Original title: "In order to prevent DeFi attacks, what should we do? "
Smart contracts have given us many features such as decentralization, no need for trust, no trust, etc., but after removing human operations, once the smart contract opens the sky, then the assets may be taken by hackers. The popularity and adoption rate of DeFi is increasing, and the project parties are mixed. How to protect assets with a keen eye is becoming more and more important.
This film briefly analyzes the examples of DeFi being attacked since 2021, and proposes prevention methods. Simple and easy to understand.

At present, the DeFi segment has two characteristics: one is that it is soaring to unprecedented heights: it is poorly regulated, and there is hardly anyone with the resources or technical skills to operate smart contracts and attract users. These two factors make this area very attractive to attackers.
How exactly do these attacks happen? How to protect yourself? We will examine the mechanics and provide examples of the biggest attacks in DeFi in order to understand which protocols require particular caution.
The Shortest DeFi Overview
DeFi provides blockchain-based financial services such as lending and interest-earning. The key point is that DeFi is inclusive and permissionless - anyone, regardless of their citizenship, social status and credit history, everyone can take advantage of it. DeFi is trustless because it runs on smart contracts - all the terms and conditions were described in advance, written in code, and can now be executed without human intervention. Here, the only thing users can trust is the ability of the protocol team to write good code. In turn, since most projects are open source, audits and the community usually check this.
Yet how does this leave room for manipulation?

How can attackers exploit insecurity in DeFi?
A hack on DeFi is when someone exploits a protocol's vulnerability to gain access to funds locked in the protocol. Here are three main "strategies" for achieving this:
DeFi projects are made very quickly, and teams don't always have the time to thoroughly check their code. Hackers exploited these vulnerabilities.
Every protocol in DeFi has its own mechanics, how users lock up their funds, and how they get rewarded. Sometimes the founders of the protocol are unaware of how these mechanisms can be abused and turned into lucrative loopholes.
Some teams create problems on purpose - they abuse their huge influence in the project by selling their stake and dumping tokens (community doesn't notice this).
The two most commonly used attack schemes in DeFi
Let’s take a look at two of the most widely used mechanisms in DeFi — carpet pulling and flash loan attacks.
Pulling the rug - withdrawing liquidity when no one expects it
In a “carpet pull,” the owner or developer suddenly withdraws liquidity from the pool, causing panic and forcing everyone to sell assets. Basically, it's an exit scam. The higher the founder’s stake in a project, the more suspicious it is: “carpet pulling” is one of the centralization risks discussed in DeFi.
Here's how it started: the founders announced a new platform with a native token offering some cool rewards. The team then creates a liquidity pool on a decentralized exchange such as Uniswap, where tokens are paired with ETH, DAI or other major currencies. Users are encouraged to bring more liquidity as it will bring them high yields. Once the token price rises, the founders withdraw their liquidity and disappear.
It's not great that developers have large stakes, but even if they did, there's a way to protect projects: developers can set up a procedure that doesn't allow them to quit until a future date. This greatly increases trust in the project.
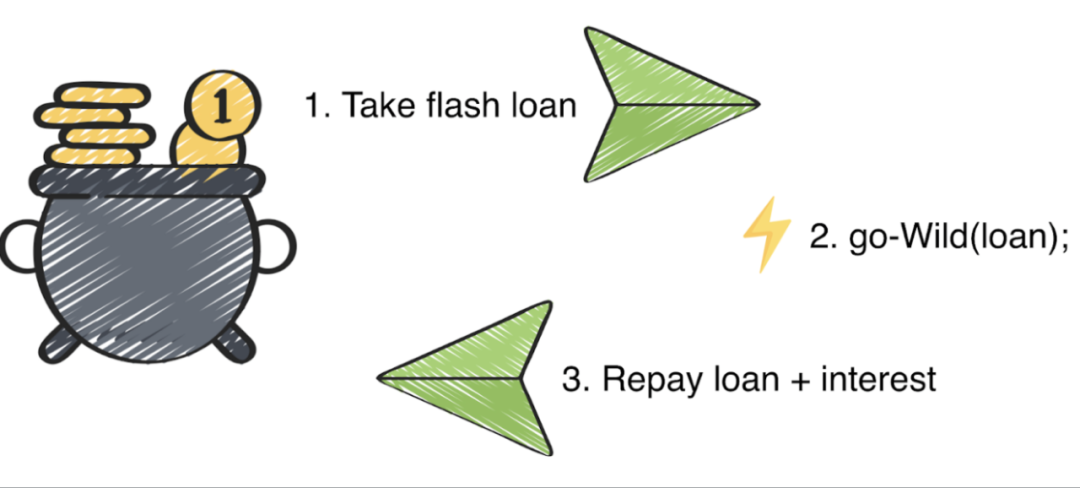
Flash Loan Attacks - Draining and Eliminating Liquidity
What is a "flash loan"? It allows users to borrow an unlimited amount of money in a very short period of time with no collateral - users must repay the loan plus interest before the next block is mined and mining takes only seconds. If the user does not repay the loan, the transaction will not end and the borrowed funds will be taken from the user.
One of the key uses of flash loans is arbitrage: profiting from the price difference of assets on different platforms. For example, Ethereum costs $2,000 on Exchange A and $2,100 on Exchange B. A user can get a flash loan worth $2,000, buy ETH on exchange A, sell it on exchange B, and the user's profit will be $100 minus gas fees and loan fees.

