
Original author: Jason Jiang
In the evolution of blockchain technology, there are two key issues that cannot be bypassed: privacy and expansion. When we searched for the standard solutions to these two problems, we found that they are inseparable from one technology, that is: zero-knowledge proof. What is a zero-knowledge proof? How does it solve the blockchain privacy and expansion problems?
1. What is a zero-knowledge proof?
In 1985, S.Goldwasser, S.Micali, and C.Rackoff from MIT first proposed zero-knowledge proofs in the research paper Knowledge Complexity of Interactive Proof Systems. This is a verification protocol for a prover to prove the correctness of its knowledge without revealing any valid information.
In order to facilitate understanding, lets give an example:
Little O has a box with a password, and he wants to make Little K believe that he knows the password to the box without telling him the real password. So how to do it?
Little O came up with a way: he asked little K to write a note that only he knew the content of in the whole world, and then little K put it into the opened box with his own hands and locked it. Then Little O takes away the box and uses the password to take out the note that Little K put in the box, and gives the note to Little K the next day. In this process, Little K did not learn any information that he did not know before (the password of the box), but he still had to believe that Little O knew the password. This verification process is zero-knowledge proof.
To put it simply, zero-knowledge proof is to establish trust between the two parties with the minimum amount of information exchanged. Without revealing more information, A can prove to B that something/a certain conclusion is correct.
According to the interaction mode in the proof process, it can be divided into two categories: interactive zero-knowledge proof and non-interactive zero-knowledge proof.
Interactive zero-knowledge proof means that in order to prove something, the prover needs to interact repeatedly with the verifier, just like a lie detector: the verifier constantly asks questions to challenge the authenticity of the prover’s commitment, and the prover needs to constantly Respond to these challenges until validators are convinced. Its flow is as follows:
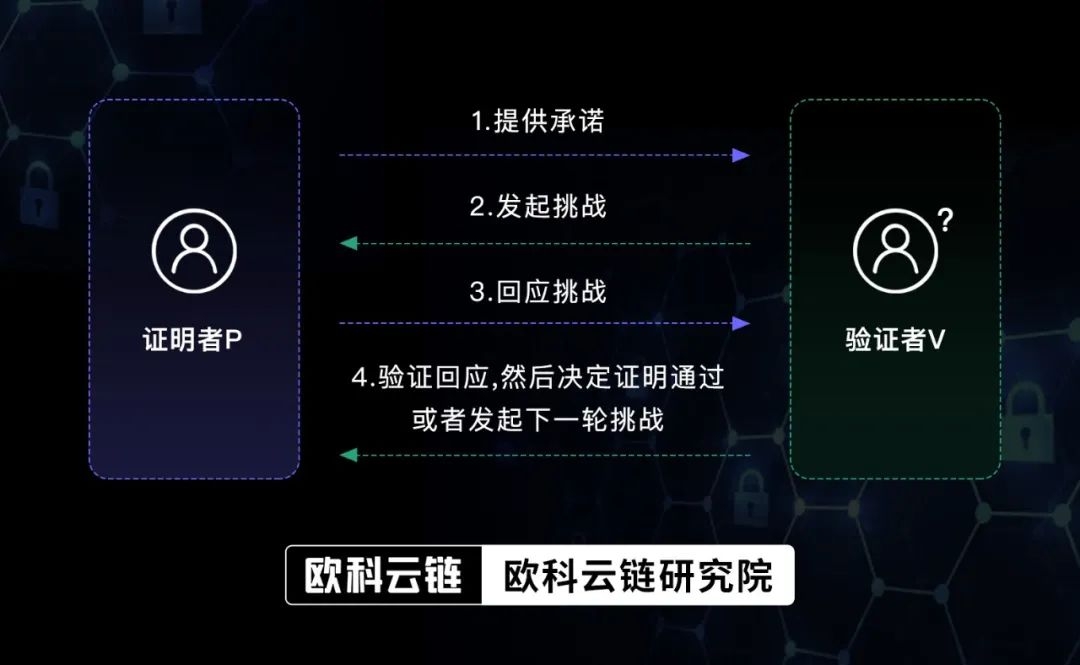
Early zero-knowledge proofs were all interactive. This method is straightforward, but the process is lengthy and inefficient: both parties must complete the verification online at the same time, and can only gain trust from one verifier at a time. If multiple people are to be trusted, the above process must be repeated. This process is tiring to think about.
