I. Introduction
The cryptocurrency market in 2023 exhibited a paradoxical phenomenon: despite tepid investor activity, market prices experienced significant increases. While most financial institutions are wary of serving cryptocurrency users, recent ETF filings mark significant progress in institutional investor adoption of the cryptocurrency space. Regulators have issued warnings about market risks and taken corresponding enforcement measures. However, the judicial department has countered this excessive supervision. At the same time, the upgrade of Ethereum enables the withdrawal of pledged assets, which in turn promotes the growth of the total amount of ETH pledged.
In terms of blockchain platforms, Ethereum continues to solidify its leadership as a Layer 1 blockchain and is focused on developing a scalability strategy with Rollup at its core. At the same time, competing blockchains such as Solana, Avalanche, and Cosmos have gradually expanded their market share through their own unique expansion strategies, with Solana’s integrated approach achieving significant results by the end of the year.
In the field of on-chain applications, although blue-chip lending and trading protocols have performed steadily, liquidity staking providers such as Lido dominate the market. DeFi has achieved substantial development in aspects such as the tokenization of physical assets. The non-fungible token (NFT) market has experienced intense competition, leading to significant market share losses for platforms like OpenSea, while the introduction of Ordinals on the Bitcoin network has spurred growth in NFT and meme tokens. Additionally, the rise of decentralized social protocols heralds a new era in blockchain application development.
In this paradoxical year, the blockchain industry has seen a series of compelling innovations and growth. This article will provide an in-depth analysis of the core development and main trends of the blockchain industry this year, providing readers with a comprehensive and profound industry perspective.
2. Blockchain platform and expansion
(1) Layer 1
In 2023, Ethereum continues to be the market leader in smart contract-based Layer 1 networks. Whether in terms of total value locked (TVL), transaction volume or transaction fees, Ethereum occupies a dominant position compared to other smart contract-based Layer 1 networks. By looking at the level of transaction fees, we can measure user demand for different blockchain networks. It is clear that in 2023, most of the demand is focused on the Ethereum network, which is evident from its higher transaction fees.
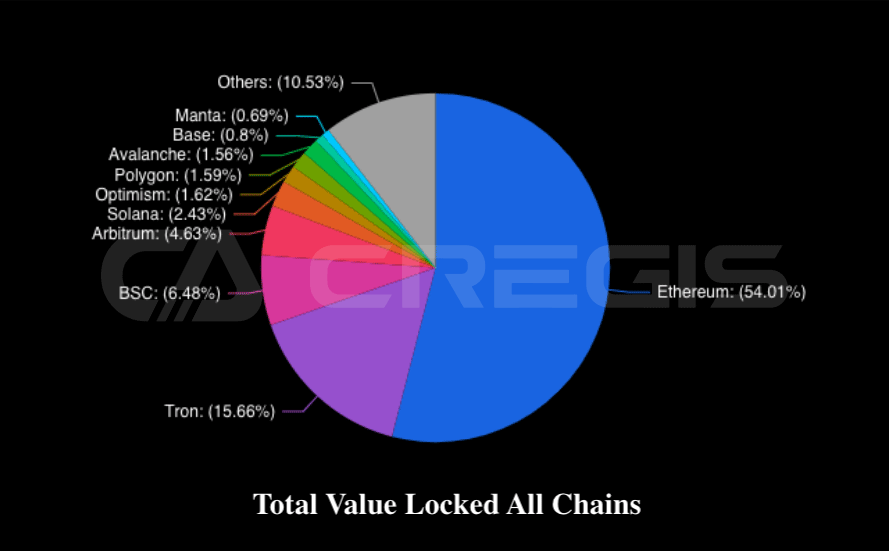
(Source: DefiLlama)
Tron and BNB Chain
In 2023, Ethereum’s main competitors have experienced some significant changes. From the beginning of the year to the end of the year, Tron’s total value locked (TVL) increased by approximately 100%, while BNB Chain’s TVL fell by approximately 38% during the same period. These changes are primarily due to the impact of macroeconomic factors and regulatory events. For example, Tron’s TVL growth is mainly attributed to the trend of stablecoin users switching from USDC and BUSD to USDT, while BNB Chain’s TVL decline is related to the market’s regulatory policies.
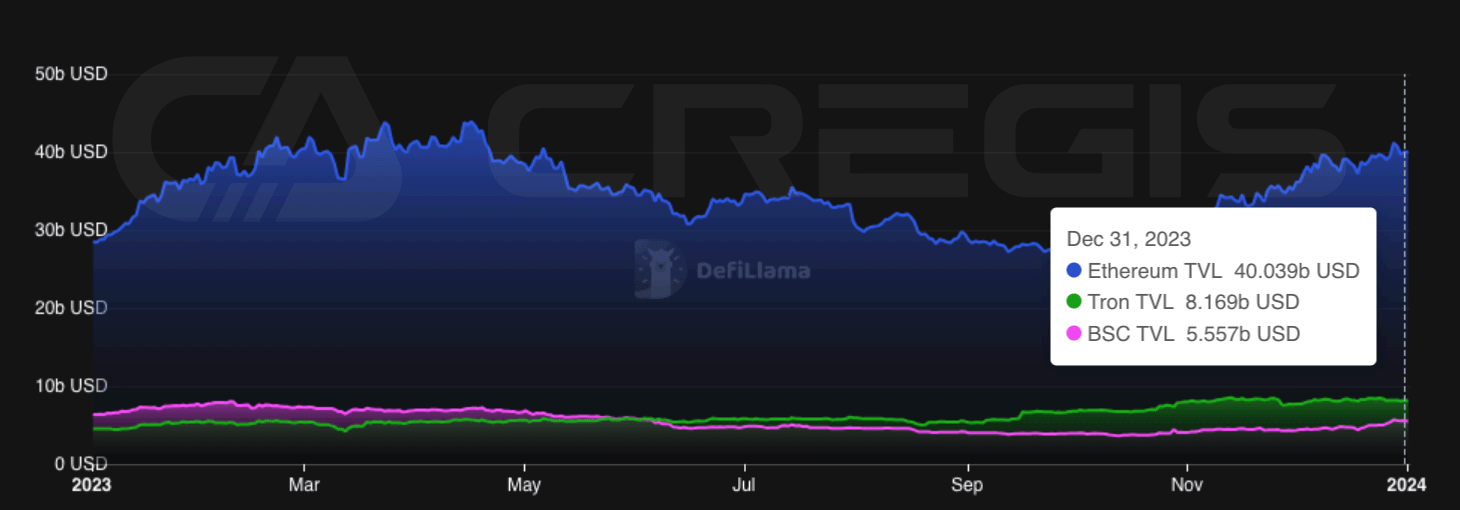
(Source: DeFiLlama)
In 2023, as stablecoin users switched from USDC to USDT, Ethereums share of the stablecoin market declined, and accordingly, Tron gained a larger market share. By December 2023, Ethereum’s share of the total stablecoin supply dropped to 51.6% from 62.1% at the beginning of the year.
Meanwhile, BNB Chain faced a series of regulatory issues in 2023, including lawsuits from the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC). Along with the suspension of Binance USD (BUSD), the supply of stablecoins on BNB Chain continues to decrease. By November, regulatory issues surrounding Binance came to a head, leading to its CEO Changpeng Zhao (CZ) entering a plea deal with the United States and resigning. From the beginning of 2023 to the end of the year, BNB’s market capitalization fell by more than $4.5 billion.
Solana and Celestia
One of the market hot spots in 2023 is about two opposite blockchain expansion solutions: Modularity and Integration. The token price market valuation of a Layer 1 network reflects the health of its ecosystem, as we can observe in the historical prices of modular and integrated blockchain representatives Celestia (TIA) and Solana (SOL), modular blocks The market value of chain Celestia rose by about 300% within a month after launching the TIA token in November, and the market value of integrated blockchain Solana (SOL) increased by about 800% in 2023.