The unlimited nature of flash loans paves the way for exploits. The following is the general scheme of a flash loan attack:
An attacker borrows 200 Token A worth $100,000 ($500 for one Token A).
He then aggressively buys token B in the A/B liquidity pool. This pushes up the price of token B, while token A falls and is now only worth $100.
When Token B skyrockets, the attacker sells it back to Token A for $100. Now, it can afford 1000 Token A (after a 5x price drop) compared to the initial 200 Tokens.
However, the attacker just reduces the price of token A in this smart contract. The lender of the flash loan still buys Token A for $500. So the attacker repays the loan with his 200 Token A and takes the remaining 800.
As seen, flash loans leverage the essence of decentralized exchanges without actual hacking. They simply dump token A and remove a significant portion of the pool’s liquidity, basically stealing liquidity providers’ funds.
Major DeFi Attacks of 2021
1. The Meerkat Finance hacker This is a typical rug-pull, however, in an unusually cynical manner. Meerkat Finance is a liquidity mining protocol where pooled funds cannot even be used by the owner. Shortly before the attack (one day after the project launched!), they upgraded the protocol, gained access, deleted all of Meerkat Finance’s social media accounts and their website, and took $13 million worth of stablecoins and 73,000 BNB worth $17 million got away. 2. Alpha Homora Flash Loan Attack
The stakes are rising! In the Alpha Homora attack in February this year, $37 million was stolen. Launched in October 2020, the lending platform was recently upgraded to version V2. In an Alpha Homora V2 pool, the attacker borrowed and lent millions of stablecoins, inflating their value and making the attacker huge profits.
3. EasyFi private key stolen

In April, Polygon-based lending protocol EasyFi suffered one of the worst DeFi hacks ever. In one hack, a network administrator's private key was stolen, allowing the attacker to gain access to the company's funds. Three million EASY tokens worth $75 million were stolen. In addition, $6 million worth of stablecoins were stolen from EasyFi’s vaults.
4. Saddle Finance Arbitrage Exploitation
Here's another flash loan attack, especially this time. Saddle Finance, a Curve-like protocol for trading wrapped assets and stablecoins, was hacked on January 21, 2021, a day after its launch. Through a series of arbitrage attacks, the attacker successfully obtained nearly 8 bitcoins of liquidity in just 6 minutes. This could be due to a bug in the pool’s smart contract — the attacker pumped the price of the stablecoin so high that one token worth 0.09 BTC was swapped for another token worth 3.2 BTC.
How to avoid choosing a vulnerable protocol?
"Flash loans" always happen unexpectedly, and people can't always see the possibility of "carpet pulling" in advance. However, following these recommendations will help users pay more attention to suspicious signs and possibly help users avoid monetary losses. pay attention:
The team and its reputation. Who are the founders and developers? Is the team public? Has it ever been involved in any trustworthy crypto projects? If not, it's not necessarily a bad thing, but it should be cause for concern.
Access the vault. Does this team exist? to what extent? If founder ownership is too high, it's not a red flag.
Multi-signature access to corporate funds. This may help prevent "carpet pulling" if the developer has enabled multi-signature access to the library and someone outside the team owns some of the signatures.
longevity and its mobility. If developers lock up their funds for a year or so, users can rest assured that the team won't exit until at least that period is up.
What measures are in place to protect DeFi from attacks?
As DeFi matures, there is a considerable amount of liquidity in the pool, and a large amount of liquidity in the pool may be a major factor in reducing the risk of flash loan attacks.
The flash loan maximum limit does not allow attacks.
Security audits of smart contracts will make room for vulnerable and misconfigured contracts.
Better regulation will help avoid knowingly releasing vulnerable protocols.
Summarize
Summarize
DeFi has revolutionized finance using permissionless and trustless tools to drive massive income in a short period of time. However, its numerous vulnerabilities are often exploited by attackers and malicious developers. Every attack requires the protocol to improve its security, and this is how DeFi hacks help the industry grow.
Source:https://medium.com/the-capital/defi-attacks-and-ways-to-avoid-them-4b827ef456be





