Original author:Hwee Yan
Original compilation: Deep Chao TechFlow
What is Layer 3 protocol?
Layer 3 protocols are built on top of Layer 2 to provide better scalability so developers can create custom, application-specific blockchains based on their needs.
Key takeaways
Layer 3 protocols are built on top of Layer 2 and are used to host application-specific decentralized applications.
Layer 3 protocols can solve various problems such as scalability, interoperability, customization, etc.
Examples of Layer 3 protocols: Orbs, Arbitrum Orbit, and zkSync Hyperchains.
How do L1, L2, and L3 work together?
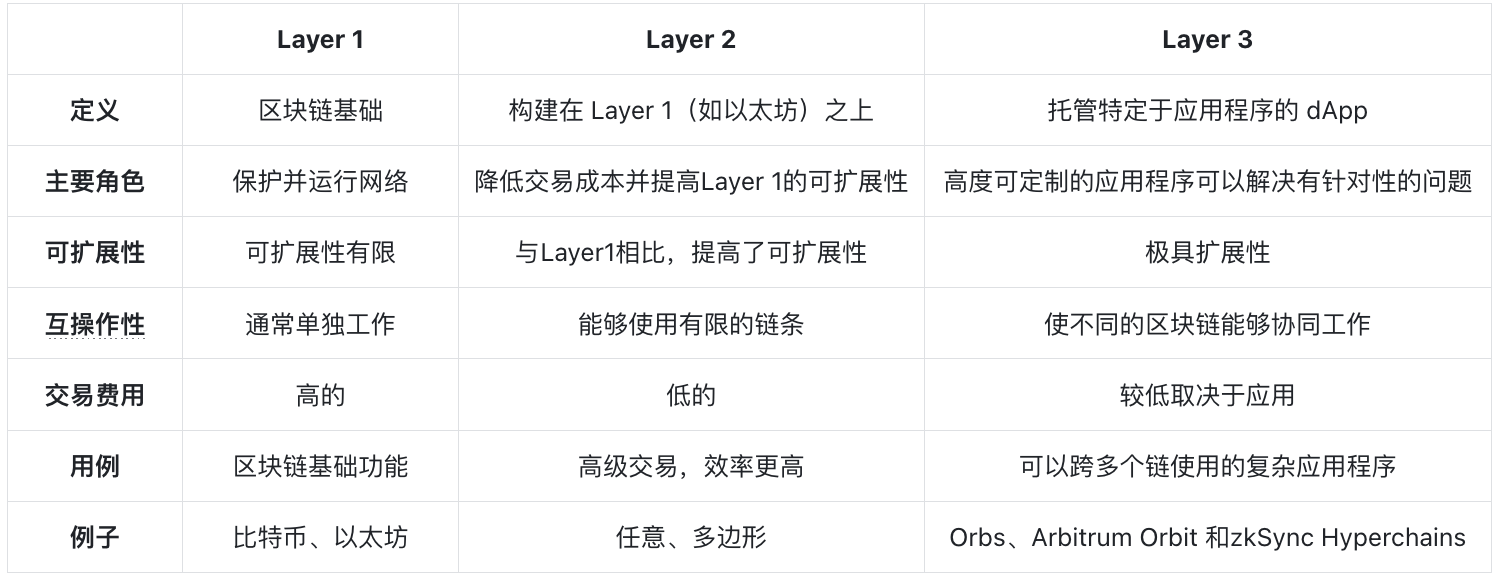
Layer 1 It is the blockchain that forms the basis on which blocks are added and transactions are finalized. However, Layer 1 faces the blockchain trilemma in that they cannot balance scalability, decentralization, or security. Blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum prioritize decentralization and security over scalability, and transaction speeds on these networks become slow as the number of users on the network increases.
This is what solves the scalability problemLayer 2Useful place. Layer 2 is off-chainvertical expansionThe solution runs on Layer 1 such as Ethereum to achieve scalability and provide users with faster transaction speeds and lower Gas fees.They can be aggregated(Rollup) or form of validation, likePolygon 2.0 The situation is the same. Many Layer 2 solutions, such as Polygon, zkSync, and Arbitrum, have released solutions that enable developers to create application-specific chains built on top of Layer 2, which brings us to Layer 3.
Layer 3 is an advanced protocol built on existing Layer 2 solutions to provideinteroperabilityand application-specific features. This means that Layer 3 is highly customizable and able to meet the specific needs of developers, such as providing solutions to targeted issues such as privacy, or supporting large volumes of transactions, while still inheriting the security of Layer 1 blockchains. Currently, most Layer 3 is built on Ethereum, and at the time of writing, some blockchains (such as Bitcoin) are not suitable for hosting Layer 3 applications.
What problems can Layer 3 solve?
Now, having understood how Layer 1, Layer 2, and Layer 3 work together, let’s take a closer look at Layer 3 and how they can further extend the blockchain.
Scalability
Layer 3 is designed to enhance scalability beyond the capabilities of current Layer 1 and Layer 2, so it is extremely scalable. As a result, Layer 3 networks are able to handle larger volumes of transactions while supporting a wider range of complex applications.