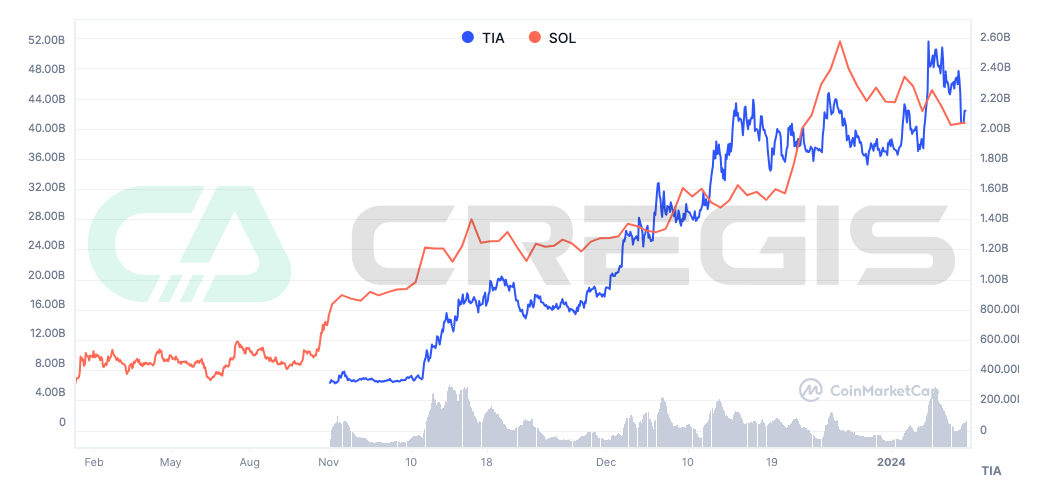
(Source: CoinMarketCap)
One of the most notable trends in 2023 is the resurgence of Solana, both in terms of its valuation and market acceptance of its integrated scaling approach. Among the smart contract protocols with the highest total value locked (TVL), Solana is unique for its use of a custom execution environment, the Solana Virtual Machine (SVM), which enables the network to execute transactions in parallel. To achieve high throughput and scalability while reducing user costs, Solana validators must be able to coordinate with other validators in the network to complete complex processing tasks. This is due to a series of customized technologies, such as the Proof of History synchronization mechanism and the Turbine block propagation protocol, all of which ultimately result in Solana validators having advantages over other Layer 1 (L1) networks. higher requirement.
Sui and Aptos
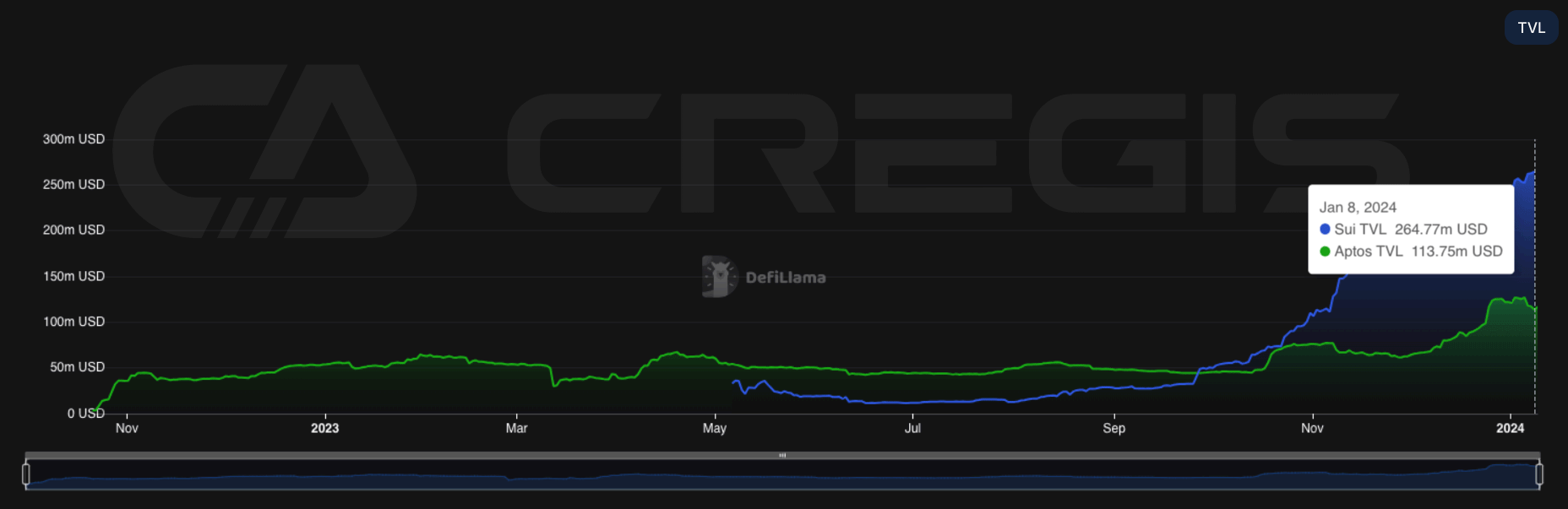
In 2023, Solana became one of the most widely used integrated architecture blockchains. In the past two years, a number of Layer 1 blockchains have begun to emerge that use integrated architectures and enable parallel execution at low cost. Among them, Aptos and Sui are particularly obvious. Both platforms are derived from Metas Diem project and use the Move virtual machine as the execution environment. As of December 2023, the combined value locked (TVL) of the two chains is approximately $377 million.
Sui, in particular, has shown faster growth compared to Aptos over the past year, with its TVL almost more than double that of Aptos at the end of December. Trends in 2023 show that integrated architecture Layer 1 blockchain may play an increasingly important role in the field of smart contract platforms. However, these emerging platforms still have a long way to go before they can surpass the dominance of the EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine).
(Source: DeFiLlama)
Cosmos and Avalanche
Since its inception, the Cosmos community has always embraced the concept of modularity. Launching a new blockchain in the Cosmos ecosystem is easier than any other, thanks to native infrastructure and tools like its Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol and the Cosmos SDK. Developers can customize chain parameters according to their needs, such as inflation rate, pledge unbinding time, verifier rewards, governance voting parameters, etc. At the same time, the IBC protocol can realize interoperability between different Cosmos chains.
The inherent advantages of modular blockchains come at the cost of fragmented user attention and Cosmos inter-chain liquidity. While IBC allows assets to be transferred between Cosmos chains, these assets must pass through the same IBC channel. If not, these assets remain non-fungible. For example, ATOMs sent from Osmosis to Canto via IBC are different than ATOMs sent from Cosmos Hub to Canto. Therefore, in terms of composability and liquidity, Cosmos application chain still has certain disadvantages compared to general Layer 1 blockchains.
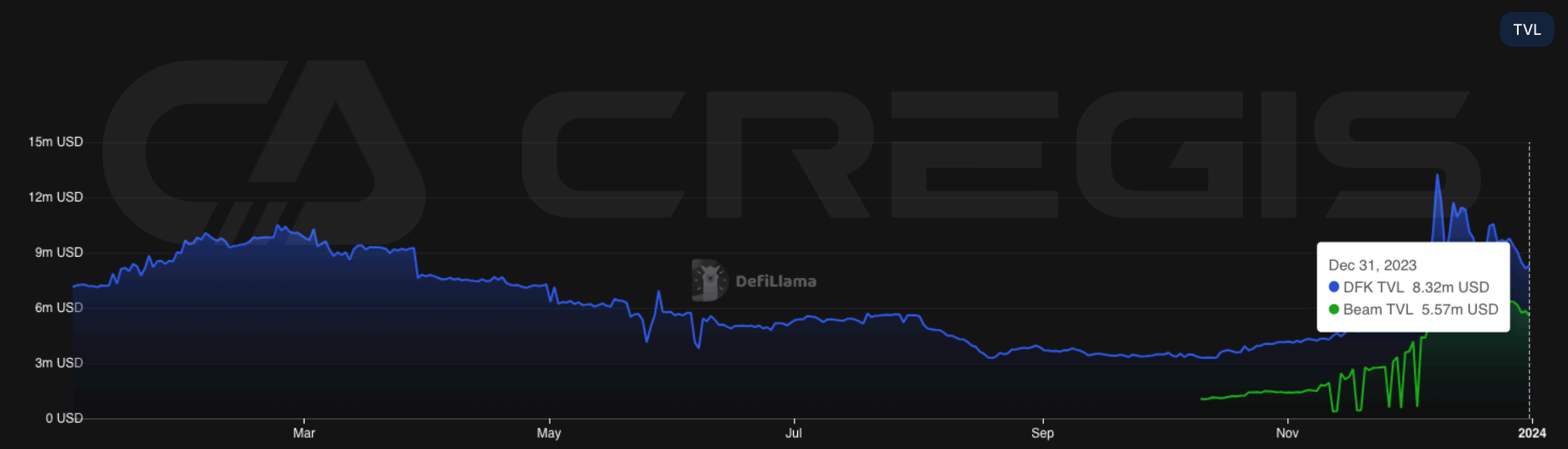
The number of active subnets in the Avalanche ecosystem continues to grow in 2023, but user activity remains low compared to the main Avalanche C-chain. By the end of the year, the total TVL of the two active subnets, DFK Chain and Beam, reached approximately $13.8 million.
(Source: DeFiLlama)
The Avalanche subnet and the newly launched Cosmos chain face similar challenges when it comes to cybersecurity. In the initial stage, these networks need to accumulate enough funds as a moat to prevent economic attacks. On Avalanche, validators are required to stake 2,000 AVAX at a price of approximately $35 per AVAX. However, most Avalanche subnets currently have no more than 10 validators in total. Among these subnets, the largest is the MELD subnet, which has only 16 validators. A smaller number of validators will potentially impact the security and decentralization of the network.