Thus, non-interactive zero-knowledge proofs emerged. In non-interactive zero-knowledge proof, the prover and the verifier agree on the verification rules in advance, the prover provides data as promised, and the verifier can verify the correctness of the data at any time. With this non-interactive verification, both parties do not need to be online at the same time, and the prover only needs to provide proof once.The applications in actual scenarios are basically non-interactive zero-knowledge proofs, such as ZK-SNARK and ZK-STARK.

2. What is the use of zero-knowledge proof in the blockchain world?
Zero-knowledge proofs are mainly used to solve two types of problems in the blockchain world:Privacy and scalability.
(1) Privacy
One of the important application results of zero-knowledge proof is the Zcash project launched in 2015 that enables private transactions. In addition to anonymous coins such as Zcash, zero-knowledge proofs can also play a role in blockchain finance, on-chain voting, identity verification and other scenarios.
In blockchain financial applications, zero-knowledge proof allows participants to flexibly choose the transactions and information they want to disclose and hide. For example, companies can selectively expose certain payments for audit trail purposes while hiding confidential customer, employee payroll, contractor, supplier, and other confidential information.
When voting on the chain, zero-knowledge proofs can also allow participants to vote anonymously and verify the validity of the voting results.
In addition, zero-knowledge proofs can help users authenticate their identities without exposing specific identity information. Polygan ID on Ethereum uses a zero-knowledge proof verification scheme, which not only helps users protect their privacy, but also meets regulatory requirements for KYC verification specifications. Users can freely choose when and what data to share.
(2) Expandability
Blockchain is in urgent need of expansion due to performance limitations that cannot meet market demand. The ZK Rollup expansion plan based on zero-knowledge proof is regarded as the ultimate solution for Layer 2 expansion. ZK-Rollups improves blockchain throughput by transferring calculations off-chain, that is, packaging a large number of transactions into a Rollup block, and generating a validity proof based on zero-knowledge proof off-chain. Smart contracts on Layer 1 only need Verifying the proof allows you to directly apply the new state, resulting in lower gas and higher security.
zkSync based on ZK-SNARKs technology and StarkNet based on zk-STARKs technology are currently the most representative ZK-Rollups projects.
Among them, zkSync is a Layer 2 expansion solution launched by Matter Labs in 2018, which improves the scalability of the Ethereum network by using Rollup based on zero-knowledge proof.In February this year, zkSync announced that the zkSync Era mainnet was officially launched. OKLink multi-chain browser then took the lead in accessing zkSync mainnet data, becoming the first multi-chain browser in the entire network to support the zkSync network.
StarkNet is a permission-free Layer 2 network developed by Israeli software company StarkWare. By using zk-STARKs technology, it can help DApps achieve greater computing scale with lower transaction costs. Since the launch of the mainnet in November 2021, the StarkNet ecosystem has developed rapidly and currently has more than 100 Dapps and services, covering different categories such as DeFi, NFT, wallets, and cross-chain bridges. As one of the projects with the highest valuation and the largest market share in the ZK Rollup track, the development of StarkNet has attracted much attention. The OKLink multi-chain browser will also be launched on the StarkNet browser in the near future, providing more comprehensive and richer on-chain data insights and services for all users who follow and participate in the StarkNet ecosystem and Layer 2 construction.

It is reported that the StarkNet browser will be the 30th blockchain browser launched by OKLink and the second ZK Rollup browser after zksync. In the future, OKLink multi-chain browser will also launch blockchain browsers based on well-known ZK Rollup projects such as Polygon-zk, Linea, Base, and Scoll based on zero-knowledge proofs.