Complex dApp support
Layer 3 is able to provide the necessary infrastructure for developing more complex decentralized applications that require more advanced functionality. This may help improve web design, include more advanced features in applications, and make them easier to use for lay users. Depending on developer needs, Layer 3 can also facilitate more complexsmart contractdesign, which cannot be handled due to the limited scalability of Layer 1 and Layer 2.
Blockchain interoperability
Layer 3 also solves interoperability issues. Layer 3 can act as a bridge between various blockchains so that transactions and data can flow across different platforms. This means that Layer 3 dApps have the functionality to connect to different blockchains such as Ethereum and Solana.
Customization
Layer 3 can also be customized to meet the unique needs of developers. For example, developers can introduce application-specific mechanisms that only allow private transactions and contracts to be executed, thereby exposing only part of the data. Due to the highly customizable capabilities of Layer 3, developers can customize the dApps governance mechanisms, rules, and functions according to their own needs.
Arbitrum Orbit allows developers to customize different aspects of their chain. For example, developers can customize and choose which tokens are accepted as transaction fees on their chain. This provides developers with the flexibility to select and potentially include a platform’s native token, allowing developers to tailor the functionality of their decentralized applications (dApps) to their unique needs.
Additionally, developers can customize their dApps to ensure users have more consistent and reliable gas prices. Developers can also launch their own blockchain networks with specific functionality, such as Arbitrum’s Nitro-powered blockchain network and theEVM+ compatibilityStylus. Some of the other custom features offered by Arbitrum Orbit include privacy, permissions, fee tokens, governance, and more.
High cost performance
Since Layer 3 networks handle some transactions and operations off-chain, this helps reduce network congestion, thereby significantly reducing transaction fees. This cost efficiency helps lower the cost barrier to entry and makes it easier for developers and users to use.
For example,Xai networkIt is a game network that specifically provides support for Web3 games. The Xai network is built through Arbitrums Layer 3 network, introducing parallel processing to improve efficiency and scalability while further reducing costs.
Accessibility
Layer 3 can also become more accessible to the masses and easier to implement. For example, Arbitrum Orbit allows anyone to build and deploy their own Layer 3 network on Arbitrum Nitro without requiring approval. In contrast, launching Layer 2 requires proposals around its trust model and how to achieve full decentralization.
Layer 3 use cases
Now that we understand what problems Layer 3 solves, here are some possible use cases for Layer 3:
Game application
One of the use cases for Layer 3 isBlockchain games. By running on Layer 3, it enables applications to run on a specific blockchain, allowing transactions to process larger volumes at a faster rate. This is especially important for gaming apps, helping developers maintain a silky smooth in-game experience for users.
Gaming applications often need to handle many microtransactions, which are often costly. Therefore, running these applications on Layer 3 allows developers to ensure cost efficiency for users since Layer 3 transaction fees are lower.
Decentralized financial applications
Another possible use case for Layer 3 is decentralized finance applications. Running on Layer 3 is ideal as it enables decentralized finance applications to be customized to the needs of the application. This means developers will be able to customize the privacy settings and different features of the app. In addition, Layer 3 is extremely scalable, which ensures that large volumes of transactions can be processed quickly, which is extremely important for real-time transactions. Layer 3 also allows interoperability between various blockchain networks, allowing users to transfer assets across different networks.
Layer 3 Example
While the concept of Layer 3 is still considered a relatively new development in the crypto space, here are some noteworthy projects:
Orbs
OrbsUsed in conjunction with existing Layer 1 and Layer 2 protocols, it is a Layer 3 blockchain focused on solving the scalability issues faced by the Ethereum blockchain. According to its website, Orbs views its Layer 3 as enhanced execution, allowing developers to develop smart contracts by running as a decentralized serverless cloud.
Source: Orbs
This means developers are able to write and deploy their smart contracts on Orbs’ own decentralized network without having to worry about the network’s underlying infrastructure. This also provides developers with the convenience of not having to maintain physical servers. Currently, Orbs works with a number of Layer 1 and Layer 2 protocols, including Ethereum, BNB Chain, Avalanche, Polygon, and more.
Arbitrum Orbit
In 2023, the Arbitrum Foundation also released a new feature - ArbitrumOrbit, which is envisioned as a Layer 3 blockchain built on the Arbitrum Nitro platform. In addition to lower transaction costs and enhanced scalability, developers will be able to create their own self-managed, private blockchains on the Arbitrum Nitro platform, which will allow developers to use customized zones based on their specific needs. Blockchain.
zkSync Hyperchains
Introduced by the zkSync teamzkSync HyperchainsCan be Layer 3, they use Layer 2 for settlement. zkSync Hyperchains are powered by the same zkEVM engine available on the ZK Stack, where all ZKP circuits are consistent and inherit Layer 1 security regardless of who deploys it. One benefit is that there will be faster messaging between Layer 3s settling on the same Layer 2 and interoperability within the broader ecosystem.
Source: zkSync Era
final thoughts
The development of Layer 3 is an interesting innovation in the field of cryptography. It improves on our previous capabilities by combining the best parts of Layer 1 and Layer 2, such as making the network more scalable while also being more secure. Nonetheless, it is still important to remember that each layer plays a vital role in the blockchain ecosystem and does not compete with each other. Currently, Layer 3 is still in the development stage, but I think it’s clear that Layer 3 will play a key role in shaping how we leverage blockchain technology in the future, making it easier for blockchains to handle high transaction volumes.