(2) Layer 2
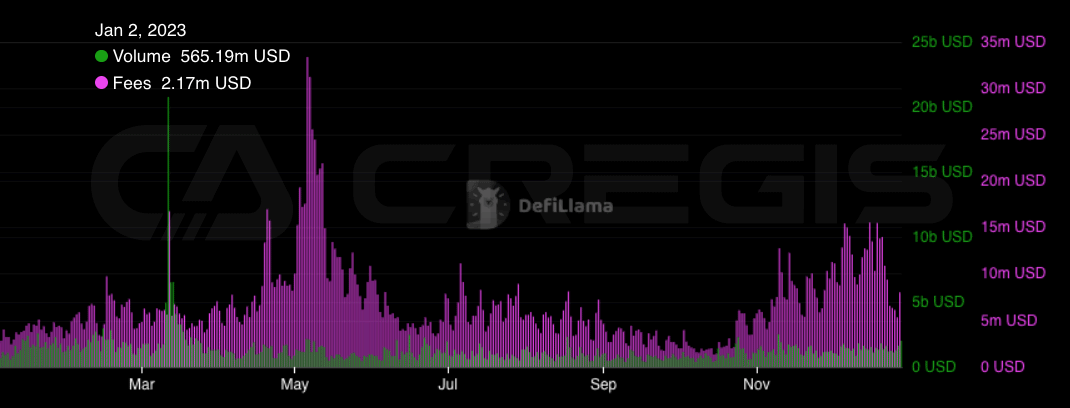
As the demand for Ethereum transactions continues to grow, its expansion problem has become increasingly urgent. Currently, Ethereum’s processing capacity is approximately 15 transactions per second (tps). This throughput is obviously unable to meet the growing demand for large-scale use. This limitation could become a key obstacle to Ethereum’s future development.
The scaling issue of Ethereum has always been a controversial topic. The core difficulty lies in the so-called impossible triangle theory, namely decentralization, security and scalability. In a distributed network, it is difficult to optimize these three characteristics at the same time, and usually only two aspects can be optimized. Enhancing scalability often requires making certain sacrifices in decentralization or security. However, the Ethereum community is cautious about making this trade-off choice and is unwilling to sacrifice decentralization or security easily.
(Source: DeFiLlama)
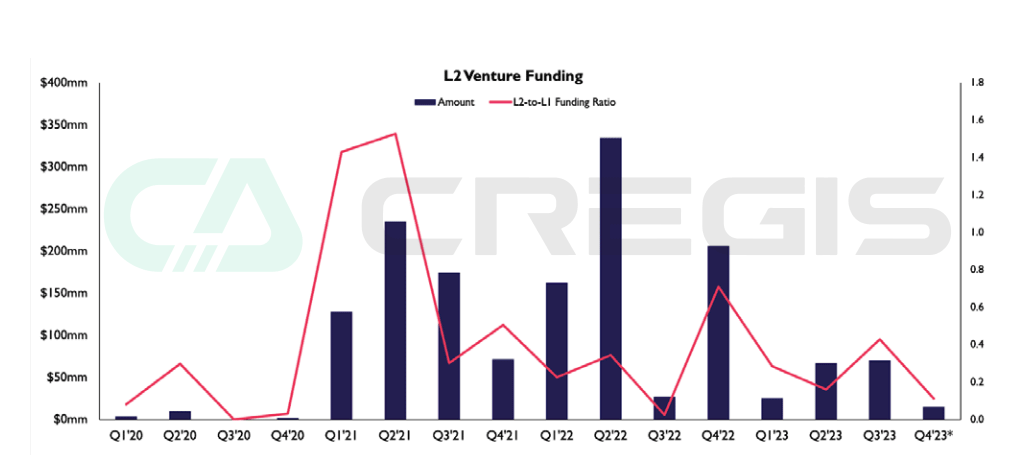
The expansion methods of Ethereum are mainly divided into two types: on-chain and off-chain. On-chain scaling involves modifications to the core Ethereum protocol, while off-chain scaling involves building additional protocols and infrastructure on top of Ethereum. Currently, off-chain expansion is developing faster than on-chain expansion. Especially from 2021 to most of 2022, off-chain scaling solutions based on optimism and rollups have gained continued attention in the venture capital market.
(Source: The Block)
Optimistic Rollups
Arbitrum One
Among the current four major categories of Layer 2 solutions in Ethereum, Optimistic Rollups (ORs) have the largest total locked value (TVL), with Arbitrum One’s TVL ranking first. Even before the launch of the ARB governance token, Arbitrum One was already the highest TVL Layer 2 platform. Following the launch of the ARB token, over $2 billion in liquidity was introduced into Arbitrum One’s ecosystem, with approximately $1.25 billion in tokens already unlocked, further solidifying Arbitrum One’s leading position among all Layer 2 platforms.
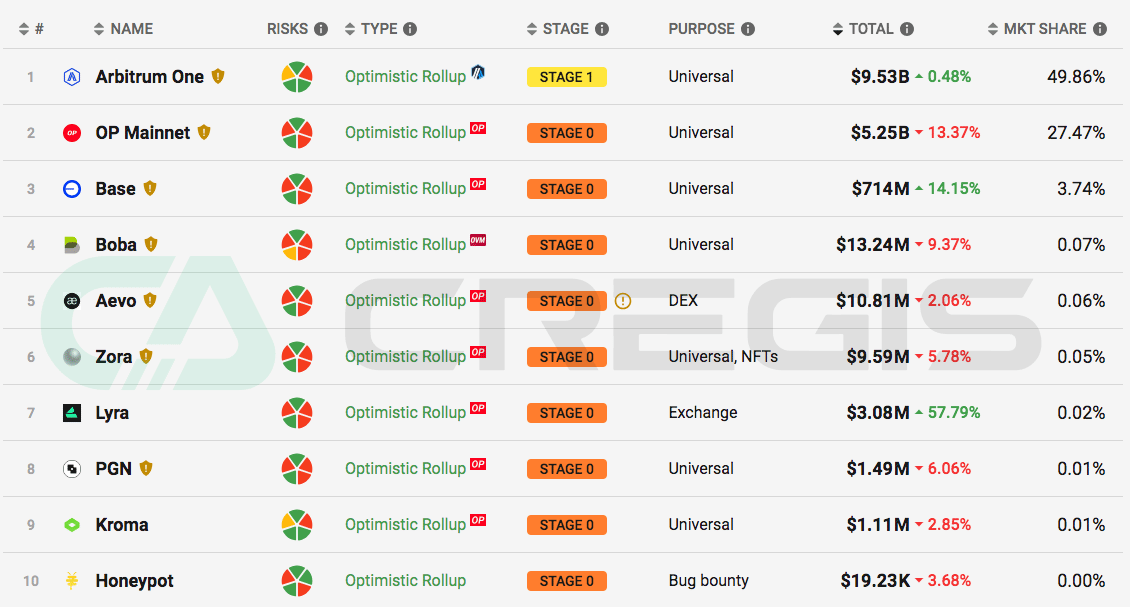
(Source: l2 beat)
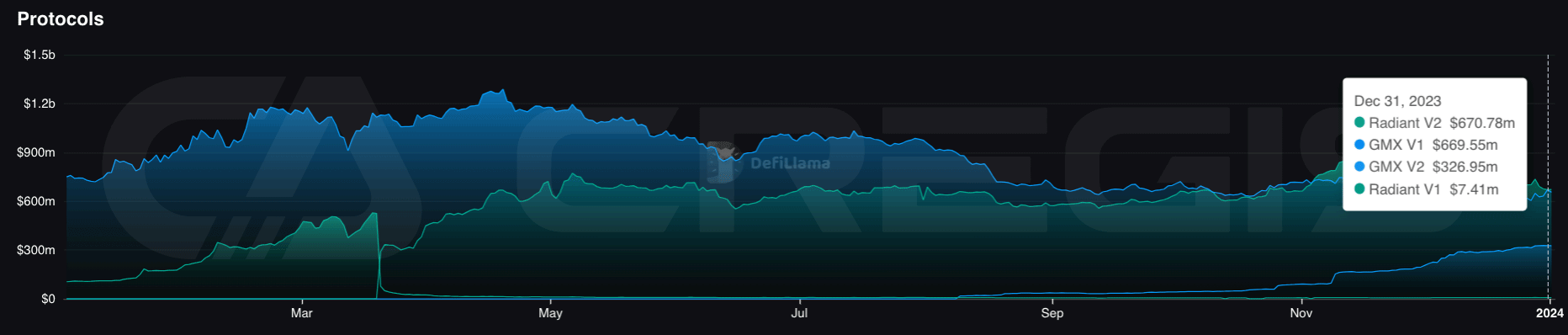
The liquidity introduced by the ARB token has facilitated the growth of Arbitrum One’s decentralized applications (Dapps). On the Arbitrum One platform, the Dapp with the highest total value locked (TVL) is exchange GMX, followed closely by lending platform Radiant. These two apps account for the majority of the TVL market share on Arbitrum One.

