. A perfect example is the DAO hack in 2016, during which hackers exploited a bug in the code.
Likewise, the fact that a DAO cannot be shut down by authorities or governments because it relies on the blockchain as a third party may soon gain increasing attention from regulators.
On top of that, its lack of verticality makes for long decision-making times. Nonetheless, we have seen the emergence of proxy voting in DAOs, which can make governance more efficient and effective. More generally, DAO structures will increasingly include representatives, sub-teams, and specialized executives.
In fact, the DAO model itself has limitations and is not suitable for all types of organizations. While we don't know the extent to which it will disrupt all forms of human coordination, one thing is for sure - we will see more and more DAOs popping up, and fast.
Get in touch with this revolutionary wave
You now understand the basic model of a DAO and are already keen to learn about this emerging trend. You may be wondering: how do I get involved? The quick answer is to join the DAO by acquiring its native token. Depending on the DAO, you'll have to buy one or more on or after the launch date, and some DAOs will even give away tokens to active contributors. However, some DAOs will be successful, while others will not perform well. Therefore, it is important to do due diligence on projects, membership quality, and analyze how/could drive value in a DAO before engaging. Although the field is still relatively new and metrics for evaluating DAOs have not yet been established, we provide below some of the factors that drive quality membership and DAO value.
Drivers of DAO Value Effective Incentives
It is important to understand how members are rewarded for their contributions in the DAO. Typically, governance rights, contribution rewards, or profit shares incentivize members to work for the DAO and actively participate in governance. This in turn makes the organization more efficient.
Another way of looking at it is that the secondary market value of the token increases as the DAO becomes more successful. If the DAO becomes more and more successful, it will attract the attention of other market watchers looking to capture the advantages of the DAO's idea/money output, treasury voting rights, etc. As a result, the DAO's token appreciates in value. As the token appreciates in value, members are incentivized to work more, which continues to drive the success of the DAO and the value of the token.
Therefore, we can expect that DAOs with consistent incentives for contributors are likely to outperform other DAOs in the long run. The more members are rewarded based on their work/contributions, the higher the value of the DAO will be pushed.
high voter participation
The value of a DAO is driven not only by the work of each member, but also by active participation in governance, which allows the organization to continuously adapt and grow. Having voting rights does not necessarily mean that members will vote. You can measure the extent to which members participate in decision-making by considering the voter participation rate of all submitted proposals, which you can do in Deep DAO.
image description
