Original - Odaily
Author - Loopy

This morning, Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin released a new version of the Ethereum roadmap. There are no major changes in this roadmap from the past. He said there have been relatively few changes as Ethereums technical path continues to solidify.
Ethereum’s 2024 roadmap emphasizes key features such as innovation, scalability, and decentralization. By establishing this major shift to PoS consensus, Ethereum will solidify its position as a leading blockchain platform ready to meet the evolving needs of its global user base.
This roadmap is designed around six core elements, as follows:
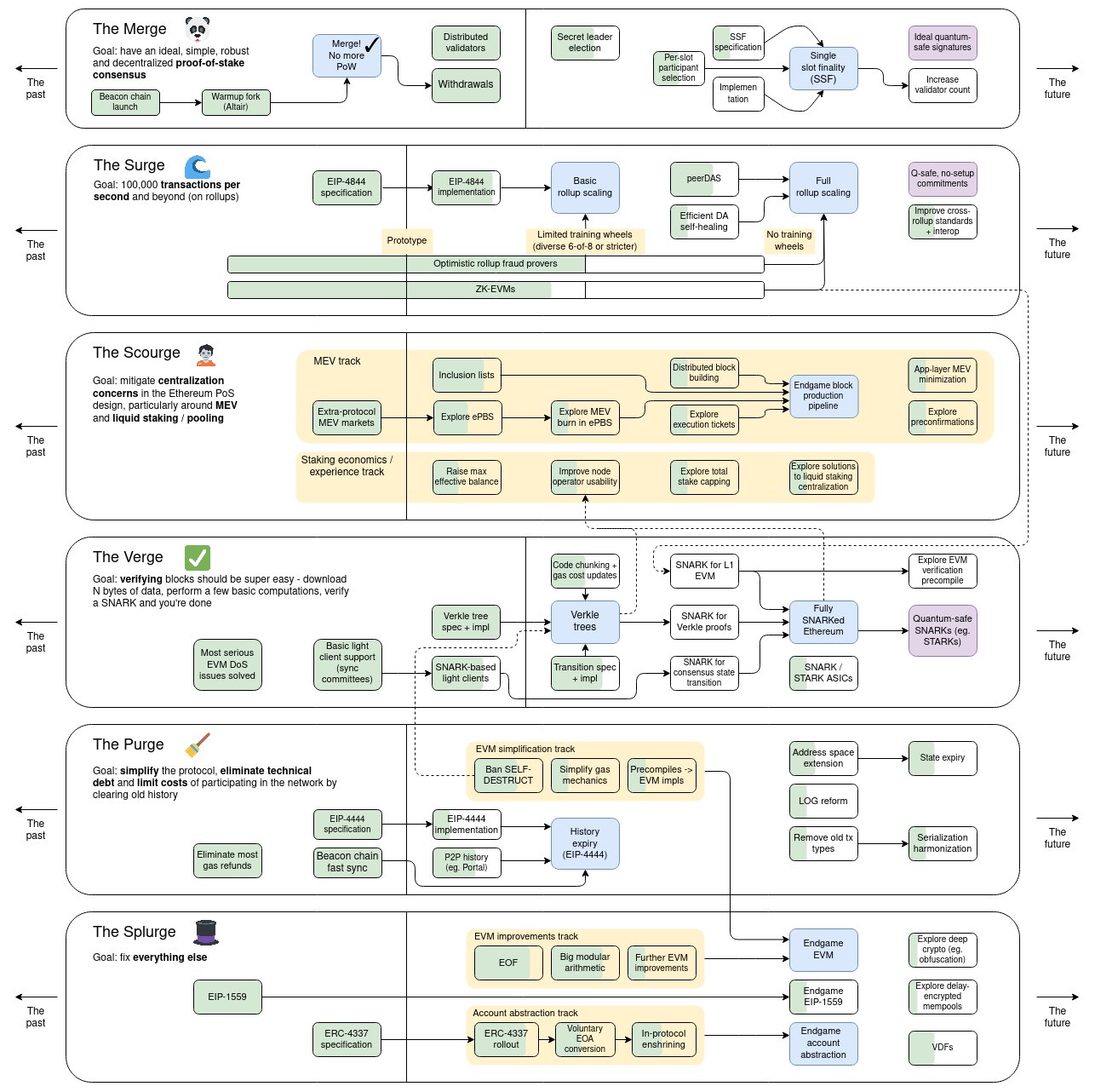
The Merge
This part was implemented as early as September 2022, marking Ethereum’s shift from Proof of Work (PoW) to a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. This shift significantly reduces the network’s energy consumption and provides the basis for further enhancements to the blockchain’s efficiency and scalability.