(Source: DeFiLlama)
OP Mainnet
Ranking second among Optimistic Rollups (ORs) by Total Value Locked (TVL) is OP Mainnet, formerly known as Optimism, with over $3.4 billion in assets. OP Mainnet’s governance token OP airdropped in May 2022, a year before Arbitrum One’s airdrop. While OP Mainnets TVL is growing at a slower rate than Arbitrum One, its growth trend is more stable.
In July 2023, as WorldCoin launched its token WLD on OP Mainnet, the network’s TVL increased significantly. WorldCoin was co-founded by OpenAI co-founder Sam Altman to build the largest digital identity and financial network. The WLD airdrop is intended to guide network growth and incentivize new users to sign up for the application. To date, more than 700,000 users have received WLD airdrops.
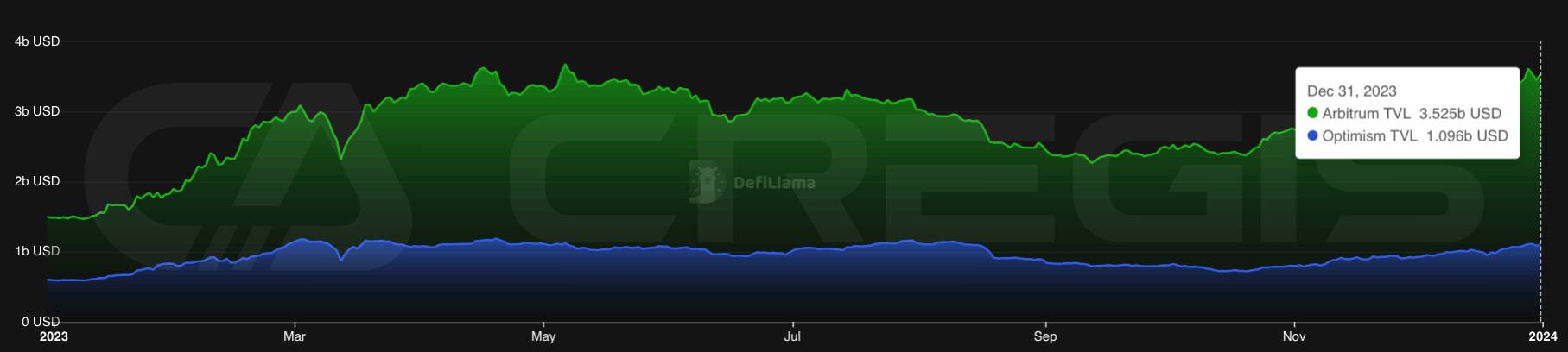
(Source: DeFiLlama)
An important development milestone for the OP Mainnet is the open source OP Stack in August 2022. OP Stack is a development stack powering OP Mainnet, built and maintained by Optimism Collective. The current version of OP Stack, also known as Optimism Bedrock, enables developers to develop their own optimistic rollups projects using the same technology as OP Mainnet.
With the open source of OP Stack, many projects developed based on OP Stack have emerged, the most notable of which is the Base mainnet launched by Coinbase in August 2023. Base aims to provide decentralized application (Dapp) services to exchange users. Base has rapidly grown to become the third largest Layer 2 network in terms of total value locked (TVL).
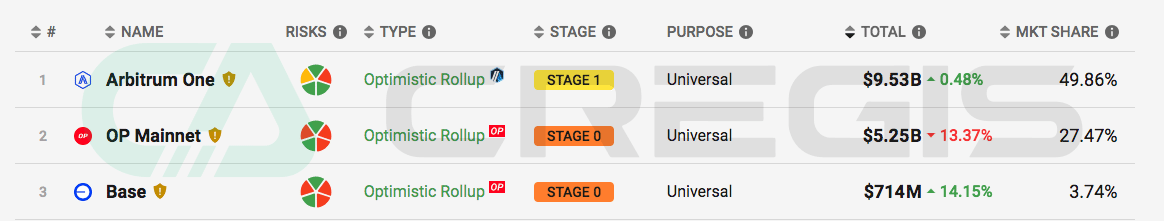
(Source: l2 beat)
Zero-Knowledge Rollups
In Zero-Knowledge Rollups (ZKR), there is currently no clear leader. Although dYdX’s TVL share previously ranked first among ZKR, it has now begun the transition to Layer 1 Cosmos. The current TVL of the zkSync Era and Starknet in ZKR are $539 million and $145 million respectively. While zkSync Era has significantly higher TVL than Starknet, part of its TVL comes from the original zkStnc Lite.
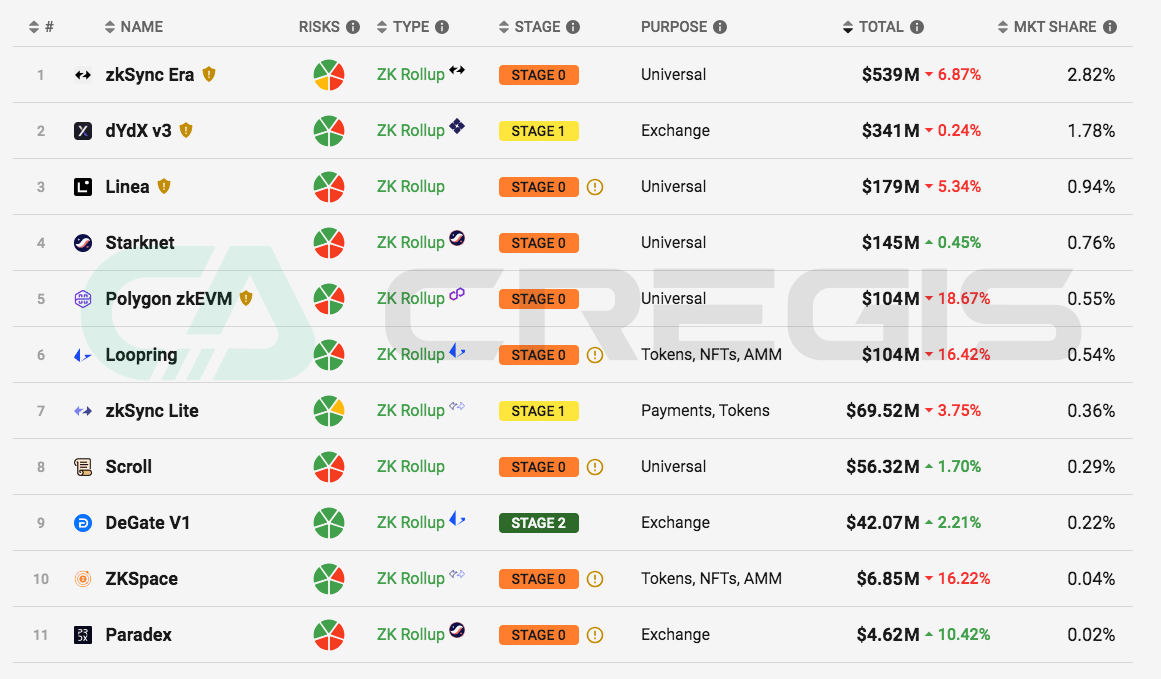
(Source: l2 beat)
Rollups as a Service
As the Rollup ecosystem matures, were starting to see rollups being used as a multi-functional tool rather than just as a means of scaling. Applications that wish to have a custom execution layer can choose to launch their own rollup, sacrificing a certain degree of decentralization and security in order to gain sufficient block space. Based on this demand, Rollups-as-a-Service (RaaS) applications began to emerge, which provide decentralized application (dapp) developers with the ability to quickly launch new rollups for deployment. Notable examples include Altlayer, a RaaS framework focused on the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), and dYmension, a RaaS framework focused on Cosmos.
Layer 3
Currently, the second layer (Layer 2) network is also beginning to experiment with the third layer (Layer 3) technology. For example, both Starknet and the zkSync Era have mentioned that in theory they can build a third-layer network on top of the existing second-layer infrastructure by leveraging the recursiveness of validity proofs. However, these solutions are currently not a priority as both Starknet and the zkSync Era are focused on the development of their second layer technologies. In addition, the use of third-layer technologies is designed to allow developers to quickly deploy customizable execution environments, similar to services provided by Rollups-as-a-Service (RaaS).
(4) Cross-chain bridge
While Multichain suffered a security hiccup in July, the bridging technology maintained its importance throughout 2023. In particular, the Portal bridge, which uses a locking and casting mechanism, has grown steadily and has become the cross-chain bridging platform with the highest total locked value (TVL). A major driver of this growth was the resurgence of Solana in Q4, making Portal the primary gateway into the Solana ecosystem.
In addition, Stargate bridging based on LayerZero technology and capital pool model followed closely and became the second largest cross-chain bridging platform, with its total value locked (TVL) remaining stable. Throughout 2023, the cross-chain ecosystem has shown a growth trend, mainly due to the continued development of Layer-2 technology.
