At 8:00 on October 19th, Beijing time, the cross-platform layered derivatives protocol Barnbridge (BOND) officially launched liquidity mining. As of 12:40 on the 22nd, the locked assets of the project exceeded the 200 million US dollar mark, reaching 203333277.51 US dollars.

As early as October 17, Coinbase Custody officially announced that it would consider providing custody services for 39 digital assets, including Barnbridge.

What exactly is the so-called "cross-platform layered derivatives agreement"? What's so special about Barnbridge? How to participate in BOND mining?Odaily recently interviewed Barnbridge co-founder Tyler Ward, combined with our personal understanding, trying to answer these questions one by one in a more popular language.
First of all, let's put aside the awkward modifier of "cross-platform hierarchical derivative agreement", and try to change a more understandable definition for Barnbridge. In terms of the problems the project wants to solve, Barnbridge can be called aRisk cutting tools for decentralized finance (DeFi).
It should be noted that Barnbridge itself does not directly provide benefits. The focus of the project is on the management of risks and benefits—it is only risk cutting, not risk elimination, because in essence, risks are determined by the market, and human intervention can only be done in certain situations. To a certain extent, risks can be transferred and dispersed, but risks cannot be completely eliminated.
white paperwhite paperThe vision for the project is presented in . Currently, 60% of global debt yields less than 1%, and more than $15 trillion in global debt yields are negative; at the same time, the total amount of funds locked in the decentralized finance (DeFi) market has increased from 1% at the beginning of the year. Hundreds of millions of dollars have risen to tens of billions of dollars, and the annualized rate of return (APY) provided by various DeFi applications is much higher than that of the traditional financial system (TradFi). Barnbridge judges that the transfer of capital from TradFi to DeFi is the general trend.
The risk preferences of these TradFi funds are different. Some funds with stronger risk tendencies may adapt to DeFi faster. They are willing to take greater risks in order to obtain higher returns; another part of more conservative funds would rather Give up a greater opportunity to rise, but also in exchange for a certain degree of security for its investment. However, in the current DeFi market, all market risks can only be borne by investors alone throughout the entire process from the start of staking to the withdrawal of returns. This hinders the entry of the second type of TradFi investors to a certain extent.
In response to this problem, Barnbridge tried to divide the income and risk of investment by issuing derivatives. in particular,secondary title
Smart Income Bonds
Smart income bonds are mainly used to cut the risk of yield fluctuations of assets. To illustrate with an example:
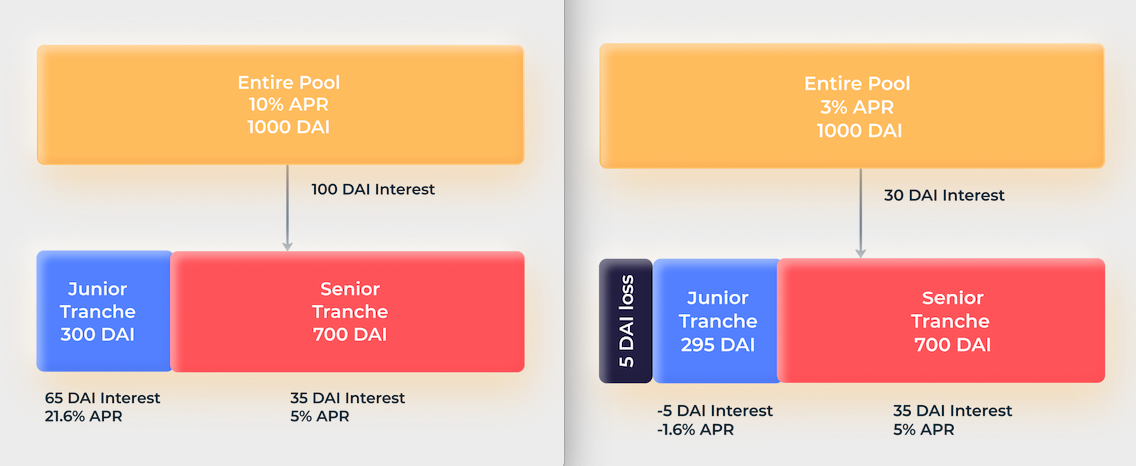
Assume that the total amount of pledged assets in a DeFi application is 1000 DAI, and the annualized rate of return (APY) is not fixed.
Theoretically, the entire pledged asset can be divided into two parts: 700 DAI belongs to the Senior part (the red area in the figure below, the risk tendency is lower), and the rate of return is fixed at 5%; 300 DAI belongs to the Junior part (the blue area in the figure below, the risk Tend to be higher) part, the rate of return is not fixed.