Single-Slot Finalization (SSF) plays an important role in post-merger Proof-of-Stake (PoS) improvements, and SSF is the best way to address the weaknesses of the current Ethereum PoS design.
SSF:The current Ethereum consensus protocol, Gasper, requires 64 to 95 slots to finalize a block, making a significant portion of the chain susceptible to reorgs. To solve this problem, they proposed a protocol that can finalize one block per time slot, paving the way for single-slot finality within Ethereum. Such a protocol will help increase the speed of transaction confirmation and economic security.
The Surge
This section aims to greatly increase Ethereum’s throughput, with the goal of reaching 100,000 transactions per second. This scaling solution is critical to supporting global adoption and increasing network capacity, spanning Ethereum and its Layer 2 network.
Significant progress has been made in this area. This includes advances in EIP-4844 and improvements in Rollup scaling itself.
Ethereum researchers are actively exploring new mortgage pool solutions to improve the decentralization, security, and efficiency of the Ethereum network. These proposals include simplified active validator caps and rotations, implementation of single-slot finality (SSF), and the introduction of new concepts such as execution tickets.
Clear(The Scourge)
This topic focuses on addressing economic centralization risks within the Ethereum ecosystem, specifically related to miner extractable value (MEV) and liquidity staking services. The goal is to maintain the decentralized nature and ensure equal and fair access to network resources.
Potential improvements:
Execution ticket:Introducing a new mechanism called “Execution Tickets”, a potential improvement to Ethereum’s consensus mechanism. This mechanism proposes an in-protocol market for buying and selling tickets that provide the right to propose future blocks. It consists of two random drawing processes, one for selecting beacon block proposers and provers, and another for selecting execution block proposers and provers. The purpose of the execution ticket system is to separate the production of beacon blocks and MEV rewards, thus isolating the decentralized set of validators from these centralized forces. This article delves into the design and analysis of this mechanism as well as some open issues that remain to be solved.
New verification mechanism:Vitalik Buterin previously proposed a simplified active validator cap and rotation proposal. This proposal aims to simultaneously ensure economic finality, low long-term variability in validator revenue, and maximize simplicity by capping the number of active validators (e.g. 2^19 validators). To handle validators exceeding the upper limit, an improved version based on the dynasty mechanism is proposed, ensuring that only a certain number of validators are awake at any time, while rotating a portion of the awake validators each time the chain is completed. , to maintain safety and low variability. The proposal also discusses possible economic impacts and alternatives.
Two-tier mortgage model:The two-tiered staking model divides participants into different tiers based on the amount of collateral or other criteria. This increases decentralization through protocol and staking pool changes and reduces pressure on the consensus layer. This model is based on how popular decentralized mortgage pools such as Lido and Rocket Pool operate, with certain improvements. These include improvements to within-pool voting tools, increased competition between pools, and the introduction of enshrined delegation within the protocol. These proposals aim to improve the security and decentralization of the Ethereum network.
The Verge
Enhancements in this area are aimed at making block verification more efficient. As transaction volume continues to grow, these optimizations are critical to maintaining Ethereum’s scalability. The content of increasing L1 gas limit has been removed from the roadmap. The gas limit can be increased at any time, indicating a flexible network capacity management method.
The latest development is that the Verkle tree is almost ready.
Verkle tree:
Verkle Tries is a data structure similar to Merkle Patricia Trees (MPT), which is the data structure used in Ethereum today. Although Verkle Tries uses a tree-like structure similar to MPT, the key difference is that each node uses a special type of hash (called a vector commit) to commit to child nodes. These vector commitments provide several important long-term benefits and help pave the way for Ethereum to be stateless.
Specific advantages include: smaller proof size; reduced hardware requirements for running nodes, thereby enhancing decentralization; new nodes can join the network immediately, synchronizing faster; scaling advantages brought by allowing higher gas limits; and zk- EVM is more compatible.
The Purge
The focus is on simplifying Ethereum’s protocol to make it more developer-friendly and accessible. This simplification is expected to improve the overall functionality and usability of the Ethereum network.
Status expiredReduced Priority: State Expiration is a relatively low priority and urgency item on the roadmap, especially given the development of stateless clients and PBS.
VDFReduced emphasis: This shift is due to cryptographic weaknesses identified in existing VDF constructs.
The Splurge
This category covers a variety of other aspects of the Ethereum ecosystem, ranging from ecosystem growth and sustainability to human coordination. It reflects Ethereum’s commitment to nurturing and supporting its vibrant community.