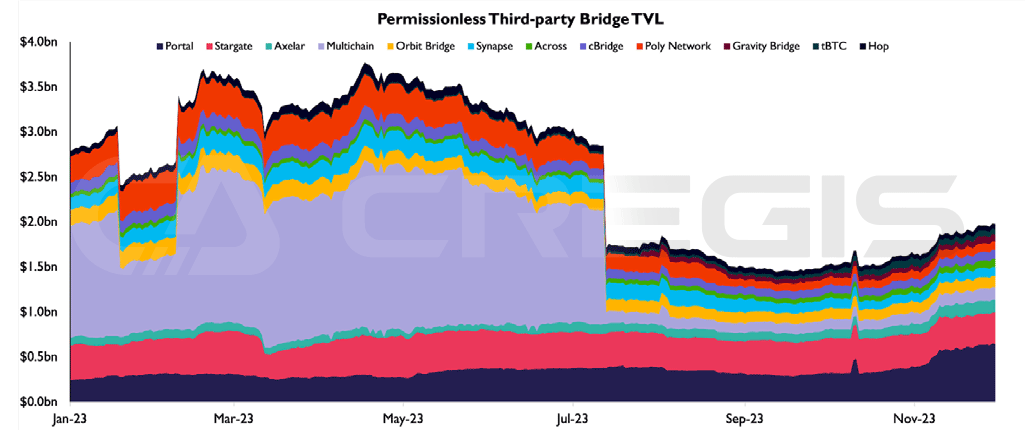
(Source: the block)
(5) BTC Layer 2
Lightning Network
Bitcoin’s Lightning Network is its most well-known scaling solution. Starting in early 2023, the total number of Bitcoins in the Lightning Network will increase from approximately 5,000 to a maximum of approximately 5,400. In the same year, its total value locked (TVL) grew from an initial US$80 million to approximately US$200 million at the end of the year, an increase of approximately 150%. The growth of TVL is mainly driven by the rise in Bitcoin prices.
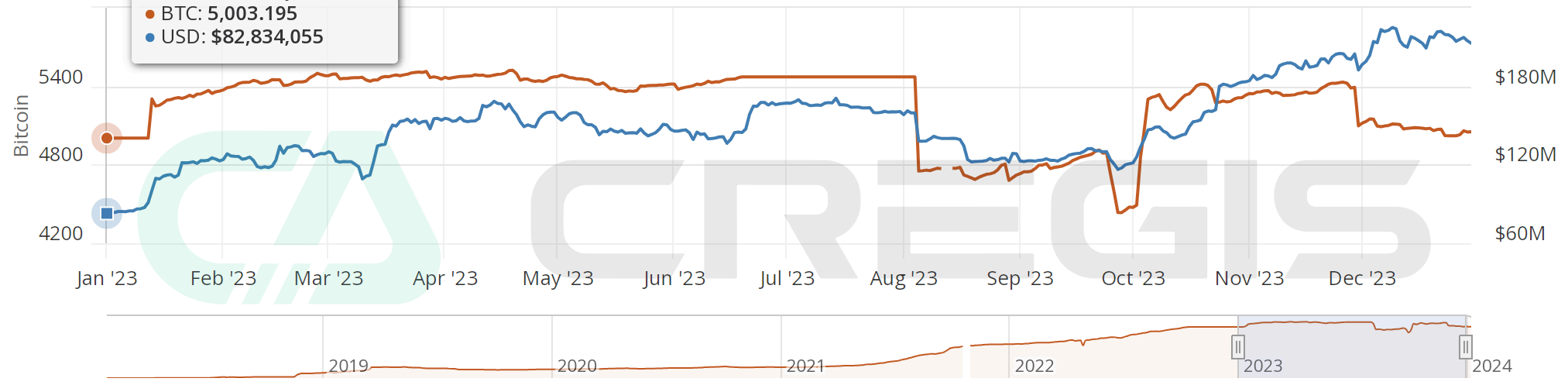
(Source: bitcoinvisuals)
Rootstock, Stacks and DeFiChain
In addition to the Lightning Network, Bitcoin has some other scaling solutions, mainly Layer 2 technology based on side chains. For example, Rootstock, Stacks, and DeFiChain have a total locked value (TVL) of $116 million, $54 million, and $128 million respectively at the end of 2023. Their total locked value is much lower than the Lightning Network’s $200 million. It’s worth noting that DeFiChain and Rootstock’s TVL also includes the value of their respective native tokens, DFI and RSK. Looking at this data, the adoption rate of these sidechain solutions is significantly lower compared to the Lightning Network.
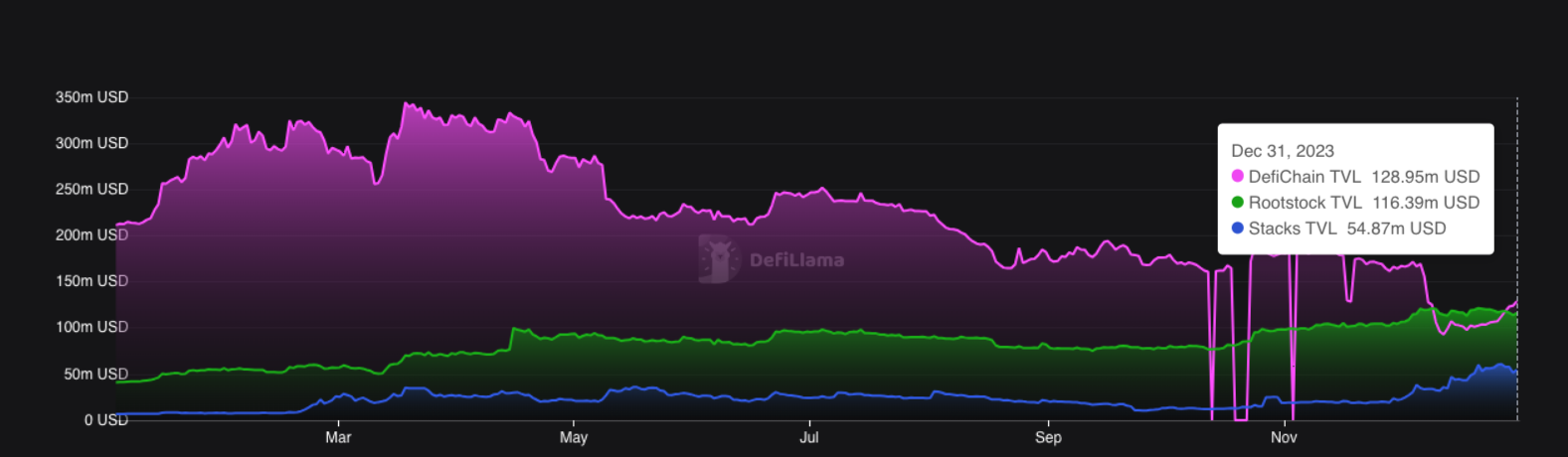
(Source: DeFiLlama)
Ordinals and BRC-20
Bitcoin’s Ordinals protocol allows satoshis (the smallest unit of Bitcoin) to be assigned unique identifiers, and leverages SegWit and Taproot upgrades to reduce transaction fees for storing metadata in satoshis. This protocol enables users to issue non-fungible tokens (NFTs) on the Bitcoin network. Subsequently, the BRC-20 standard based on the Ordinals protocol further expanded its functionality to enable the minting of tokens. BRC-20 tokens and Bitcoin NFTs have sparked a lot of speculation, increased on-chain activity on the Bitcoin blockchain, and resulted in a significant increase in the portion of miner fees that comes from transaction fees.
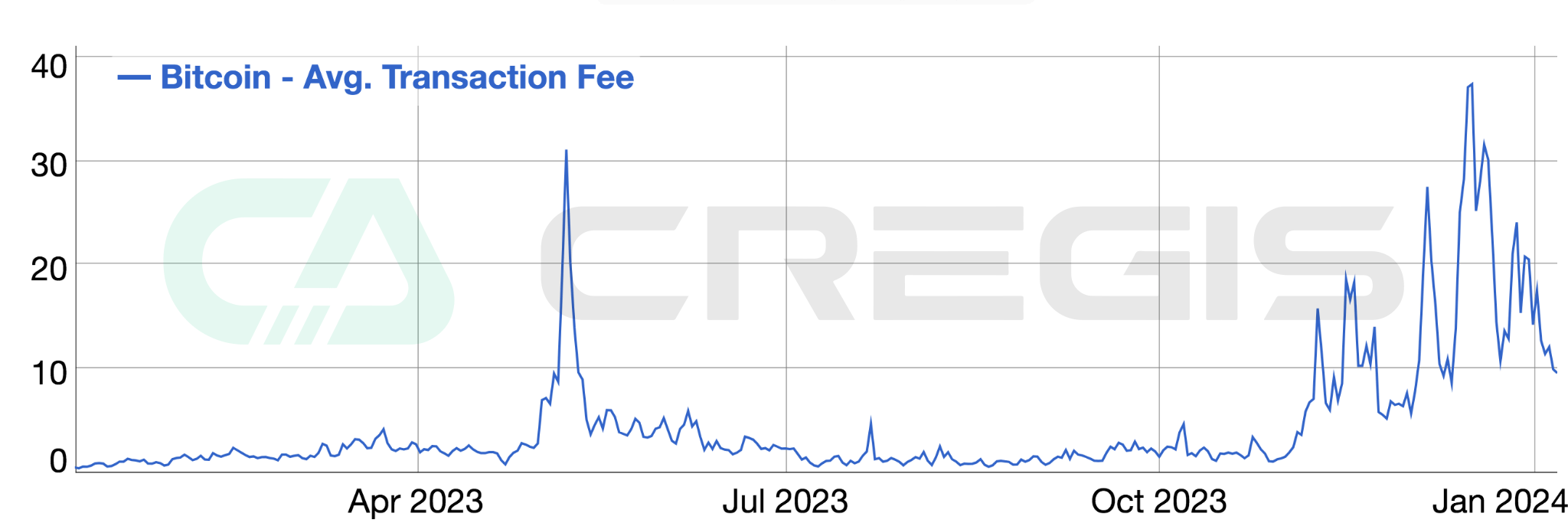
(Source: bitinfocharts)
While the technical architecture of the Ordinal NFT and BRC-20 tokens themselves are not designed to extend the capabilities of Bitcoin, they do demonstrate the possibilities for innovation on the Bitcoin blockchain. Considering the limitations of Bitcoin’s scripting language, we expect to see more innovation on the Bitcoin blockchain in the future.