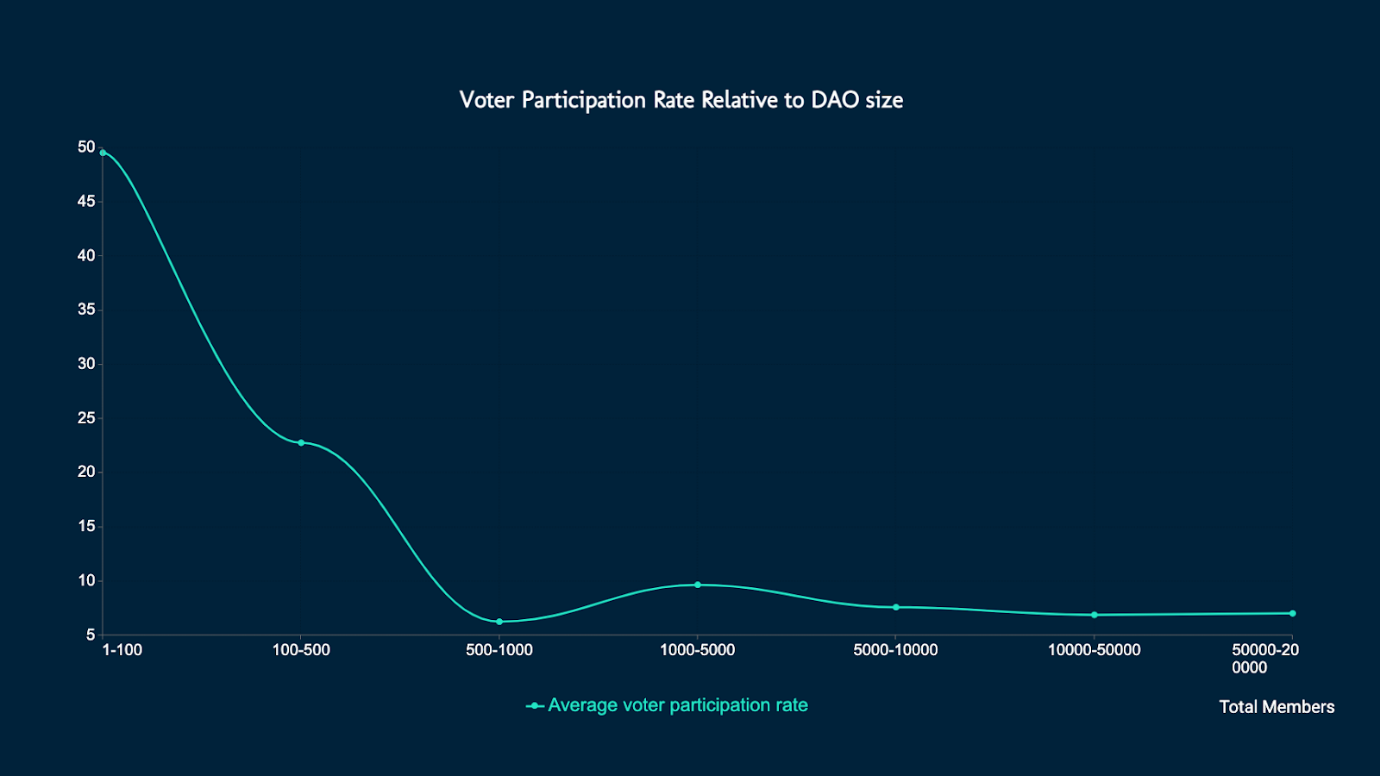
Voter Participation Rate Relative to DAO Size
image description
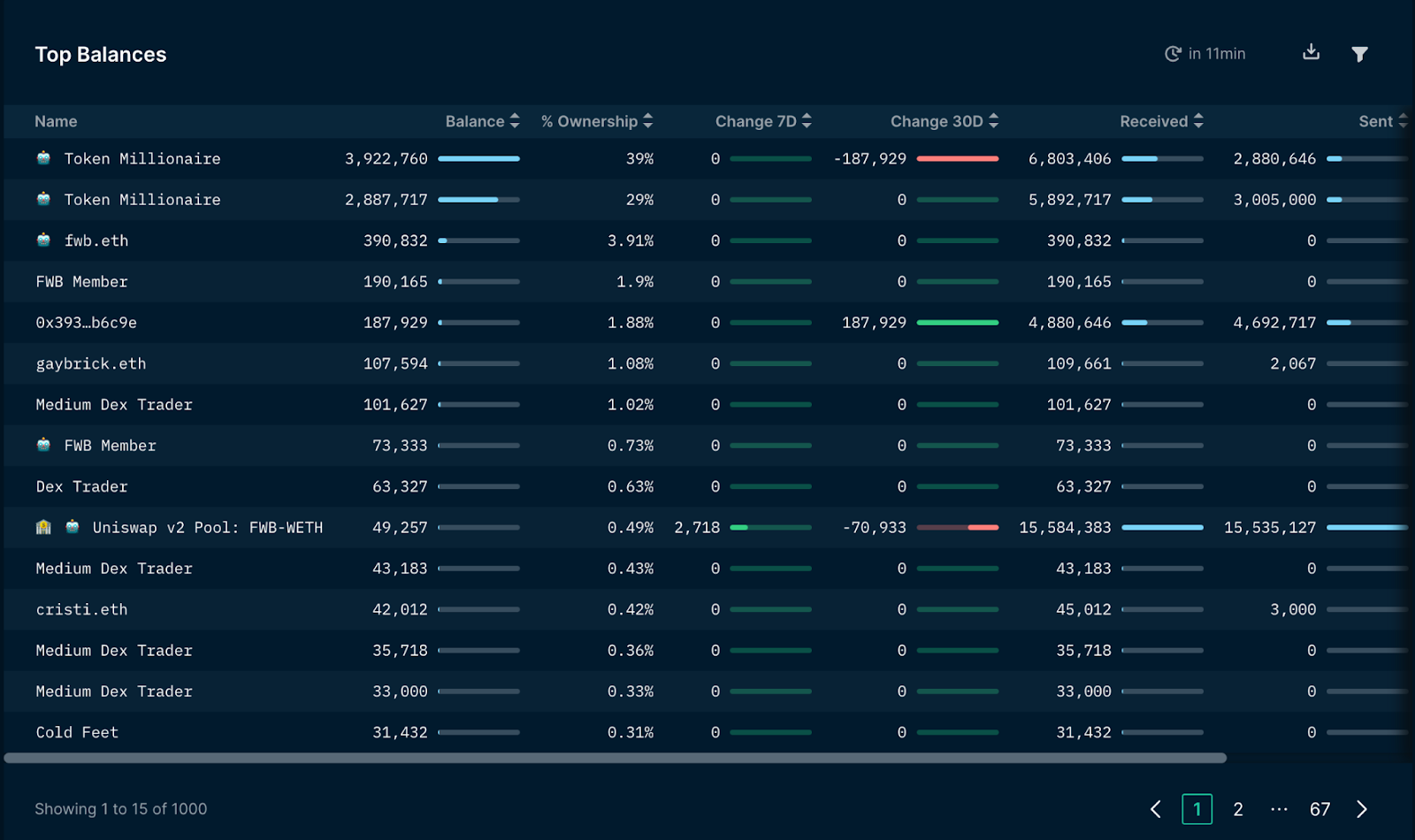
Maximum balance of FwB tokens
image description
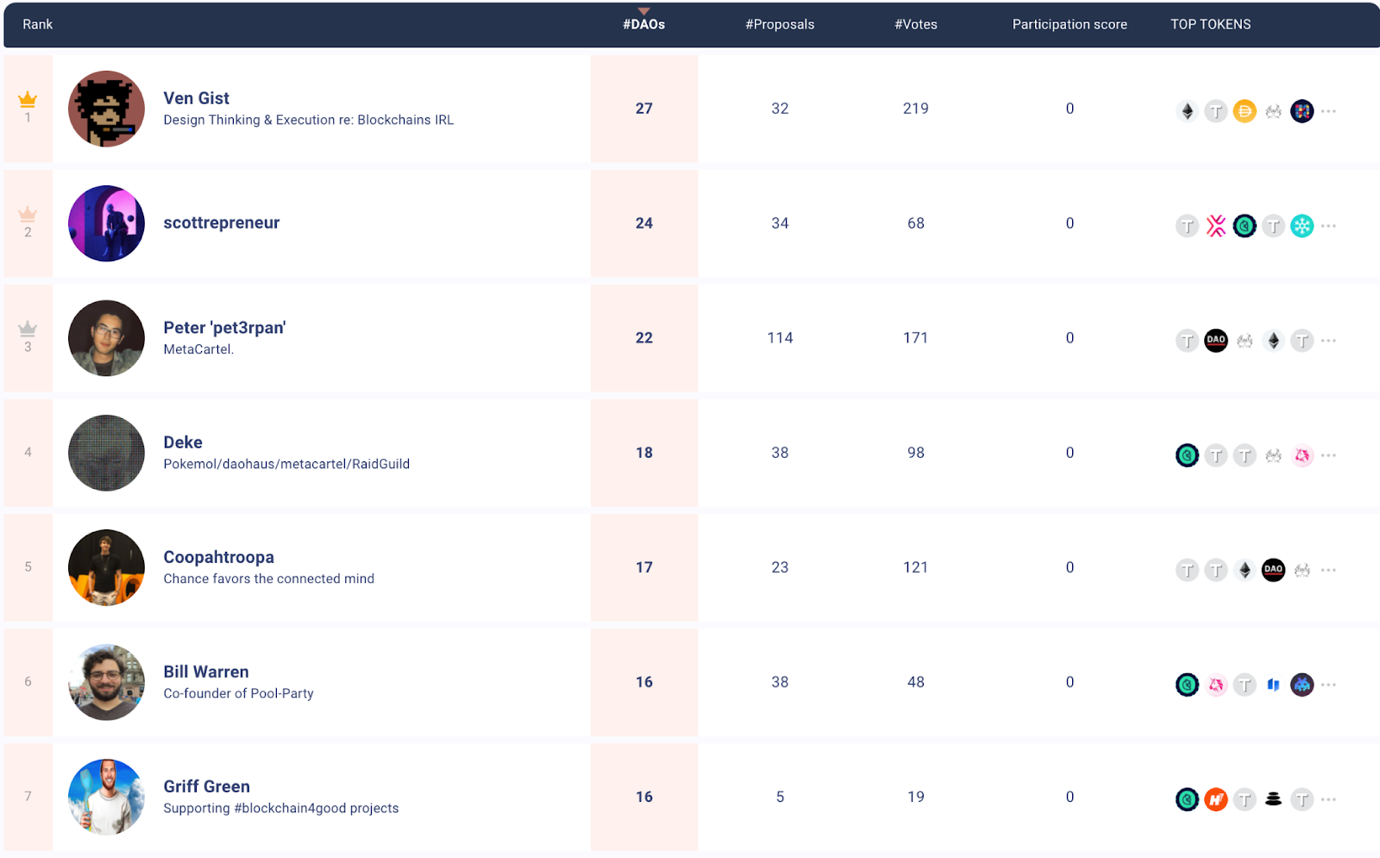
Top 7 Top Contributor Projects in the DAO Space Continue
If there is a good incentive structure and members actively contribute, then the DAO should consistently deliver projects and initiatives. A DAO that promotes projects on a regular basis is usually a good indicator of collective engagement, ability to execute, and potential for long-term value appreciation.
A perfect example is PleasrDAO. Since its first Uniswap V3 NFT purchase last March, the DAO purchased and subdivided the Doge Meme NFT, acquired the Wu-Tang Family CD and even organized an exclusive event for its members in New York.
in conclusion
in conclusion
In conclusion, The DAO marks a new chapter in crypto history. Although we don't know the extent to which it will disrupt all forms of human organization, the DAO governance model has proven particularly successful for crypto-native communities. It should go beyond traditional organizations as it enables internet users to collectively create and exchange value in a trusted environment and rewards them for the value they create. While this new governance model inherently faces challenges such as vulnerability to attack, it will continue to thrive. Today, there are only 169 DAOs. One day, there will be tens of thousands of people. Now is the perfect time to join the revolutionary wave and get involved with one or more of these DAOs.