If the final APY of the application can reach 10%, then the annualized income will be 100 DAI, of which the Senior part will get 700 * 5% = 35 DAI, and the Junior part will get 75 DAI, compared to the principal of 300 DAI , with a yield as high as 21.6%.
If the final APY of the application can reach 10%, then the annualized income will be 100 DAI, of which the Senior part will get 700 * 5% = 35 DAI, and the Junior part will get 75 DAI, compared to the principal of 300 DAI , with a yield as high as 21.6%.
If the final APY of the application is only 3%, then the annualized income will be 30 DAI, of which the Senior part will still get 700 * 5% = 35 DAI, and the Junior part will need to make up for the loss of 5 DAI.
secondary title
Smart Alpha Bonds
Smart Alpha bonds are mainly used to cut the price fluctuation risk of the token itself. Its principle is similar to smart income bonds, except that the object is changed from the yield rate to the price of the asset itself. Tyler gives an example of this:
Suppose the price of 1 ETH is 100 USD;
In theory, we can still cut this ETH into two equal parts, both of which have an original value of $50.
The $50 in the Senior (lower risk appetite) tranche will cover 30% of the price movement; the $50 in the Junior (more risk-prone) tranche will cover 70% of the price movement.
When this ETH rises to $110, the Senior part can get a profit of (110 - 100) * 30% = $3, while the Junior part can get a profit of $7; on the contrary, when the assets fall , the loss that the Senior needs to bear will be smaller.
In this way, users can make investment choices that are more suitable for them according to their own risk preferences. Even if the market falls sharply, the Senior part can keep more costs in a relatively sense. For investors who choose the Junior side, it is actually adding leverage to their investment choices.
Whether it is a Smart Income Bond or a Smart Alpha Bond, each risk tier (Senior or Junior) will be ERC-20 tokenized and tradable as an independent digital asset. Investors can directly invest in corresponding tokens according to different risk preferences, or quickly exit the market by selling tokens. Regarding this point, Tyler said that the trading of tokens will operate in a pool-like manner, and Senior investors can still choose to buy part of Junior tokens to adjust their risk structure. At present, Barnbridge's Smart Income Bond and Smart Alpha Bond have not yet been officially launched. We will try the product as soon as it is launched and bring you more details.
Carefully combing the design of income bonds and Alpha bonds, we can find that the market risk has not been eliminated in essence, but has been cut, stripped, and transferred along with the income.It is worth mentioning that, in addition to market risk, there is another risk factor in the DeFi market that must not be ignored-contract risk.
independent auditindependent audit。
secondary title
Are you mining, my friend?
As mentioned above, Barnbridge (BOND) liquidity mining has officially started on October 19th. BOND's liquidity is divided into two parts: Yield Farming and Liquidity Pool Incentivization.

1. Yield farming:
Supported currencies: USDC, DAI, sUSD;
Start time: 8:00, October 19;
Duration: 25 weeks;
Total amount that can be mined: 800,000 pieces (total supply is 10 million pieces, accounting for 8%);
Weekly release quantity: 32000 pieces.

2. Liquidity pool incentive plan:
Start time: after the end of the first week of income farming;
Duration: 100 weeks;
Total amount that can be mined: 2 million pieces (total supply is 10 million pieces, accounting for 20%);
Weekly release quantity: 20,000 pieces.