BitVM
BitVM is the latest Bitcoin upgrade proposed in late 2023 to introduce Turing completeness to Bitcoin. According to BitVM’s white paper, the technical implementation described is through “bit-value commitment” and the method of constructing logic gate commitments, so that Bitcoin contracts have Turing-complete expression capabilities. This method can achieve Turing completeness without changing the consensus mechanism of the Bitcoin network.
(Source: BitVM white paper)
Under the BitVM architecture, any logic can be encapsulated and published to the Bitcoin chain, while its execution occurs off-chain. A fraud proof mechanism will be used during off-chain execution to verify execution results. If an entity wants to challenge the proposal of an on-chain publisher, they can implement a fraud proof on-chain. This mechanism allows the logic of any smart contract to be expressed and verified on-chain while being executed off-chain. Although this approach is more complex than Ethereums smart contracts, it brings huge potential for Bitcoins Turing completeness, which exceeds the limitations that Bitcoin currently exhibits. Over time, BitVM may bring a new wave of innovation to Bitcoin.
3. Application on the chain
(1) Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized finance (DeFi) is a form of financial services that does not rely on traditional financial institutions such as banks or exchanges. It provides users with an open and borderless financial service experience, allowing users to enjoy these services without going through the approval of traditional financial institutions. DeFi has attracted a lot of attention since 2020 and has experienced a series of peaks and troughs. During previous bull markets, DeFi demonstrated its huge potential as an alternative financial system.
However, events like the Luna crash expose the underlying risks of DeFi systems. Currently, DeFi is still in its early stages of development, and many aspects are still not mature and stable enough. In addition, because DeFi is separated from the regulatory system of the traditional market, it also brings some inherent risks.
Although the cryptocurrency market experienced a winter-like bear market in 2022, the DeFi ecosystem in 2023 will be distinguished by integration and resilience. The year saw consolidation across major areas of DeFi, covering key segments such as decentralized exchanges (DEXs), lending markets, liquidity staking and collateralized debt warehouses. It is particularly worth noting that liquidity staking accounts for the largest total value locked (TVL) in the DeFi ecosystem, which not only highlights the stability of liquidity staking yields, but also reflects its strong performance in the competition.
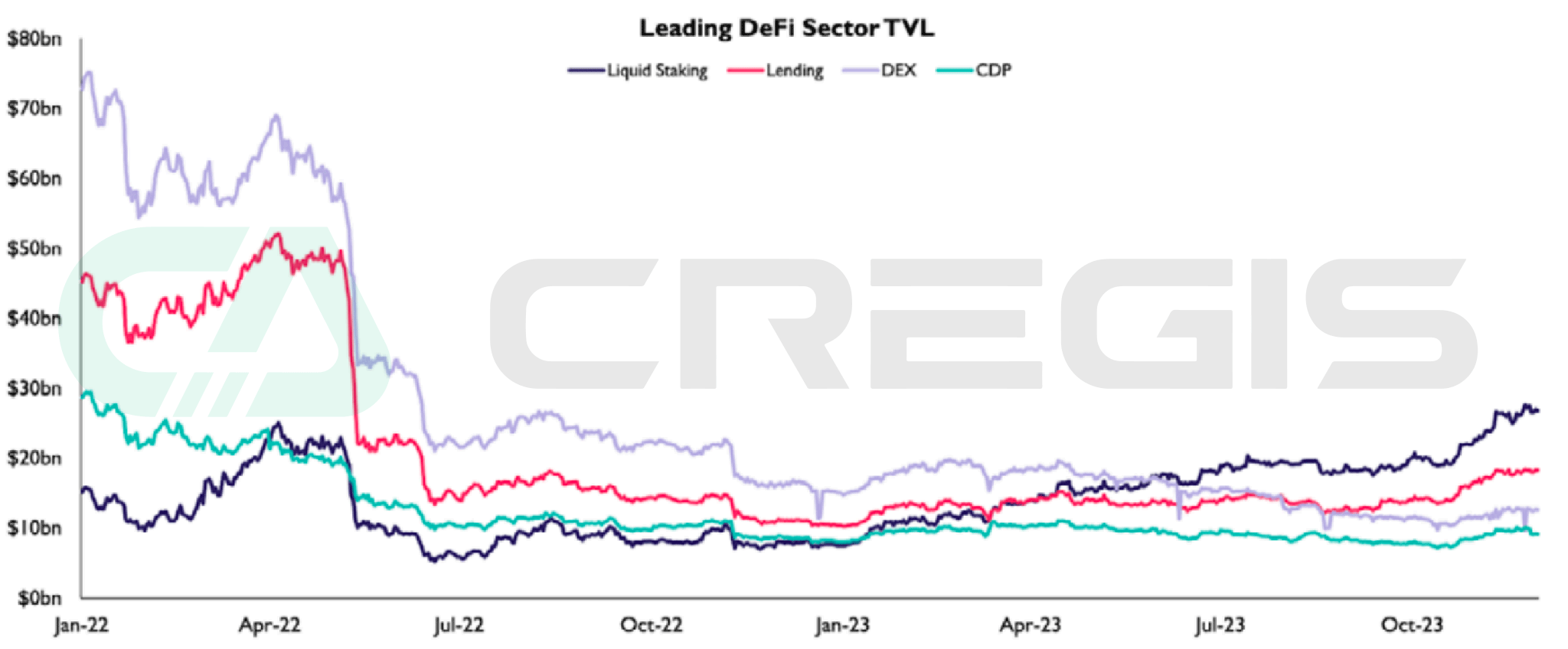
(Source: DefiLlama)
Decentralized exchange
In the first half of 2023, many spot traders fled from centralized exchanges (CEX) to decentralized exchanges (DEX) as the bankruptcy of FTX heightened concerns about the reliability of centralized custodians. The explosion of cryptocurrency centralized projects in 2022 highlights the importance of decentralization and emphasizes the unique advantages provided by DeFi.
Affected by the bear market, market interest continued to be sluggish, and DEX spot trading volume fluctuated in 2023, followed by signs of market recovery in the fourth quarter. In 2023, Uniswap maintained its lead, accounting for 53% of the transaction share for the year, with the majority of the transaction volume coming from Ethereum and Arbitrum One.
By comparison, Curves market share fell from 10% last year to 3.7% this year. The main reason is that the shrinking market hinders the diversity of stablecoins, thereby reducing the market demand for stablecoin swap DEX.
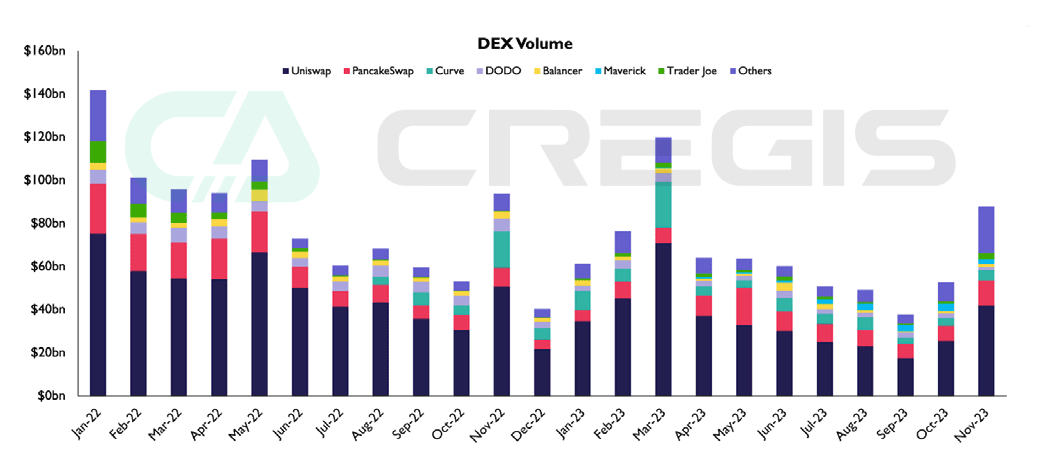
(Source: the block)
loan
In the lending space, Aave continues to maintain its dominance, with a market share of over 60% of total debt outstanding, with Compound not far behind in second place. In 2023, lending activity gradually recovered from the deleveraging in 2022 and showed a steady recovery trend.
One noteworthy development was that in May, SparkLend, part of the Maker brand, entered the lending market. Meanwhile, a fork of Aave quickly gained traction and quickly grew to become the third-largest lending protocol by total outstanding debt, with total outstanding debt exceeding $600 million six months after launch. SparkLend is unique in that it offers predictable interest rates to borrowers of DAI, the largest decentralized stablecoin by market capitalization, by directly leveraging Maker’s line of credit.
Ethereum Liquidity Staking
Ethereum’s liquidity staking space has shown remarkable resilience in 2023, becoming a bright spot in the DeFi space. This is mainly due to two aspects: First, in a bear market characterized by low volatility, the returns generated by liquidity staking are more attractive than those generated by other DeFi activities. Second, the development of “liquidity staking finance” protocols enhances the utility of liquidity staking tokens.
Although ETHs liquidity staking demand appears to have peaked in the second half of 2022, its demand has shown rapid growth in 2023, and this growth has not been affected by the Ethereum Shanghai upgrade and pledge withdrawal functions implemented in April. . In the liquidity staking space, Lido continues to maintain its leadership position with 78% of the market share, while Rocket Pool holds on to second place with 10% of the market share
With the growing development of liquidity staking finance, several other segments in DeFi are beginning to emerge in 2023. In particular, the real-world asset (RWA) tokenization market has seen explosive expansion. RWA collateralized debt positions have issued 2.8 billion DAI, accounting for more than half of the entire 5.4 billion DAI supply. Fees generated by these RWA positions account for 80% of Makers revenue
Derivatives
In 2023, decentralized perpetual contract (perps) exchanges showed a vibrant development trend, especially in November, when the trading volume of perpetual contracts reached the highest point of the year. Although dYdXs market share has decreased, it still maintains its leading position as a mature decentralized perpetual contract exchange (DEX). The battle for the second spot is getting fierce with platforms like Vertex, GMX, Synthetix, ApeX, and others. dYdX is gradually migrating from the Ethereum-based StarkEx ZKR to the Cosmos sidechain, which brings new competitive factors to the perpetual contract DEX market.
Meanwhile, decentralized options trading is starting to gain momentum with the launch of Aevo in Q3. Aevo has quickly become the leading decentralized options exchange, with far more trading volume than Lyra. The dynamics of decentralized derivatives trading volumes throughout the year demonstrate the early-stage nature of the industry and hint at the huge potential within the market as it continues to develop and mature.
(2) Non-fungible tokens (NFT)
In 2023, the non-fungible token (NFT) market is undergoing a critical transformation, which means that NFT assets are moving towards financialization.
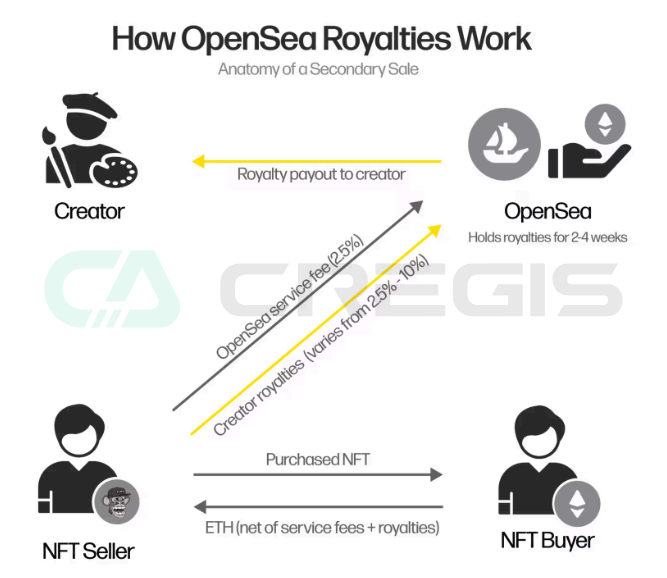
OpenSea and Blur are two platforms active in the NFT market, each with different business models. OpenSea’s business model relies on transaction fees, which charge a certain percentage of each NFT transaction as its source of revenue, but the drawback of this model is that it will have an impact on market liquidity. Blur’s business model disrupts the industry by prioritizing efficiency and liquidity over traditional fee structures that reward creators.
In early 2022, OpenSea became a giant in the NFT ecosystem, with a valuation reaching $13.3 billion after completing a $300 million Series C financing, accounting for more than 80% of the transaction volume in all secondary markets. Its revenue model relies heavily on platform fees, with monthly revenue ranging from US$5 to US$120 million, and annualized revenue will exceed US$1 billion by early 2022.
However, by mid-2023, the situation reversed, with their platform revenue reduced to less than $2 million per month. This significant drop (nearly 90% from previous earnings) can be largely attributed to the rise of “zero-fee platforms,” with users moving transactions from platforms such as OpenSea to zero-fee platforms such as Blur. The NFT market is re-evaluating traditional fee models in favor of liquidity-focused strategies.
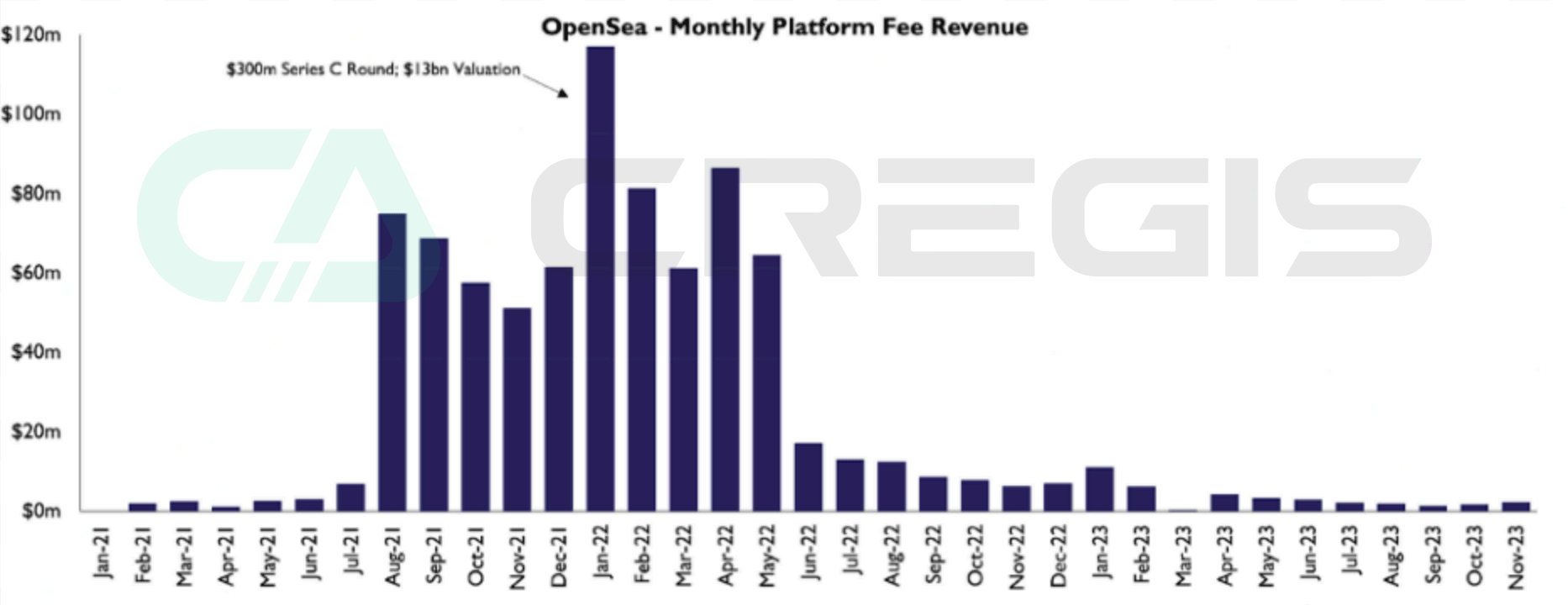
(Source: the block)
In OpenSea’s fee structure, NFT royalties typically range from 2.5% to 10% of final sales. Sellers are required to pay royalties and transaction fees that OpenSea charges on each transaction. Although Blurs business model has increased liquidity and transaction volume, it has also significantly reduced royalties for NFT creators, raising market concerns about sustainable development.