 3. Token distribution:
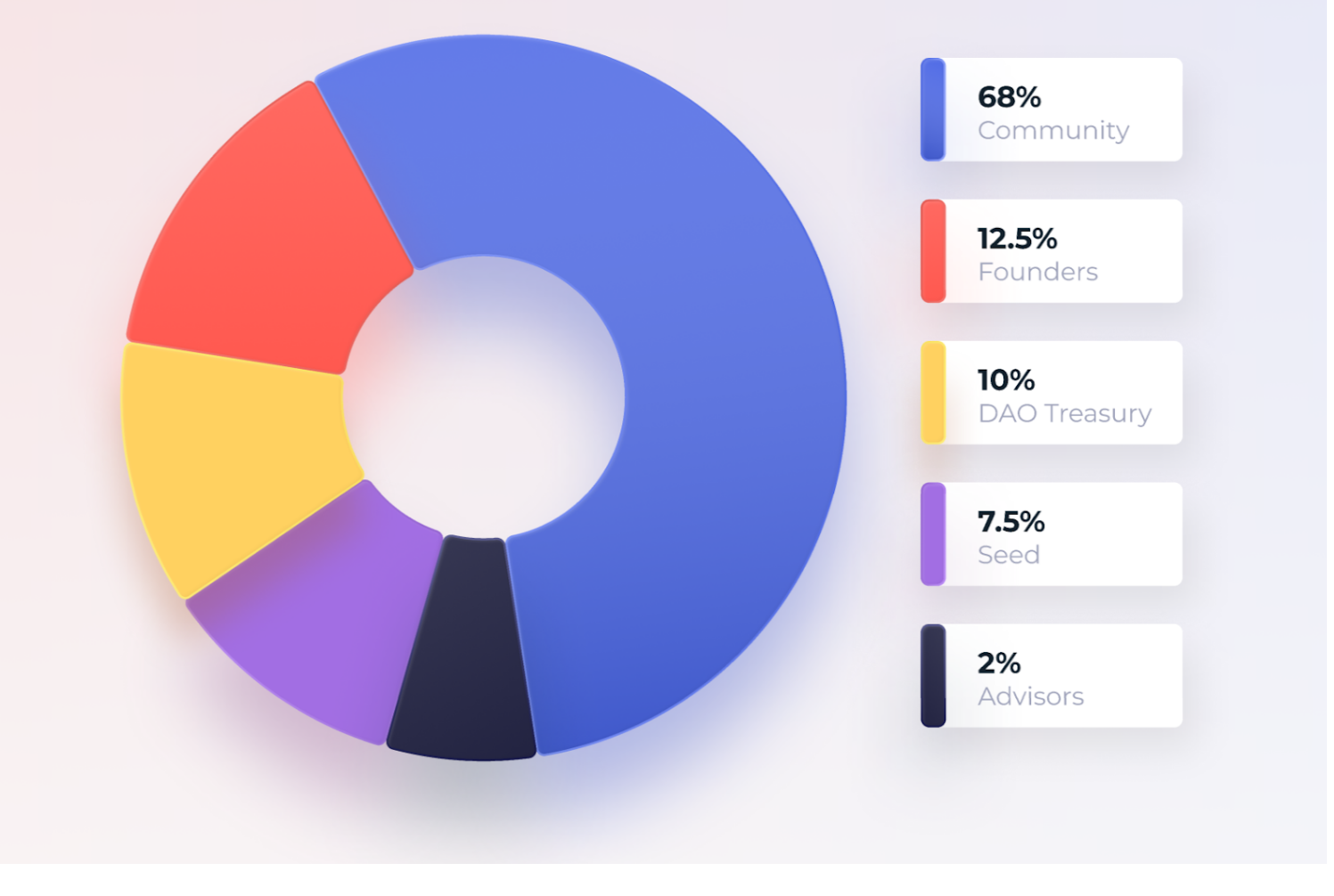
3. Token distribution:
Belonging to the community (including liquidity mining): 68%;
Belonging to DAO treasury: 10%;
Belonging to founders, early investors and consultants: 22% (12.5%+7.5%+2%), unlocked linearly in 100 weeks, 22,000 coins are unlocked every week.
In September this year, BarnBridge announced that it had completed a seed round of financing of US$1 million (100,000 was funded by the founding team). Investors included Fourth Revolution Capital, ParaFi Capital, Synthetix founder Kain Warwick, Aave founder Stani Kulechov, DARMA Capital managing partner People Andrew Keys, Centrality, Blockchain Companies, Dahret Group. On the evening of the 19th held by the DeFi Farmers CooperativeAMAoutlook
outlook
After months of frenzy, DeFi investors are used to the roller coaster of APY volatility. At the same time, more and more projects are also considering introducing fixed yields into the DeFi market.
On October 20, Yield Protocol, a decentralized fixed-rate lending protocol incubated by Paradigm, also launched a beta version. Earlier, the fixed-rate lending agreement Mainframe also released a white paper and announced a token economic model.
The characteristic of BarnBridge is that it does not provide interest rate income itself, but achieves fixed income by dividing the income and risks of other DeFi protocols. In terms of user acquisition, BarnBridge does not need to "grab customers" with those old-fashioned DeFi projects, or even It can also provide these users with new risk management services. From this perspective, there may indeed be a greater room for imagination.
Cryptocurrency analyst Ashwath Balakrishnan in his latestAnalysis articlepointed out that what Barnbridge wants to do is to introduce the secured debt certificate (CDO) in the traditional financial market into DeFi. Someone who has seen the famous movie "The Big Short" may think that CDO is a "financial product from hell", but when used correctly, CDO can go a long way in reducing risk.