(Source: galaxy)
NFT Finance
2023 is a critical turning point for the non-fungible token (NFT) market, marking a shift towards innovative liquidity solutions. NFT lending platforms have played an important role in this transformation, providing asset holders with a new ability to unlock the value of their digital assets. This marks an important development in the financialization of NFTs, especially for those collectibles of the non-personal image (PFP) category that have traditionally been less liquid.
In the field of NFT trading, platforms such as OpenSea mainly focus on retail transactions. In contrast, NFT loan platforms are committed to serving user groups who are risk-averse and frequent transactions, and bring more richness to the ecosystem by introducing new leverage methods similar to traditional asset endorsements. This market shift resulted in significant growth in loan volume, exceeding $3.3 billion.
In the NFT finance space, the Blend platform launched by Blur dominates, with loan volume reaching $197 million in the second quarter of 2023. With over 6,100 borrowers and 3,300 lenders onboarding, Blends activity has significantly driven overall loan volume growth, which has increased by 270% since the start of the year. But a deeper analysis shows that 10% of lenders and 26% of borrowers account for the majority of transaction volume
Bitcoin NFT
The Ordinals protocol, developed by Casey Rodarmor, allows data to be embedded directly on the Bitcoin blockchain. This protocol numbers Satoshis (Sats), the smallest unit of Bitcoin, and allows a variety of content to be burned on these Satoshis, from images to code, creating a new type of Bitcoin NFT. During the roughly 10 months of Ordinals development, Bitcoin developers built NFT tools similar to those on other major Layer 1 blockchains such as Ethereum, Polygon and Solana.
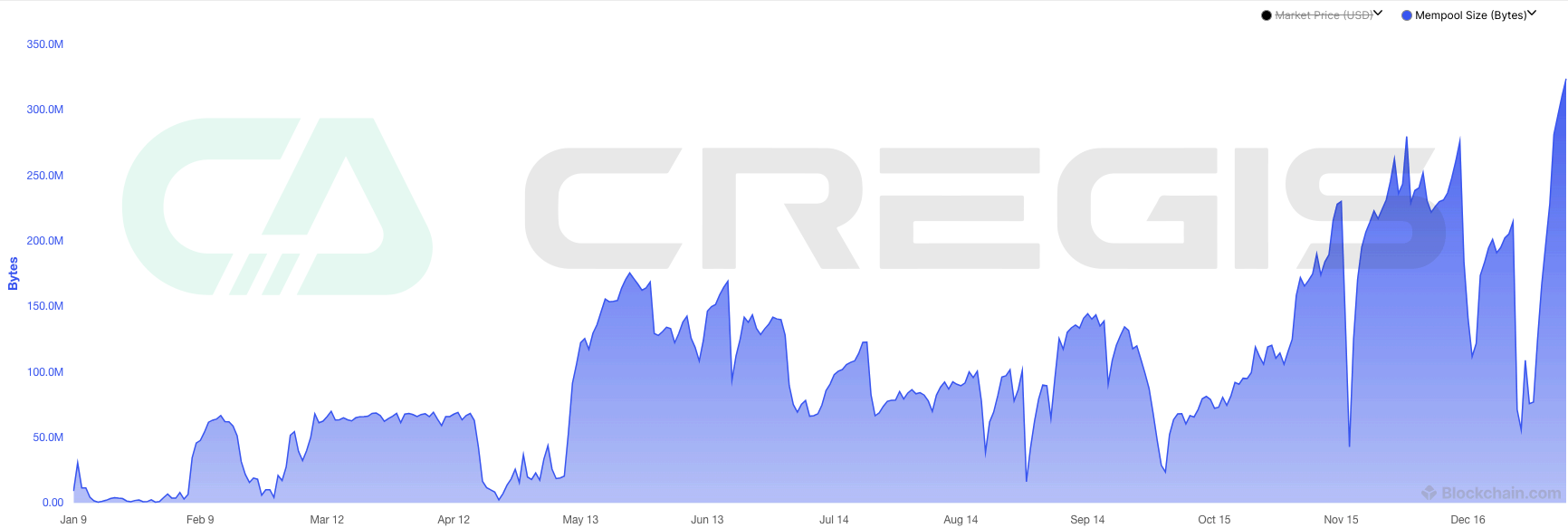
Throughout 2023, the Bitcoin ecosystem has undergone significant changes due to the development of inscriptions. Since the start of the year, miners have racked up more than $530 million in total fees, with roughly $90 million of that coming from Ordinals-related activity. These burning activities resulted in increased fees and congestion in the Bitcoin mempool (transaction pool), with the total byte size of transactions awaiting confirmation reaching an all-time high.
In order to achieve faster transaction confirmation, users began to pay higher fees, increasing competition for the limited space in each block. Transaction fees began to grow significantly in early 2023, reaching a peak around April, driven primarily by the creation of the BRC-20 meme token.
(Source: blockchain)
(3) Decentralized social networking
FriendTech&SoFi
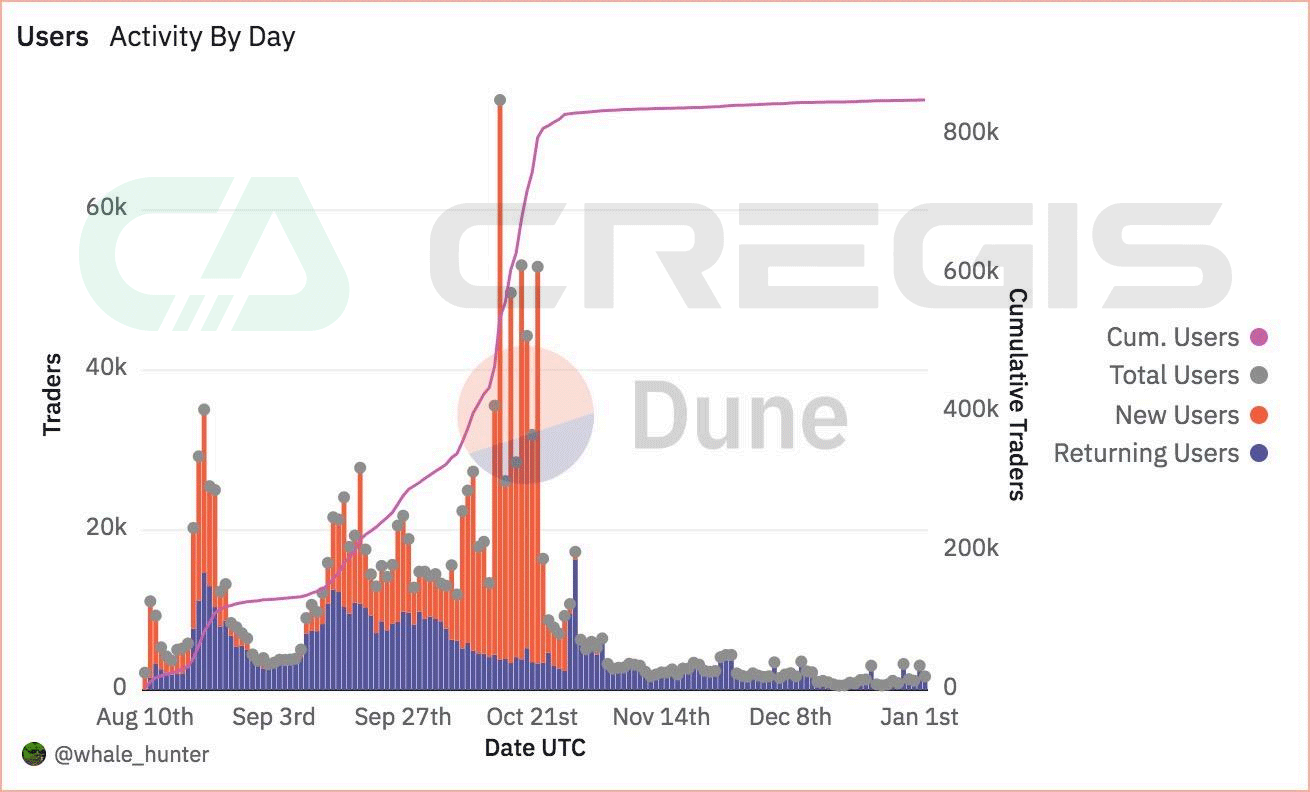
FriendTech is a cryptocurrency-infused social media platform that calls itself a “friends marketplace.” Similar to other non-encrypted social media platforms that are still in the testing phase, Friend.tech implements an invitation code system, and users need to obtain the invitation code of an existing user to complete the registration. The platform has introduced a unique mechanism that allows users to purchase “keys” that enable them to send messages to other users. This novel feature has attracted many users to join. In less than three months since its launch, Friend.tech has already attracted widespread attention from the community, with more than 900,000 platform users and $475 million in transaction volume.
(Source data: Dune)
FriendTechs success is rooted in the fundamental human need for social interaction. On this platform, users can publicly display their score or value, and gain recognition and respect from other users in this way. This not only satisfies users’ inherent desire for social recognition and affirmation, but also strengthens their sense of participation and belonging on the platform.
contact us
Official website
Discord





